Page 685 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 685
662 S P E C I A LT Y P R A C T I C E I N C R I T I C A L C A R E
TABLE 24.5 Factors contributing to the success or failure of defibrillation
Success Failure Precautions
l Early defibrillation l Inadequate contact with the chest (Excessive chest l Place defibrillation electrodes at least 8 cm away
(<4 min) hair) from ECG electrodes, or implantable medical devices
l Presenting l Faulty positioning of the paddles pacemakers, vascular access devices
rhythm (VT/VF) l Synchronise button in the on position, flat battery or l Remove medication patches, wipe the area before
fractures lead applying defibrillation electrodes
l Positioning over bone/fat or breast tissue l Do not defibrillate unless all clear of the bed/patient
l Drying out of gel conduction pads l Do not charge/discharge paddles in the air
l Patient factors: acidosis, hypoxia, electrolyte imbalance, l Do not have the patient in contact with metal
drug toxicity, hypothermia l Do not allow oxygen to flow onto the patient during
l Time of respiration (best delivered at end-expiration) delivery of the shock (at least 1 m from the patient)
l PEEP and auto-PEEP (air-trapping) should be minimised l Ensure the chest is dry
l Paddles/electrodes too small (8–12 cm electrodes for l Do not use electrode gels and pastes as these can
adults) spread between the paddles and potentially spark.
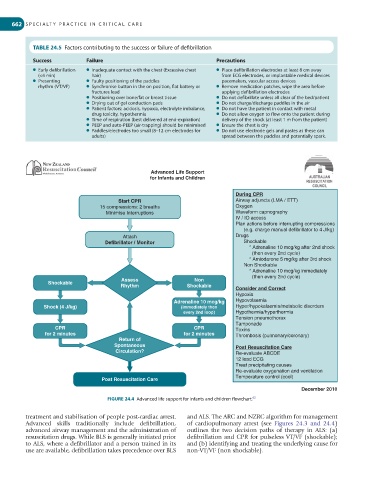
Advanced Life Support
for Infants and Children
During CPR
Start CPR Airway adjuncts (LMA / ETT)
15 compressions: 2 breaths Oxygen
Minimise Interruptions Waveform capnography
IV / IO access
Plan actions before interrupting compressions
(e.g. charge manual defibrillator to 4 J/kg)
Attach Drugs
Defibrillator / Monitor Shockable
* Adrenaline 10 mcg/kg after 2nd shock
(then every 2nd cycle)
* Amiodarone 5 mg/kg after 3rd shock
Non Shockable
* Adrenaline 10 mcg/kg immediately
(then every 2nd cycle)
Assess Non
Shockable
Rhythm Shockable Consider and Correct
Hypoxia
Adrenaline 10 mcg/kg Hypovolaemia
Shock (4 J/kg) (immediately then Hyper/hypokalaemia/metabolic disorders
every 2nd loop) Hypothermia/hyperthermia
Tension pneumothorax
Tamponade
CPR CPR Toxins
for 2 minutes for 2 minutes Thrombosis (pulmonary/coronary)
Return of
Spontaneous Post Resuscitation Care
Circulation? Re-evaluate ABCDE
12 lead ECG
Treat precipitating causes
Re-evaluate oxygenation and ventilation
Temperature control (cool)
Post Resuscitation Care
December 2010
62
FIGURE 24.4 Advanced life support for infants and children flowchart.
treatment and stabilisation of people post-cardiac arrest. and ALS. The ARC and NZRC algorithm for management
Advanced skills traditionally include defibrillation, of cardiopulmonary arrest (see Figures 24.3 and 24.4)
advanced airway management and the administration of outlines the two decision paths of therapy in ALS: (a)
resuscitation drugs. While BLS is generally initiated prior defibrillation and CPR for pulseless VT/VF (shockable);
to ALS, where a defibrillator and a person trained in its and (b) identifying and treating the underlying cause for
use are available, defibrillation takes precedence over BLS non-VT/VF (non shockable).