Page 316 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 316
Cardiac Surgery and Transplantation 293
patient presents with collapse, severe hypotension and
4
dyspnoea. Patients with chronic regurgitation may
remain asymptomatic for years, finally presenting with
signs of left heart failure. On auscultation, a diastolic
murmur can be heard.
Left subclavian
Mitral valve disease artery
Mitral valve stenosis often occurs as a result of rheumatic
heart disease and less often from systemic lupus erythro- Internal mammary
(internal thoracic) artery
matosus. These diseases cause damage to the leaflets
and chordae tendineae, so that during healing the scars
contract and seal, restricting the aperture. Left atrial
pressure rises with resultant pulmonary hypertension.
In chronic conditions, this pressure may also affect the
5
right ven tricle. Lung compliance is also reduced,
causing dyspnoea. On auscultation a low-pitched
diastolic murmur and an opening snap can be heard.
Mitral valve regurgitation results when the mitral valve Anterior descending
and chordae tendineae are damaged, often due to myo- branch of the left
coronary artery
cardial infarction, rheumatic disease and infectious endo-
carditis. Backflow into the left atrium during systole
creates elevated atrial and pulmonary pressures, and
5
pulmonary oedema can result. On auscultation, a third
heart sound and a pansystolic murmur can be heard.
Ischaemic Heart Disease
Site of graft
The pathophysiology and implications of ischaemic heart
5
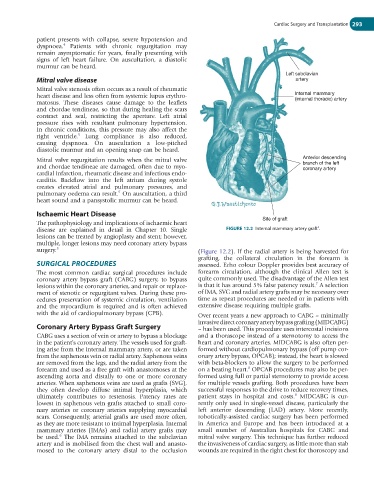
disease are explained in detail in Chapter 10. Single FIGURE 12.2 Internal mammary artery graft .
lesions can be treated by angioplasty and stent; however,
multiple, longer lesions may need coronary artery bypass
surgery. 5 (Figure 12.2). If the radial artery is being harvested for
grafting, the collateral circulation in the forearm is
SURGICAL PROCEDURES assessed. Echo colour Doppler provides best accuracy of
The most common cardiac surgical procedures include forearm circulation, although the clinical Allen test is
coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery, to bypass quite commonly used. The disadvantage of the Allen test
7
lesions within the coronary arteries, and repair or replace- is that it has around 5% false patency result. A selection
ment of stenotic or regurgitant valves. During these pro- of IMA, SVG and radial artery grafts may be necessary over
cedures preservation of systemic circulation, ventilation time as repeat procedures are needed or in patients with
and the myocardium is required and is often achieved extensive disease requiring multiple grafts.
with the aid of cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB). Over recent years a new approach to CABG – minimally
invasive direct coronary artery bypass grafting (MIDCABG)
Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery – has been used. This procedure uses intercostal incisions
CABG uses a section of vein or artery to bypass a blockage and a thorascope instead of a sternotomy to access the
in the patient’s coronary artery. The vessels used for graft- heart and coronary arteries. MIDCABG is also often per-
ing arise from the internal mammary artery, or are taken formed without cardiopulmonary bypass (off pump cor-
from the saphenous vein or radial artery. Saphenous veins onary artery bypass, OPCAB); instead, the heart is slowed
are removed from the legs, and the radial artery from the with beta-blockers to allow the surgery to be performed
8
forearm and used as a free graft with anastomoses at the on a beating heart. OPCAB procedures may also be per-
ascending aorta and distally to one or more coronary formed using full or partial sternotomy to provide access
arteries. When saphenous veins are used as grafts (SVG), for multiple vessels grafting. Both procedures have been
they often develop diffuse intimal hyperplasia, which successful responses to the drive to reduce recovery times,
8
ultimately contributes to restenosis. Patency rates are patient stays in hospital and costs. MIDCABG is cur-
lowest in saphenous vein grafts attached to small coro- rently only used in single-vessel disease, particularly the
nary arteries or coronary arteries supplying myocardial left anterior descending (LAD) artery. More recently,
scars. Consequently, arterial grafts are used more often, robotically-assisted cardiac surgery has been performed
as they are more resistant to intimal hyperplasia. Internal in America and Europe and has been introduced at a
mammary arteries (IMAs) and radial artery grafts may small number of Australian hospitals for CABG and
6
be used. The IMA remains attached to the subclavian mitral valve surgery. This technique has further reduced
artery and is mobilised from the chest wall and anasto- the invasiveness of cardiac surgery, as little more than stab
mosed to the coronary artery distal to the occlusion wounds are required in the right chest for thoroscopy and