Page 1076 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1076
Chapter 60 Myelodysplastic Syndromes 959
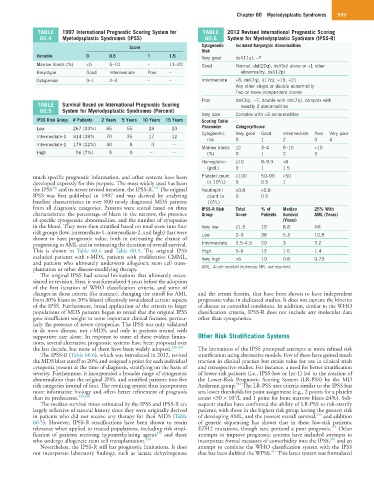
TABLE 1997 International Prognostic Scoring System for TABLE 2012 Revised International Prognostic Scoring
60.4 Myelodysplastic Syndromes (IPSS) 60.6 System for Myelodysplastic Syndrome (IPSS-R)
Score Cytogenetic Included Karyotypic Abnormalities
Risk
Variable 0 0.5 1 1.5 Very good del(11q), −Y
Marrow blasts (%) <5 5–10 – 11–20 Good Normal, del(20q), del(5q) alone or +1 other
Karyotype Good Intermediate Poor – abnormality, del(12p)
Cytopenias 0–1 2–3 – – Intermediate +8, del(7q), i(17q), +19, +21
Any other single or double abnormality
Two or more independent clones
Poor der(3q), −7, double with del(7q), complex with
TABLE Survival Based on International Prognostic Scoring exactly 3 abnormalities
60.5 System for Myelodysplastic Syndromes (Percent)
Very poor Complex with >3 abnormalities
IPSS Risk Group # Patients 2 Years 5 Years 10 Years 15 Years Scoring Table
Low 267 (33%) 85 55 28 20 Parameter Category/Score
Cytogenetic Very good Good Intermediate Poor Very poor
Intermediate-1 314 (38% 70 35 17 12
risk 0 1 2 3 4
Intermediate-2 179 (22%) 30 8 0 –
Marrow blasts ≤2 3–4 5–10 >10
High 56 (7%) 5 0 – – (%) 0 1 2 3
Hemoglobin ≥10 8–9.9 <8
(g/dL) 0 1 1.5
much specific prognostic information, and other systems have been Platelet count ≥100 50–99 <50
9
developed expressly for this purpose. The most widely used has been (× 10 /L) 0 0.5 1
331
330
the IPSS and its newer revised iteration, the IPSS-R. The original Neutrophil ≥0.8 <0.8
IPSS was first published in 1997 and was derived by analyzing count (× 0 0.5
baseline characteristics in over 800 newly diagnosed MDS patients 10 /L)
9
from all diagnostic categories. Patients were scored based on three IPSS-R Risk Total % of Median 25% With
characteristics: the percentage of blasts in the marrow, the presence Group Score Patients Survival AML (Years)
of specific cytogenetic abnormalities, and the number of cytopenias (Years)
in the blood. They were then stratified based on total score into four Very low ≤1.5 19 8.8 NR
risk groups (low, intermediate-1, intermediate-2, and high) that were Low 2–3 38 5.3 10.8
shown to have prognostic value, both in estimating the chance of
progressing to AML and in estimating the duration of overall survival. Intermediate 3.5–4.5 20 3 3.2
This is shown in Table 60.4 and Table 60.5. The original IPSS High 5–6 13 1.6 1.4
excluded patients with t-MDS, patients with proliferative CMML, Very high >6 10 0.8 0.73
and patients who ultimately underwent allogeneic stem cell trans-
plantation or other disease-modifying therapy. AML, Acute myeloid leukemia; NR, not reached.
The original IPSS had several limitations that ultimately neces-
sitated its revision. First, it was formulated 4 years before the adoption
of the first iteration of WHO classification criteria, and some of
changes in those criteria (for instance, changing the cutoff for AML and the serum ferritin, that have been shown to have independent
from 30% blasts to 20% blasts) effectively invalidated certain aspects prognostic value in dedicated studies. It does not capture the kinetics
of the IPSS. Furthermore, broad application of the criteria to larger of disease or comorbid conditions. In addition, similar to the WHO
populations of MDS patients began to reveal that the original IPSS classification criteria, IPSS-R does not include any molecular data
gave insufficient weight to some important clinical features, particu- other than cytogenetics.
larly the presence of severe cytopenias. The IPSS was only validated
in de novo disease, not t-MDS, and only in patients treated with
supportive care alone. In response to some of these evident limita- Other Risk Stratification Systems
tions, several alternative prognostic systems have been proposed over
the last decade, but none of them have been widely adopted. 332–334 The limitations of the IPSS prompted attempts at more refined risk
The IPSS-R (Table 60.6), which was introduced in 2012, revised stratification using alternative models. Few of these have gained much
the MDS blast cutoff to 20% and assigned a point for each individual traction in clinical practice but retain value for use in clinical trials
cytopenia present at the time of diagnosis, stratifying on the basis of and retrospective studies. For instance, a need for better stratification
severity. Furthermore, it incorporated a broader range of cytogenetic of lower-risk patients (i.e., IPSS-low or Int-1) led to the creation of
abnormalities than the original IPSS, and stratified patients into five the Lower-Risk Prognostic Scoring System (LR-PSS) by the MD
332
risk categories instead of four. The resulting system thus incorporates Anderson group. The LR-PSS uses criteria similar to the IPSS but
more informative biology and offers better refinement of prognosis sets lower thresholds for point assignment (e.g., 2 points for a platelet
9
than its predecessor. 335,336 count <50 × 10 /L and 1 point for bone marrow blasts ≥4%). Sub-
The median survival times estimated by the IPSS and IPSS-R are sequent studies have confirmed the ability of LR-PSS to risk-stratify
largely reflective of natural history since they were originally derived patients, with those in the highest risk group having the greatest risk
339
in patients who did not receive any therapy for their MDS (Table of developing AML, and the poorest overall survival, and addition
60.5). However, IPSS-R stratifications have been shown to retain of genetic sequencing has shown that in these low-risk patients,
112
relevance when applied to treated populations, including risk strati- EZH2 mutations, though rare, portend a poor prognosis. Other
337
fication of patients receiving hypomethylating agents and those attempts to improve prognostic systems have included attempts to
340
who undergo allogeneic stem cell transplantation. 338 incorporate formal measures of comorbidity into the IPSS, and an
Nevertheless, the IPSS-R still has prognostic limitations. It does attempt to combine the WHO classification system with the IPSS
341
not incorporate laboratory findings, such as lactate dehydrogenase that has been dubbed the WPSS. This latter system was formulated