Page 1123 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1123
Chapter 62 Acute Myeloid Leukemia in Children 989
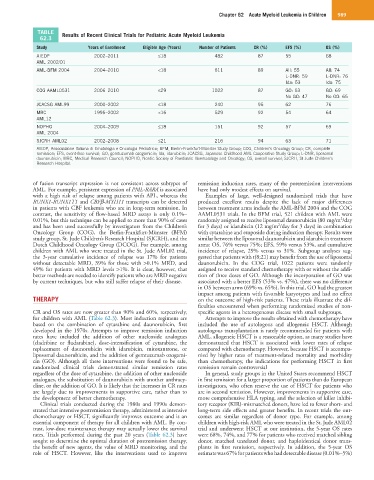
TABLE Results of Recent Clinical Trials for Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia
62.3
Study Years of Enrollment Eligible Age (Years) Number of Patients CR (%) EFS (%) OS (%)
AIEOP 2002–2011 ≤18 482 87 55 68
AML 2002/01
AML-BFM 2004 2004–2010 <18 611 89 All: 55 All: 74
L-DNR: 59 L-DNR: 76
Ida: 53 Ida: 75
COG AAML0531 2006–2010 ≤29 1022 87 GO: 53 GO: 69
No GO: 47 No GO: 65
JCACSG AML99 2000–2002 ≤18 240 95 62 76
MRC 1995–2002 <16 529 92 54 64
AML12
NOPHO 2004–2009 ≤18 151 92 57 69
AML 2004
SJCRH AML02 2002–2008 ≤21 216 94 63 71
AIEOP, Associazione Italiana di Ematologia e Oncologia Pediatrica; BFM, Berlin-Frankfurt-Münster Study Group; COG, Children’s Oncology Group; CR, complete
remission; EFS, event-free survival; GO, gemtuzumab ozogamicin; Ida, idarubicin; JCACSG, Japanese Childhood AML Cooperative Study Group; L-DNR, liposomal
daunorubicin; MRC, Medical Research Council; NOPHO, Nordic Society of Paediatric Haematology and Oncology; OS, overall survival; SJCRH, St Jude Children’s
Research Hospital.
of fusion transcript expression is not consistent across subtypes of remission induction rates, many of the postremission interventions
AML. For example, persistent expression of PML-RARA is associated have had only modest effects on survival.
with a high risk of relapse among patients with APL, whereas the Examples of large, well-designed randomized trials that have
RUNX1-RUNX1T1 and CBFβ-MYH11 transcripts can be detected produced excellent results despite the lack of major differences
in patients with CBF leukemia who are in long-term remission. In between treatment arms include the AML-BFM 2004 and the COG
contrast, the sensitivity of flow-based MRD assays is only 0.1%– AAML0531 trials. In the BFM trial, 521 children with AML were
2
0.01%, but this technique can be applied to more than 90% of cases randomly assigned to receive liposomal daunorubicin (80 mg/m /day
2
and has been used successfully by investigators from the Children’s for 3 days) or idarubicin (12 mg/m /day for 3 days) in combination
Oncology Group (COG), the Berlin-Frankfurt-Münster (BFM) with cytarabine and etoposide during induction therapy. Results were
study group, St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital (SJCRH), and the similar between the liposomal daunorubicin and idarubicin treatment
Dutch Childhood Oncology Group (DCOG). For example, among arms: OS, 76% versus 75%; EFS, 59% versus 53%, and cumulative
children with AML who were treated in the St. Jude AML02 trial, incidence of relapse, 29% versus vs 31%. Subgroup analyses sug-
the 3-year cumulative incidence of relapse was 17% for patients gested that patients with t(8;21) may benefit from the use of liposomal
without detectable MRD, 39% for those with >0.1% MRD, and daunorubicin. In the COG trial, 1022 patients were randomly
49% for patients with MRD levels >1%. It is clear, however, that assigned to receive standard chemotherapy with or without the addi-
better methods are needed to identify patients who are MRD negative tion of three doses of GO. Although the incorporation of GO was
by current techniques, but who still suffer relapse of their disease. associated with a better EFS (53% vs. 47%), there was no difference
in OS between arms (69% vs. 65%). In this trial, GO had the greatest
impact among patients with favorable karyotypes and had no effect
THERAPY on the outcome of high-risk patients. These trials illustrate the dif-
ficulties encountered when performing randomized studies of non-
CR and OS rates are now greater than 90% and 60%, respectively, specific agents in a heterogeneous disease with small subgroups.
for children with AML (Table 62.3). Most induction regimens are Attempts to improve the results obtained with chemotherapy have
based on the combination of cytarabine and daunorubicin, first included the use of autologous and allogeneic HSCT. Although
developed in the 1970s. Attempts to improve remission induction autologous transplantation is rarely recommended for patients with
rates have included the addition of other nucleoside analogues AML, allogeneic HSCT is a reasonable option, as many studies have
(cladribine or fludarabine), dose-intensification of cytarabine, the demonstrated that HSCT is associated with lower rates of relapse
replacement of daunorubicin with idarubicin, mitoxantrone, or compared with chemotherapy. However, because HSCT is accompa-
liposomal daunorubicin, and the addition of gemtuzumab ozogami- nied by higher rates of treatment-related mortality and morbidity
cin (GO). Although all these interventions were found to be safe, than chemotherapy, the indications for performing HSCT in first
randomized clinical trials demonstrated similar remission rates remission remain controversial
regardless of the dose of cytarabine, the addition of other nucleoside In general, study groups in the United States recommend HSCT
analogues, the substitution of daunorubicin with another anthracy- in first remission for a larger proportion of patients than do European
cline, or the addition of GO. It is likely that the increases in CR rates investigators, who often reserve the use of HSCT for patients who
are largely due to improvements in supportive care, rather than to are in second remission. However, improvements in supportive care,
the development of better chemotherapy. more comprehensive HLA typing, and the selection of killer inhibi-
Clinical trials conducted during the 1980s and 1990s demon- tory receptor (KIR)-mismatched donors, have led to fewer short- and
strated that intensive postremission therapy, administered as intensive long-term side effects and greater benefits. In recent trials the out-
chemotherapy or HSCT, significantly improves outcome and is an comes are similar regardless of donor type. For example, among
essential component of therapy for all children with AML. By con- children with high-risk AML who were treated in the St. Jude AML02
trast, low-dose maintenance therapy may actually lower the survival trial and underwent HSCT at our institution, the 5-year OS rates
rates. Trials performed during the past 20 years (Table 62.3) have were 68%, 74%, and 77% for patients who received matched sibling
sought to determine the optimal duration of postremission therapy, donor, matched unrelated donor, and haploidentical donor trans-
the benefit of new agents, the value of MRD monitoring, and the plants in first remission, respectively. In addition, the 5-year OS
role of HSCT. However, like the interventions used to improve estimate was 67% for patients who had detectable disease (0.01%–5%)