Page 61 - Color Atlas Of Pathophysiology (S Silbernagl Et Al, Thieme 2000)
P. 61
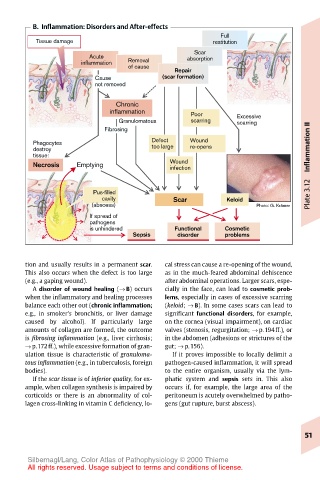
B. Inflammation: Disorders and After-effects
Full
Tissue damage restitution
Scar
Acute absorption
inflammation Removal
of cause
Repair
Cause (scar formation)
not removed
Chronic
inflammation Poor Excessive
Granulomatous scarring scarring II
Fibrosing
Phagocytes Defect Wound
destroy too large re-opens Inflammation
tissue:
Necrosis Emptying Wound
infection
Pus-filled Plate 3.12
cavity Scar Keloid
(abscess) Photo: G. Krämer
If spread of
pathogens
is unhindered Functional Cosmetic
Sepsis disorder problems
tion and usually results in a permanent scar. cal stress can cause a re-opening of the wound,
This also occurs when the defect is too large as in the much-feared abdominal dehiscence
(e.g., a gaping wound). after abdominal operations. Larger scars, espe-
A disorder of wound healing (→ B) occurs cially in the face, can lead to cosmetic prob-
when the inflammatory and healing processes lems, especially in cases of excessive scarring
balance each other out (chronic inflammation; (keloid; → B). In some cases scars can lead to
e.g., in smoker’s bronchitis, or liver damage significant functional disorders, for example,
caused by alcohol). If particularly large on the cornea (visual impairment), on cardiac
amounts of collagen are formed, the outcome valves (stenosis, regurgitation; → p.194ff.), or
is fibrosing inflammation (e.g., liver cirrhosis; in the abdomen (adhesions or strictures of the
→ p.172ff.), while excessive formation of gran- gut; → p.156).
ulation tissue is characteristic of granuloma- If it proves impossible to locally delimit a
tous inflammation (e.g., in tuberculosis, foreign pathogen-caused inflammation, it will spread
bodies). to the entire organism, usually via the lym-
If the scar tissue is of inferior quality, for ex- phatic system and sepsis sets in. This also
ample, when collagen synthesis is impaired by occurs if, for example, the large area of the
corticoids or there is an abnormality of col- peritoneum is acutely overwhelmed by patho-
lagen cross-linking in vitamin C deficiency, lo- gens (gut rupture, burst abscess).
51
Silbernagl/Lang, Color Atlas of Pathophysiology © 2000 Thieme
All rights reserved. Usage subject to terms and conditions of license.