Page 318 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 318
Cardiac Surgery and Transplantation 295
A B
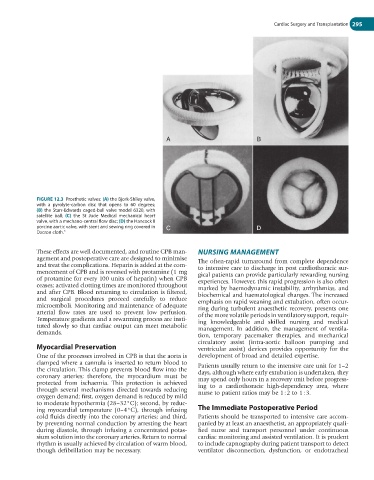
FIGURE 12.3 Prosthetic valves: (A) the Bjork-Shiley valve,
with a pyrolyte-carbon disc that opens to 60 degrees;
(B) the Starr-Edwards caged-ball valve model 6320, with
satellite ball; (C) the St Jude Medical mechanical heart
valve, with a mechano-central flow disc; (D) the Hancock II
porcine aortic valve, with stent and sewing ring covered in C D
Dacron cloth. 5
These effects are well documented, and routine CPB man- NURSING MANAGEMENT
agement and postoperative care are designed to minimise The often-rapid turnaround from complete dependence
and treat the complications. Heparin is added at the com- to intensive care to discharge in post cardiothoracic sur-
mencement of CPB and is reversed with protamine (1 mg gical patients can provide particularly rewarding nursing
of protamine for every 100 units of heparin) when CPB experiences. However, this rapid progression is also often
ceases; activated clotting times are monitored throughout marked by haemodynamic instability, arrhythmias, and
and after CPB. Blood returning to circulation is filtered, biochemical and haematological changes. The increased
and surgical procedures proceed carefully to reduce emphasis on rapid weaning and extubation, often occur-
microemboli. Monitoring and maintenance of adequate ring during turbulent anaesthetic recovery, presents one
arterial flow rates are used to prevent low perfusion. of the more volatile periods in ventilatory support, requir-
Temperature gradients and a rewarming process are insti- ing knowledgeable and skilled nursing and medical
tuted slowly so that cardiac output can meet metabolic management. In addition, the management of ventila-
demands.
tion, temporary pacemaker therapies, and mechanical
cir culatory assist (intra-aortic balloon pumping and
Myocardial Preservation ventricular assist) devices provides opportunity for the
One of the processes involved in CPB is that the aorta is development of broad and detailed expertise.
clamped where a cannula is inserted to return blood to Patients usually return to the intensive care unit for 1–2
the circulation. This clamp prevents blood flow into the days, although where early extubation is undertaken, they
coronary arteries; therefore, the myocardium must be may spend only hours in a recovery unit before progress-
protected from ischaemia. This protection is achieved ing to a cardiothoracic high-dependency area, where
through several mechanisms directed towards reducing nurse to patient ratios may be 1 : 2 to 1 : 3.
oxygen demand: first, oxygen demand is reduced by mild
to moderate hypothermia (28–32°C); second, by reduc-
ing myocardial temperature (0–4°C), through infusing The Immediate Postoperative Period
cold fluids directly into the coronary arteries; and third, Patients should be transported to intensive care accom-
by preventing normal conduction by arresting the heart panied by at least an anaesthetist, an appropriately quali-
during diastole, through infusing a concentrated potas- fied nurse and transport personnel under continuous
sium solution into the coronary arteries. Return to normal cardiac monitoring and assisted ventilation. It is prudent
rhythm is usually achieved by circulation of warm blood, to include capnography during patient transport to detect
though defibrillation may be necessary. ventilator disconnection, dysfunction, or endotracheal