Page 131 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 131
102 Part II Cellular Basis of Hematology
244
transcribing DNA into RNA. Because the intrinsic phenotype or state regulated, at least in part, by the antagonism of lineage-specific tran-
of a cell is the result of its gene expression, it is governed by the concerted scription factors. To promote a given lineage, transcription factors need
action of transcription factors (guided by the epigenetic landscape dis- to actively counteract factor(s) supporting other cell fates. Third, and
cussed further below). The balance between self-renewal and differentia- most relevant to clinical situations, most hematopoietic transcription
tion of HSCs is intricately regulated by transcription factors of many factors are subject to somatic mutation and/or chromosomal transloca-
245
different classes. Several general principles have emerged. First, given tion in one or more hematopoietic malignancies. Thus, malignancy can
the relative limited number of transcription factors, they are used at be viewed as a disruption of normal development. Fig. 9.2 depicts key
multiple stages in development, such that they may be required in HSCs transcription factors within the hematopoietic hierarchy, and Table 9.1
18
and also subsequently in lineage differentiation. Second, the balance summarizes main roles of critical transcription factors in HSPCs and
between self-renewal and lineage commitment is thought to be hematologic malignancies.
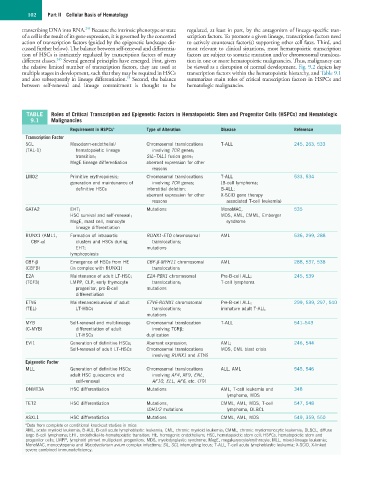
TABLE Roles of Critical Transcription and Epigenetic Factors in Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells (HSPCs) and Hematologic
9.1 Malignancies
Requirement in HSPCs a Type of Alteration Disease Reference
Transcription Factor
SCL Mesoderm-endothelial/ Chromosomal translocations T-ALL 245, 263, 533
(TAL-1) hematopoietic lineage involving TCR genes;
transition; SIL–TAL1 fusion gene;
MegE lineage differentiation aberrant expression for other
reasons
LMO2 Primitive erythropoiesis; Chromosomal translocations T-ALL 533, 534
generation and maintenance of involving TCR genes; (B-cell lymphoma;
definitive HSCs interstitial deletion; B-ALL;
aberrant expression for other X-SCID gene therapy
reasons associated T-cell leukemia)
GATA2 EHT; Mutations MonoMAC, 535
HSC survival and self-renewal; MDS, AML, CMML, Emberger
MegE, mast cell, monocyte syndrome
lineage differentiation
RUNX1 (AML1, Formation of intraaortic RUNX1-ETO chromosomal AML 536, 299, 288
CBF-α) clusters and HSCs during translocations;
EHT; mutations
lymphopoiesis
CBF-β Emergence of HSCs from HE CBF-β-MYH11 chromosomal AML 288, 537, 538
(CBFB) (in complex with RUNX1) translocations
E2A Maintenance of adult LT-HSC; E2A-PBX1 chromosomal Pre-B-cell ALL; 245, 539
(TCF3) LMPP, CLP, early thymocyte translocations; T-cell lymphoma
progenitor, pro-B-cell mutations
differentiation
ETV6 Maintenance/survival of adult ETV6-RUNX1 chromosomal Pre-B-cell ALL; 299, 539, 297, 540
(TEL) LT-HSCs translocations; immature adult T-ALL
mutations
MYB Self-renewal and multilineage Chromosomal translocation T-ALL 541–543
(C-MYB) differentiation of adult involving TCRβ;
LT-HSCs duplication
EVI1 Generation of definitive HSCs; Aberrant expression; AML; 246, 544
Self-renewal of adult LT-HSCs Chromosomal translocations MDS, CML blast crisis
involving RUNX1 and ETV6
Epigenetic Factor
MLL Generation of definitive HSCs; Chromosomal translocations ALL, AML 545, 546
adult HSC quiescence and involving AF4, AF9, ENL,
self-renewal AF10, ELL, AF6, etc. (79)
DNMT3A HSC differentiation Mutations AML, T-cell leukemia and 348
lymphoma, MDS
TET2 HSC differentiation Mutations, CMML, AML, MDS, T-cell 547, 548
IDH1/2 mutations lymphoma, DLBCL
ASXL1 HSC differentiation Mutations CMML, AML, MDS 549, 359, 550
a Data from complete or conditional knockout studies in mice
AML, acute myeloid leukemia; B-ALL, B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia; CML, chronic myeloid leukemia; CMML, chronic myelomonocytic leukemia; DLBCL, diffuse
large B-cell lymphoma; EHT, endothelial-to-hematopoietic transition; HE, hemogenic endothelium; HSC, hematopoietic stem cell; HSPCs, hematopoietic stem and
progenitor cells; LMPP, lymphoid primed multipotent progenitors; MDS, myelodysplastic syndrome; MegE, megakaryocyte/erythrocyte; MLL, mixed-lineage leukemia;
MonoMAC, monocytopenia and Mycobacterium avium complex infections; SIL, SCL interrupting locus; T-ALL, T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia; X-SCID, X-linked
severe combined immunodeficiency.