Page 1053 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1053
936 Part VII Hematologic Malignancies
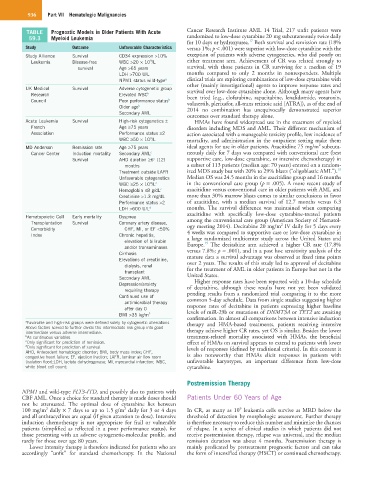
TABLE Prognostic Models in Older Patients With Acute Cancer Research Institute AML 14 Trial, 217 unfit patients were
59.3 Myeloid Leukemia randomized to low-dose cytarabine 20 mg subcutaneously twice daily
17
for 10 days or hydroxyurea. Both survival and remission rate (18%
Study Outcome Unfavorable Characteristics versus 1%; p < .001) were superior with low-dose cytarabine with the
Study Alliance Survival CD34 expression >10% exception of patients with adverse cytogenetics, who did poorly on
9
Leukemia Disease-free WBC >20 × 10 /L either treatment arm. Achievement of CR was related strongly to
survival Age >65 years survival, with those patients in CR surviving for a median of 19
LDH >700 U/L months compared to only 2 months in nonresponders. Multiple
NPM1 status wild-type a clinical trials are exploring combinations of low-dose cytarabine with
other (mainly investigational) agents to improve response rates and
UK Medical Survival Adverse cytogenetic group survival over low-dose cytarabine alone. Although many agents have
Research Elevated WBC b been tried (e.g., clofarabine, sapacitabine, lenalidomide, vosaroxin,
Council Poor performance status b volasertib, plerixafor, all-trans retinoic acid [ATRA]), as of the end of
Older age b 2014 no combination has unequivocally demonstrated superior
Secondary AML outcomes over standard therapy alone.
Acute Leukemia Survival High-risk cytogenetics ± HMAs have found widespread use in the treatment of myeloid
French Age ≥75 years disorders including MDS and AML. Their different mechanism of
Association Performance status ≥2 action associated with a manageable toxicity profile, low incidence of
WBC ≥50 × 10 /L mortality, and administration in the outpatient setting make them
9
2
MD Anderson Remission rate Age ≥75 years ideal agents for use in older patients. Azacitidine 75 mg/m subcuta-
Cancer Center Induction mortality Secondary AML c neously daily for 7 days was compared with conventional care (best
c
Survival AHD duration ≥6 (12) supportive care, low-dose cytarabine, or intensive chemotherapy) in
months a subset of 113 patients (median age: 70 years) entered on a random-
18
Treatment outside LAFR ized MDS study but with 20% to 29% blasts (“oligoblastic AML”).
Unfavorable cytogenetics Median OS was 24.5 months in the azacitidine group and 16 months
9
WBC ≥25 × 10 /L c in the conventional care group (p = .005). A more recent study of
Hemoglobin ≤8 g/dL c azacitidine versus conventional care in older patients with AML and
Creatinine >1.3 mg/dL more than 30% marrow blasts comes to similar conclusions in favor
Performance status >2 of azacitidine, with a median survival of 12.7 months versus 6.3
LDH >600 U/L d months. The survival difference was maintained when comparing
azacitidine with specifically low-dose cytarabine-treated patients
Hematopoietic Cell Early mortality Dyspnea among the conventional care group (American Society of Hematol-
Transplantation Survival Coronary artery disease, ogy meeting 2014). Decitabine 20 mg/m IV daily for 5 days every
2
Comorbidity CHF, MI, or EF <50% 4 weeks was compared to supportive care or low-dose cytarabine in
Index Chronic hepatitis, a large randomized multicenter study across the United States and
elevation of bilirubin Europe. The decitabine arm achieved a higher CR rate (17.8%
19
and/or transaminases
Cirrhosis versus 7.8%; p = .001), and in a post hoc sensitivity analysis of the
mature data a survival advantage was observed at fixed time points
Elevations of creatinine, over 2 years. The results of this study led to approval of decitabine
dialysis, renal for the treatment of AML in older patients in Europe but not in the
transplant
Secondary AML United States.
Higher response rates have been reported with a 10-day schedule
Depression/anxiety of decitabine, although these results have not yet been validated
requiring therapy
Continued use of pending results from a randomized trial comparing it to the more
common 5-day schedule. Data from single studies suggesting higher
antimicrobial therapy response rates of decitabine in patients expressing higher baseline
after day 0
BMI >35 kg/m 2 levels of miR-29b or mutations of DNMT3A or TET2 are awaiting
confirmation. In almost all comparisons between intensive induction
a Favorable and high-risk groups were defined solely by cytogenetic aberrations. therapy and HMA-based treatments, patients receiving intensive
Above factors served to further divide the intermediate risk group into good therapy achieve higher CR rates, yet OS is similar. Besides the lower
intermediate versus adverse intermediate.
b As continuous variables. treatment-related mortality associated with HMAs, the beneficial
c Only significant for prediction of remission. effect of HMAs on survival appears to extend to patients with lower
d Only significant for prediction of survival. levels of responses (defined by traditional criteria). In this context it
AHD, Antecedent hematologic disorder; BMI, body mass index; CHF, is also noteworthy that HMAs elicit responses in patients with
congestive heart failure; EF, ejection fraction; LAFR, laminar air flow room
(isolation floor);LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; MI, myocardial infarction; WBC, unfavorable karyotypes, an important difference from low-dose
white blood cell count; cytarabine.
Postremission Therapy
NPM1 and wild-type FLT3-ITD, and possibly also to patients with
CBF AML. Once a choice for standard therapy is made doses should Patients Under 60 Years of Age
not be attenuated. The optimal dose of cytarabine lies between
9
2
2
100 mg/m daily × 7 days to up to 1.5 g/m daily for 3 or 4 days In CR, as many as 10 leukemia cells survive as MRD below the
and all anthracyclines are equal (if given attention to dose). Intensive threshold of detection by morphologic assessment. Further therapy
induction chemotherapy is not appropriate for frail or vulnerable is therefore necessary to reduce this number and minimize the chances
patients (simplified as reflected in a poor performance status), for of relapse. In a series of clinical studies in which patients did not
those presenting with an adverse cytogenetic-molecular profile, and receive postremission therapy, relapse was universal, and the median
rarely for those over age 80 years. remission duration was about 4 months. Postremission therapy is
Lower intensity therapy is therefore indicated for patients who are mainly predicated by pretreatment prognostic factors and can take
accordingly “unfit” for standard chemotherapy. In the National the form of intensified therapy (HSCT) or continued chemotherapy.