Page 317 - Color Atlas Of Pathophysiology (S Silbernagl Et Al, Thieme 2000)
P. 317
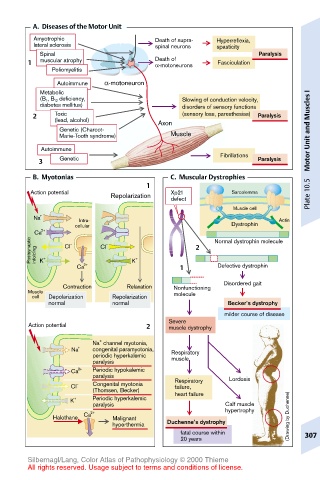
A. Diseases of the Motor Unit
Amyotrophic Death of supra- Hyperreflexia,
lateral sclerosis spinal neurons spasticity
Spinal Paralysis
1 muscular atrophy Death of Fasciculation
α-motoneurons
Poliomyelitis
Autoimmune α-motoneuron
Metabolic I
(B 1 , B 12 deficiency, Slowing of conduction velocity,
diabetes mellitus) disorders of sensory functions
2 Toxic (sensory loss, paresthesias) Paralysis and Muscles
(lead, alcohol)
Axon
Genetic (Charcot-
Marie-Tooth syndrome) Muscle
Autoimmune Motor Unit
3 Genetic Fibrillations Paralysis
B. Myotonias C. Muscular Dystrophies
1
Action potential Xp21 Sarcolemma
Repolarization defect Plate 10.5
Muscle cell
Na + Intra- Actin
cellular Dystrophin
Ca 2+ Normal dystrophin molecule
Postsynaptic infolding + Cl – Cl – + 2
K
Ca 2+ K 1 Defective dystrophin
Disordered gait
Contraction Relaxation Nonfunctioning
Muscle molecule
cell Depolarization Repolarization
normal normal Becker’s dystrophy
milder course of disease
Severe
Action potential 2 muscle dystrophy
+
Na channel myotonia,
Na + congenital paramyotonia, Respiratory
periodic hyperkalemic
paralysis muscle
Ca 2+ Periodic hypokalemic
paralysis Lordosis
failure,
Cl – Congenital myotonia Respiratory
(Thomsen, Becker) heart failure
K + Periodic hyperkalemic
paralysis Calf muscle
hypertrophy
Halothane Ca 2+ Malignant (Drawing by Duchenne)
hyperthermia Duchenne’s dystrophy
fatal course within 307
20 years
Silbernagl/Lang, Color Atlas of Pathophysiology © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.