Page 1226 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1226
1072 Part VII Hematologic Malignancies
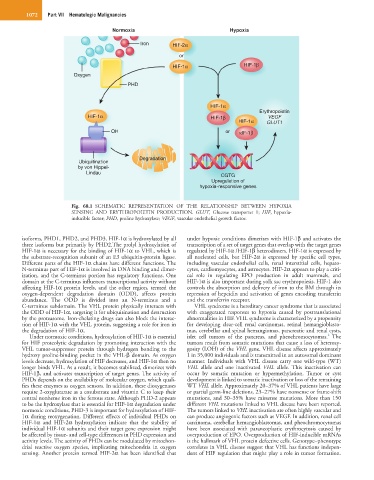
Normoxia Hypoxia
Iron HIF-2α
or
HIF-1α HIF-1β
Oxygen
PHD
HIF-1α
Erythropoietin
HIF-1α HIF-1β VEGF
HIF-1α GLUT1
OH or κIF-1β
Degradation
Ubiquitination
by von Hippel-
Lindau
CGTG
Upregulation of
hypoxia-responsive genes
Fig. 68.1 SCHEMATIC REPRESENTATION OF THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN HYPOXIA
SENSING AND ERYTHROPOIETIN PRODUCTION. GLUT, Glucose transporter 1; HIF, hypoxia-
inducible factor; PHD, proline hydroxylase; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.
isoforms, PHD1, PHD2, and PHD3. HIF-1α is hydroxylated by all under hypoxic conditions dimerizes with HIF-1β and activates the
three isoforms but primarily by PHD2.The prolyl hydroxylation of transcription of a set of target genes that overlap with the target genes
HIF-1α is necessary for the binding of HIF-1α to VHL, which is regulated by HIF-1α /HIF-1β heterodimers. HIF-1α is expressed by
the substrate-recognition subunit of an E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase. all nucleated cells, but HIF-2α is expressed by specific cell types,
Different parts of the HIF-1α chains have different functions. The including vascular endothelial cells, renal interstitial cells, hepato-
N-terminus part of HIF-1α is involved in DNA binding and dimer- cytes, cardiomyocytes, and astrocytes. HIF-2α appears to play a criti-
ization, and the C-terminus portion has regulatory functions. One cal role in regulating EPO production in adult mammals, and
domain at the C-terminus influences transcriptional activity without HIF-1α is also important during yolk sac erythropoiesis. HIF-1 also
affecting HIF-1α protein levels, and the other region, termed the controls the absorption and delivery of iron to the BM through its
oxygen-dependent degradation domain (ODD), affects protein repression of hepcidin and activation of genes encoding transferrin
abundance. The ODD is divided into an N-terminus and a and the transferrin receptor.
C-terminus subdomain. The VHL protein physically interacts with VHL syndrome is a hereditary cancer syndrome that is associated
the ODD of HIF-1α, targeting it for ubiquitination and destruction with exaggerated responses to hypoxia caused by posttranslational
by the proteasome. Iron-chelating drugs can also block the interac- abnormalities in HIF. VHL syndrome is characterized by a propensity
tion of HIF-1α with the VHL protein, suggesting a role for iron in for developing clear-cell renal carcinomas, retinal hemangioblasto-
the degradation of HIF-1α. mas, cerebellar and spinal hemangiomas, pancreatic and renal cysts,
2
Under normoxic conditions, hydroxylation of HIF-1α is essential islet cell tumors of the pancreas, and pheochromocytomas. The
for HIF proteolytic degradation by promoting interaction with the tumors result from somatic mutations that cause a loss of heterozy-
VHL tumor-suppressor protein through hydrogen bonding to the gosity (LOH) of the VHL gene. VHL disease affects approximately
hydroxy proline-binding pocket in the VHL-β domain. As oxygen 1 in 35,000 individuals and is transmitted in an autosomal dominant
levels decrease, hydroxylation of HIF decreases, and HIF-1α then no manner. Individuals with VHL disease carry one wild-type (WT)
longer binds VHL. As a result, it becomes stabilized, dimerizes with VHL allele and one inactivated VHL allele. This inactivation can
HIF-1β, and activates transcription of target genes. The activity of occur by somatic mutation or hypermethylation. Tumor or cyst
PHDs depends on the availability of molecular oxygen, which quali- development is linked to somatic inactivation or loss of the remaining
fies these enzymes as oxygen sensors. In addition, these dioxygenases WT VHL allele. Approximately 20–37% of VHL patients have large
require 2-oxyglutarate as a cosubstrate and vitamin C to keep their or partial germ-line deletions, 23–27% have nonsense or frame-shift
central nonheme iron in the ferrous state. Although PHD-2 appears mutations, and 30–35% have missense mutations. More than 150
to be the hydroxylase that is essential for HIF-1α degradation under different VHL mutations linked to VHL disease have been reported.
normoxic conditions, PHD-3 is important for hydroxylation of HIF- The tumors linked to VHL inactivation are often highly vascular and
1α during reoxygenation. Different effects of individual PHDs on can produce angiogenic factors such as VEGF. In addition, renal cell
HIF-1α and HIF-2α hydroxylation indicate that the stability of carcinoma, cerebellar hemangioblastomas, and pheochromocytomas
individual HIF-1α subunits and their target gene expression might have been associated with paraneoplastic erythrocytosis caused by
be affected by tissue- and cell-type differences in PHD expression and overproduction of EPO. Overproduction of HIF-inducible mRNAs
activity levels. The activity of PHDs can be modulated by mitochon- is the hallmark of VHL protein defective cells. Genotype–phenotype
drial reactive oxygen species, implicating mitochondria in oxygen correlates in VHL disease suggest that VHL has functions indepen-
sensing. Another protein termed HIF-2α has been identified that dent of HIF regulation that might play a role in tumor formation.