Page 128 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 128
Chapter 9 Hematopoietic Stem Cell Biology 99
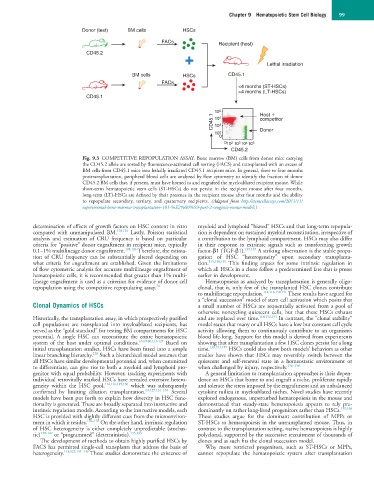
Donor (test) BM cells HSCs
FACs Recipient (host)
CD45.2
Lethal irradiation
BM cells HSCs CD45.1
FACs
<4 months (ST-HSCs)
>4 months (LT-HSCs)
CD45.1
CD45.1 10 5 4 3 Host +
10
competitor
10
10 2 Donor
0
0 10 10 10 10 5
3
4
2
CD45.2
Fig. 9.3 COMPETITIVE REPOPULATION ASSAY. Bone marrow (BM) cells from donor mice carrying
the CD45.2 allele are sorted by fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS) and transplanted with an excess of
BM cells from CD45.1 mice into lethally irradiated CD45.1 recipient mice. In general, three to four months
posttransplantation, peripheral blood cells are analyzed by flow cytometry to identify the fraction of donor
CD45.2 BM cells that, if present, must have homed to and engrafted the myeloablated recipient mouse. While
short-term hematopoietic stem cells (ST-HSCs) do not persist in the recipient mouse after four months,
long-term (LT)-HSCs are defined by their presence in the recipient mouse after four months and the ability
to repopulate secondary, tertiary, and quaternary recipients. (Adapted from http://stemcellassays.com/2011/11/
experimental-bone-marrow-transplantation-101-%E2%80%93-part-2-congenic-mouse-model/.)
determination of effects of growth factors on HSC content in vitro myeloid and lymphoid “biased” HSCs and that long-term repopula-
compared with unmanipulated BM. 103,125 Lastly, Poisson statistical tion is dependent on sustained myeloid reconstitution, irrespective of
analysis and estimation of CRU frequency is based on particular a contribution to the lymphoid compartment. HSCs may also differ
criteria for “positive” donor engraftment in recipient mice, typically in their response to extrinsic signals such as transforming growth
0.1–1% multilineage donor engraftment. 103,126 Therefore, the estima- factor-β1 (TGF-β1). 145,147 A striking observation is the stable propa-
tion of CRU frequency can be substantially altered depending on gation of HSC “heterogeneity” upon secondary transplanta-
what criteria for engraftment are established. Given the limitations tion. 115,148,149 This finding argues for some intrinsic regulation in
of flow cytometric analysis for accurate multilineage engraftment of which all HSCs in a clone follow a predetermined fate that is preset
hematopoietic cells, it is recommended that greater than 1% multi- earlier in development.
lineage engraftment is used as a criterion for evidence of donor cell Hematopoiesis as analyzed by transplantation is generally oligo-
repopulation using the competitive repopulating assay. 78 clonal, that is, only few of the transplanted HSC clones contribute
to multilineage repopulation. 114,116,150,151 These results have argued for
a “clonal succession” model of stem cell activation which posits that
Clonal Dynamics of HSCs a small number of HSCs are sequentially activated from a pool of
otherwise noncycling quiescent cells, but that these HSCs exhaust
Historically, the transplantation assay, in which prospectively purified and are replaced over time. 114,152,153 In contrast, the “clonal stability”
cell populations are transplanted into myeloablated recipients, has model states that many or all HSCs have a low but constant cell cycle
served as the “gold standard” for testing BM compartments for HSC activity allowing them to continuously contribute to an organism’s
potential. A single HSC can reconstitute the entire hematopoietic blood life-long. Support for this model is derived from experiments
system of the host under optimal conditions. 63,69,80,115,127 Based on showing that after transplantation a few HSC clones persist for a long
initial transplantation studies, HSCs have been fitted into a simple time. 139,154,155 HSCs could also show both models’ behaviors as other
128
linear branching hierarchy. Such a hierarchical model assumes that studies have shown that HSCs may reversibly switch between the
all HSCs have similar developmental potential and, when committed quiescent and self-renewal state in a homeostatic environment or
to differentiate, can give rise to both a myeloid and lymphoid pro- when challenged by injury, respectively. 156–158
genitor with equal probability. However, tracking experiments with A general limitation to transplantation approaches is their depen-
individual retrovirally marked HSCs have revealed extensive hetero- dence on HSCs that home to and engraft a niche, proliferate rapidly
geneity within the HSC pool, 114,116,129,130 which was subsequently and tolerate the stress imposed by the engraftment and an unbalanced
confirmed by limiting dilution transplantation. 63,127,131–135 Several cytokine milieu in myeloablated niches. Novel studies have recently
models have been put forth to explain how diversity in HSC func- explored endogenous, unperturbed hematopoiesis in the mouse and
tionality is generated. These are broadly separated into instructive and demonstrated that steady-state hematopoiesis appears to rely pre-
intrinsic regulation models. According to the instructive models, each dominantly on rather long-lived progenitors rather than HSCs. 159,160
HSC is provided with slightly different cues from the microenviron- These studies argue for the dominant contribution of MPPs or
ment in which it resides. 136–138 On the other hand, intrinsic regulation ST-HSCs to hematopoiesis in the untransplanted mouse. Thus, in
of HSC heterogeneity is either completely unpredictable (stochas- contrast to the transplantation setting, native hematopoiesis is highly
tic) 139–142 or “programmed” (deterministic). 135,143 polyclonal, supported by the successive recruitment of thousands of
The development of methods to obtain highly purified HSCs by clones and as such fits the clonal succession model.
FACS has permitted single-cell transplants that address the basis of Why more restricted progenitors, such as ST-HSCs or MPPs,
heterogeneity. 115,127,144–146 These studies demonstrate the existence of cannot repopulate the hematopoietic system after transplantation