Page 1057 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1057
940 Part VII Hematologic Malignancies
immediate administration of steroids (dexamethasone 10 mg twice
daily until resolution of signs and symptoms) and interruption of
therapy if no response or in the case of life-threatening complications.
This intervention will rapidly reverse the manifestations of differen-
tiation syndrome and has substantially reduced mortality to below
5%. Some investigators have proposed prophylactic use of dexa-
2
methasone 2.5 mg/m every 12 hours for the first 15 days in patients
with WBC exceeding 5000/µL.
Subsequent clinical studies confirmed significantly better disease-
free survival for the combination of ATRA plus chemotherapy. In the
French APL 93 trial, concurrent administration of ATRA with che-
motherapy achieved identical CR rates of 92% but a lower relapse
rate at 2 years (6%) compared with sequential administration (16%,
p = .04). As standard induction therapy for patients with APL hence
emerged the combination of ATRA with an anthracycline (daunoru-
bicin or idarubicin). In two large trials from Italy (GIMEMA) and
Spain (PETHEMA), CR rates were 95% and 89%, respectively, and
26
2-year disease-free survival was 79%. A risk-stratification model was
proposed based on WBC and platelet count. High risk was defined
as a WBC of greater than 10,000/µL at diagnosis with significant
differences in relapse-free survival between patients with high- and
those with intermediate-/low-risk disease. The role of cytarabine in
APL therapy is controversial. In two randomized studies of ATRA/
A B anthracycline ± cytarabine from the AML MRC15 trial and the
European APL Group, rates for CR and induction failure were
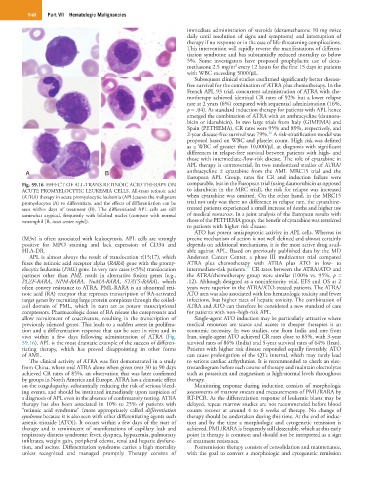
Fig. 59.16 EFFECT OF ALL-TRANS RETINOIC ACID THERAPY ON comparable, but in the European trial (using daunorubicin as opposed
ACUTE PROMYELOCYTIC LEUKEMIA CELLS. All-trans retinoic acid to idarubicin in the MRC trial), the risk for relapse was increased
(ATRA) therapy in acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL)causes the malignant when cytarabine was omitted. On the other hand, in the MRC15
promyelocytes (A) to differentiate, and the effects of differentiation can be trial not only was there no difference in relapse rate, the cytarabine-
seen within days of treatment (B). The differentiated APL cells are still treated patients experienced a small increase of deaths and higher use
somewhat atypical, frequently with bilobed nuclei (compare with normal of medical resources. In a joint analysis of the European results with
neutrophil [B, inset center right]). those of the PETHEMA group, the benefit of cytarabine was restricted
to patients with higher risk disease.
ATO has potent antiapoptotic activity in APL cells. Whereas its
(M3v) is often associated with leukocytosis. APL cells are strongly precise mechanism of action is not well defined and almost certainly
positive for MPO staining and lack expression of CD34 and depends on additional mechanisms, it is the most active drug avail-
HLA-DR. able against APL. Based on previously published data by the MD
APL is almost always the result of translocation t(15;17), which Anderson Cancer Center, a phase III multicenter trial compared
fuses the retinoic acid receptor alpha (RARA) gene with the promy- ATRA plus chemotherapy with ATRA plus ATO in low- to
27
elocytic leukemia (PML) gene. In very rare cases (<5%) translocation intermediate-risk patients. CR rates between the ATRA/ATO and
partners other than PML result in alternative fusion genes (e.g., the ATRA/chemotherapy group were similar (100% vs. 95%, p =
PLZF-RARA, NPM-RARA, NuMA-RARA, STAT5-RARA), which .12). Although designed as a noninferiority trial, EFS and OS at 2
often convey resistance to ATRA. PML-RARA is an abnormal reti- years were superior in the ATRA/ATO-treated patients. The ATRA/
noic acid (RA) receptor that represses transcription of RA-activated ATO arm was also associated with less hematologic toxicity and fewer
target genes by recruiting large protein complexes through the coiled- infections, but higher rates of hepatic toxicity. The combination of
coil domain of PML, which in turn act as potent transcriptional ATRA and ATO can therefore be considered a new standard of care
corepressors. Pharmacologic doses of RA release the corepressors and for patients with non–high-risk APL.
allow recruitment of coactivators, resulting in the transcription of Single-agent ATO induction may be particularly attractive where
previously silenced genes. This leads to a sudden arrest in prolifera- medical resources are scarce and access to cheaper therapies is an
tion and a differentiation response that can be seen in vitro and in economic necessity. In two studies, one from India and one from
vivo within a few days following administration of ATRA (Fig. Iran, single-agent ATO achieved CR rates close to 85%, with 3-year
59.16). APL is the most dramatic example of the success of differen- survival rates of 86% (India) and 5-year survival rates of 64% (Iran).
tiating therapy, which has proved disappointing in other forms Patients with higher risk disease responded equally favorably. ATO
of AML. can cause prolongation of the QTc interval, which may rarely lead
The clinical activity of ATRA was first demonstrated in a study to serious cardiac arrhythmias. It is recommended to check an elec-
from China, where oral ATRA alone when given over 30 to 90 days trocardiogram before each course of therapy and maintain electrolytes
achieved CR rates of 85%, an observation that was later confirmed such as potassium and magnesium at high-normal levels throughout
by groups in North America and Europe. ATRA has a dramatic effect therapy.
on the coagulopathy, substantially reducing the risk of serious bleed- Monitoring response during induction consists of morphologic
ing events, and should be instituted immediately upon suspicion of assessments of marrow smears and measurements of PML/RARA by
a diagnosis of APL even in the absence of confirmatory testing. ATRA RT-PCR. As the differentiation response of leukemic blasts may be
therapy has also been associated in 10% to 25% of patients with delayed, repeat marrow studies are not recommended before blood
“retinoic acid syndrome” (more appropriately called differentiation counts recover at around 4 to 6 weeks of therapy. No change of
syndrome because it is also seen with other differentiating agents such therapy should be undertaken during this time. At the end of induc-
arsenic trioxide [ATO]). It occurs within a few days of the start of tion and by the time a morphologic and cytogenetic remission is
therapy and is reminiscent of manifestations of capillary leak and achieved, PML/RARA is frequently still detectable, which at this early
respiratory distress syndrome: fever, dyspnea, hypoxemia, pulmonary point in therapy is common and should not be interpreted as a sign
infiltrates, weight gain, peripheral edema, renal and hepatic dysfunc- of treatment resistance.
tion, and ascites. Differentiation syndrome carries a high mortality Postremission therapy consists of consolidation and maintenance,
unless recognized and managed promptly. Therapy consists of with the goal to convert a morphologic and cytogenetic remission