Page 90 - ACCCN's Critical Care Nursing
P. 90
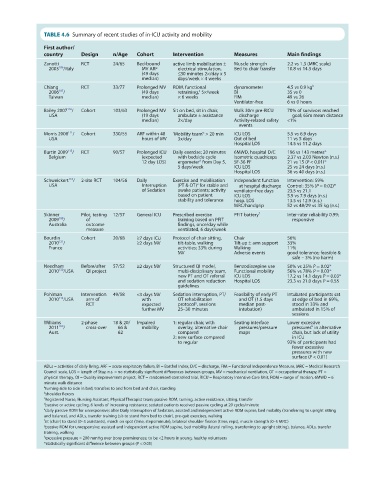
TABLE 4.6 Summary of recent studies of in-ICU activity and mobility
First author/
country Design n/Age Cohort Intervention Measures Main findings
Zanotti RCT 24/65 Bed-bound active limb mobilisation ± Muscle strength 2.2 vs 1.3 (MRC scale)
2003 /Italy MV ARF electrical stimulation, Bed to chair transfer 10.8 vs 14.3 days
186
(49 days ≤30 minutes 2×/day x 5
median) days/week × 4 weeks
Chiang RCT 33/77 Prolonged MV ROM, functional dynamometer 4.5 vs 0.9 kg b
187
2006 / (49 days retraining, 5×/week BI 35 vs 0
a
Taiwan median) × 6 weeks FIM 49 vs 26
Ventilator-free 6 vs 0 hours
110
Bailey 2007 / Cohort 103/63 Prolonged MV Sit on bed, sit in chair, Walk 30m pre-RICU 70% of survivors reached
USA (19 days ambulate ± assistance discharge goal; 65m mean distance
median) 2×/day Activity-related safety <1%
events
c
Morris 2008 / Cohort 330/55 ARF within 48 ‘Mobility team’ > 20 min ICU LOS 5.5 vs 6.9 days
111
USA hours of MV 3x/day Out of bed 11 vs 5 days
Hospital LOS 14.5 vs 11.2 days
115
Burtin 2009 / RCT 90/57 Prolonged ICU Daily exercise; 20 minutes 6MWD, hospital D/C 196 vs 143 metres*
Belgium (expected with bedside cycle Isometric quadriceps 2.37 vs 2.03 Newton (n.s.)
d
12 day LOS) ergometer from Day 5, SF-36 PF 21 vs 15 (P < 0.01)*
5 days/week ICU LOS 25 vs 24 days (n.s.)
Hospital LOS 36 vs 40 days (n.s.)
Schweickert / 2-site RCT 104/56 Daily Exercise and mobilisation independent function Intervention: 59%
116
e
USA Interruption (PT & OT) for stable and at hospital discharge Control: 35% (P = 0.02)*
of Sedation awake patients; activity ventilator-free days 23.5 vs 21.1
based on patient ICU LOS 5.9 vs 7.9 days (n.s.)
stability and tolerance hosp. LOS 13.5 vs 12.9 (n.s.)
MRC/handgrip 52 vs 48/29 vs 35 kg (n.s.)
Skinner Pilot, testing 12/57 General ICU Prescribed exercise PFIT battery f Inter-rater reliability 0.99;
2009 / of training based on PFIT responsive
188
Australia outcome findings, once/day while
measure ventilated, 6 days/week
Bourdin Cohort 20/68 ≥7 days ICU Protocol of chair sitting, Chair 56%
121
2010 / ≥2 days MV tilt-table, walking Tilt-up ± arm support 33%
France activities; 33% during Walking 11%
MV Adverse events good tolerance; feasible &
safe – 3% (no harm)
Needham Before/after 57/52 ≥2 days MV Structured QI model, Benzodiazepine use 50% vs 25% P = 0.02*
2010 /USA QI project multi-disciplinary team, Functional mobility 56% vs 78% P = 0.03*
130
new PT and OT referral ICU LOS 17.2 vs 14.1 days P = 0.03*
and sedation reduction Hospital LOS 23.3 vs 21.0 days P = 0.55
guidelines
Pohlman Intervention 49/58 <3 days MV Sedation interruption, PT/ Feasibility of early PT Intubated participants sat
112
2010 /USA arm of with OT rehabilitation and OT (1.5 days at edge of bed in 69%,
g
RCT expected protocol , sessions median post- stood in 33% and
further MV 25–30 minutes intubation) ambulated in 15% of
sessions
Williams 2-phase 18 & 20/ Impaired 1: regular chair, with Seating interface Lower excessive
h
2011 / cross-over 66 & mobility overlay, alternative chair pressures/pressure pressures in alternative
189
Aust. 62 compared maps chair, but lack of utility
2: new surface compared in ICU
to regular 93% of participants had
fewer excessive
pressures with new
surface (P < 0.01)
ADLs = activities of daily living, ARF = acute respiratory failure, BI = Barthel Index, D/C = discharge, FIM = Functional Independence Measure, MRC = Medical Research
Council scale, LOS = length of Stay, n.s. = no statistically significant differences between groups, MV = mechanical ventilation, OT = occupational therapy, PT =
physical therapy, QI = Quality improvement project, RCT = randomised controlled trial, RICU = Respiratory Intensive Care Unit, ROM = range of motion, 6MWD = 6
minute walk distance
a turning side to side in bed, transfers to and from bed and chair, standing
b shoulder flexors
c Registered Nurse, Nursing Assistant, Physical Therapist team; passive ROM, turning, active resistance, sitting, transfer
d passive or active cycling, 6 levels of increasing resistance; sedated patients received passive cycling at 20 cycles/minute
e daily passive ROM for unresponsive; after Daily Interruption of Sedation, assisted and independent active ROM supine, bed mobility (transferring to upright sitting
and balance), and ADLs, transfer training (sit-to stand from bed to chair), pre-gait exercises, walking
f sit (chair) to stand (0–3 assistants), march on spot (time, steps/minute), bilateral shoulder flexion (time, reps), muscle strength (0–5 MRC)
g passive ROM for unresponsive; assisted and independent active ROM supine, bed mobility (lateral rolling, transferring to upright sitting), balance, ADLs, transfer
training, walking
h excessive pressure = 200 mmHg over bony prominences; to be <2 hours in young, healthy volunteers
*statistically significant difference between groups (P < 0.05)