Page 1054 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1054
Chapter 59 Clinical Manifestations and Treatment of Acute Myeloid Leukemia 937
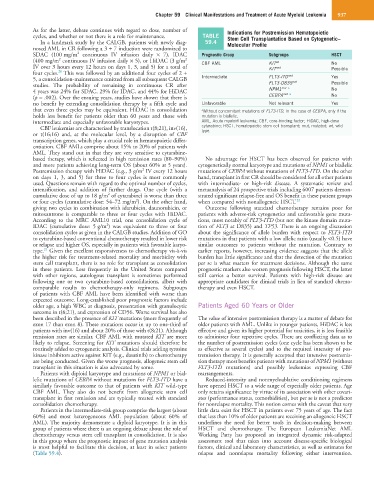
As for the latter, debate continues with regard to dose, number of Indications for Postremission Hematopoietic
cycles, and whether or not there is a role for maintenance. TABLE Stem Cell Transplantation Based on Cytogenetic–
In a landmark study by the CALGB, patients with newly diag- 59.4 Molecular Profile
nosed AML in CR following a 3 + 7 induction were randomized to
2
SDAC (100 mg/m continuous IV infusion daily × 7), IDAC Prognostic Group Subgroups HSCT
2
2
(400 mg/m continuous IV infusion daily × 5), or HiDAC (3 g/m CBF AML KIT wt No
IV over 3 hours every 12 hours on days 1, 3, and 5) for a total of KIT mut Possible
20
four cycles. This was followed by an additional four cycles of 2 + mut
5, a consolidation-maintenance omitted from all subsequent CALGB Intermediate FLT3-ITD mut Yes
studies. The probability of remaining in continuous CR after FLT3-D835 Possible
mut a
4 years was 24% for SDAC, 29% for IDAC, and 44% for HiDAC NPM1 mut a No
(p = .002). Over the ensuing years, studies have shown that there is CEBPA No
no benefit by extending consolidation therapy by a fifth cycle and Unfavorable Not relevant Yes
that even three cycles may be equivalent. HiDAC in consolidation a Without concomitant mutations of FLT3-ITD. In the case of CEBPA, only if the
holds less benefit for patients older than 60 years and those with mutation is biallelic.
intermediate and especially unfavorable karyotypes. AML, Acute myeloid leukemia; CBF, core-binding factor; HiDAC, high-dose
CBF leukemias are characterized by translocation t(8;21), inv(16), cytarabine; HSCT, hematopoietic stem cell transplant; mut, mutated; wt, wild
or t(16;16) and, at the molecular level, by a disruption of CBF type.
transcription genes, which play a crucial role in hematopoietic differ-
entiation. CBF AMLs comprise about 15% to 20% of patients with
AML. They stand out in that they are very sensitive to cytarabine-
based therapy, which is reflected in high remission rates (80–90%) No advantage for HSCT has been observed for patients with
and more patients achieving long-term OS (about 60% at 5 years). cytogenetically normal karyotype and mutations of NPM1 or biallelic
2
Postremission therapy with HiDAC (e.g., 3 g/m IV every 12 hours mutations of CEBPA without mutations of FLT3-ITD. On the other
on days 1, 3, and 5) for three to four cycles is most commonly hand, transplant in first CR should be considered for all other patients
used. Questions remain with regard to the optimal number of cycles, with intermediate- or high-risk disease. A systematic review and
intensification, and addition of further drugs. One cycle (with a metaanalysis of 24 prospective trials including 6007 patients demon-
2
cumulative dose of up to 18 g/m of cytarabine) is worse than three strated significant relapse-free and OS benefit in these patient groups
2
or four cycles (cumulative dose: 54–72 mg/m ). On the other hand, when compared with nonallogeneic HSCT. 22
giving two cycles in combination with idarubicin, daunorubicin, or Outcome following standard chemotherapy remains poor for
mitoxantrone is comparable to three or four cycles with HiDAC. patients with adverse-risk cytogenetics and unfavorable gene muta-
According to the MRC AML10 trial, one consolidation cycle of tions, most notably of FLT3-ITD (but not the kinase domain muta-
2
IDAC (cumulative dose: 5 g/m ) was equivalent to three or four tion of FLT3 at D835) and TP53. There is an ongoing discussion
consolidation cycles as given in the CALGB studies. Addition of GO about the significance of allele burden with respect to FLT3-ITD
to cytarabine-based conventional chemotherapy resulted in lower risk mutations in that patients with a low allelic ratio (usually <0.5) have
or relapse and higher OS, especially in patients with favorable karyo- similar outcomes to patients without the mutation. Contrary to
21
type. Given the excellent responsiveness to chemotherapy vis-à-vis earlier reports, however, increasing evidence suggests that the allele
the higher risk for treatment-related mortality and morbidity with burden has little significance and that the detection of the mutation
stem cell transplant, there is no role for transplant as consolidation per se is what matters for treatment decisions. Although the same
in these patients. Less frequently in the United States compared prognostic markers also worsen prognosis following HSCT, the latter
with other regions, autologous transplant is sometimes performed still carries a better survival. Patients with high-risk disease are
following one or two cytarabine-based consolidations, albeit with appropriate candidates for clinical trials in lieu of standard chemo-
comparable results to chemotherapy-only regimens. Subgroups therapy and even HSCT.
of patients with CBF AML have been identified with worse than
expected outcome. Long-established poor prognostic factors include
older age, a high WBC at diagnosis, presentation with granulocytic Patients Aged 60 Years or Older
sarcoma in t(8;21), and expression of CD56. Worse survival has also
been described in the presence of KIT mutations (more frequently of The value of intensive postremission therapy is a matter of debate for
exon 17 than exon 8). These mutations occur in up to one-third of older patients with AML. Unlike in younger patients, HiDAC is less
patients with inv(16) and about 20% of those with t(8;21). Although effective and given its higher potential for toxicities, it is less feasible
remission rates are similar, CBF AML with mutated KIT are more to administer four repetitive cycles. There are conflicting data as to
likely to relapse. Screening for KIT mutations should therefore be the number of postremission cycles (one cycle has been shown to be
routinely added to cytogenetic analysis. Clinical trials adding tyrosine as effective as several cycles) and to the required intensity of pos-
kinase inhibitors active against KIT (e.g., dasatinib) to chemotherapy tremission therapy. It is generally accepted that intensive postremis-
are being conducted. Given the worse prognosis, allogeneic stem cell sion therapy most benefits patients with mutations of NPM1 (without
transplant in this situation is also advocated by some. FLT3-ITD mutations) and possibly leukemias expressing CBF
Patients with diploid karyotype and mutations of NPM1 or bial- rearrangements.
lelic mutations of CEBPA without mutations for FLT3-ITD have a Reduced-intensity and nonmyeloablative conditioning regimens
similarly favorable outcome to that of patients with KIT wild-type have opened HSCT to a wide range of especially older patients. Age
CBF AML. They also do not benefit from allogeneic stem cell only retains significance by virtue of its association with other covari-
transplant in first remission and are typically treated with standard ates (performance status, comorbidities), but per se is not a predictor
consolidation chemotherapy. for nonrelapse mortality. This notion comes with the caveat that very
Patients in the intermediate-risk group comprise the largest (about little data exist for HSCT in patients over 75 years of age. The fact
60%) and most heterogeneous AML population (about 60% of that less than 10% of older patients are receiving an allogeneic HSCT
AML). The majority demonstrate a diploid karyotype. It is in this underlines the need for better tools in decision-making between
group of patients where there is an ongoing debate about the role of HSCT and chemotherapy. The European LeukemiaNet AML
chemotherapy versus stem cell transplant in consolidation. It is also Working Party has proposed an integrated dynamic risk-adapted
in this group where the prognostic impact of gene mutation analysis assessment tool that takes into account disease-specific biological
is most helpful to facilitate this decision, at least in select patients factors, clinical and laboratory characteristics, as well as estimates for
(Table 59.4). relapse and nonrelapse mortality following either intervention.