Page 1306 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1306
1152 Part VII Hematologic Malignancies
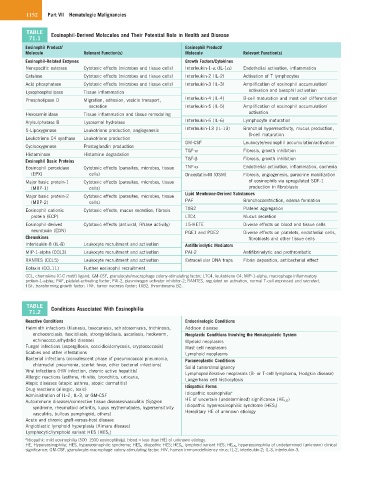
TABLE Eosinophil-Derived Molecules and Their Potential Role in Health and Disease
71.1
Eosinophil Product/ Eosinophil Product/
Molecule Relevant Function(s) Molecule Relevant Function(s)
Eosinophil-Related Enzymes Growth Factors/Cytokines
Nonspecific esterase Cytotoxic effects (microbes and tissue cells) Interleukin-1-α (IL-1α) Endothelial activation, inflammation
Catalase Cytotoxic effects (microbes and tissue cells) Interleukin-2 (IL-2) Activation of T lymphocytes
Acid phosphatase Cytotoxic effects (microbes and tissue cells) Interleukin-3 (IL-3) Amplification of eosinophil accumulation/
Lysophospholipase Tissue inflammation activation and basophil activation
Phospholipase D Migration, adhesion, vesicle transport, Interleukin-4 (IL-4) B-cell maturation and mast cell differentiation
secretion Interleukin-5 (IL-5) Amplification of eosinophil accumulation/
Hexosaminidase Tissue inflammation and tissue remodeling activation
Arylsulphatase B Lysosomal hydrolase Interleukin-6 (IL-6) Lymphocyte maturation
5-Lipoxygenase Leukotriene production, angiogenesis Interleukin-13 (IL-13) Bronchial hyperreactivity, mucus production,
B-cell maturation
Leukotriene C4 synthase Leukotriene production
GM-CSF Leukocyte/eosinophil accumulation/activation
Cyclooxygenase Prostaglandin production
TGF-α Fibrosis, growth inhibition
Histaminase Histamine degradation
Eosinophil Basic Proteins TGF-β Fibrosis, growth inhibition
Eosinophil peroxidase Cytotoxic effects (parasites, microbes, tissue TNF-α Endothelial activation, inflammation, cachexia
(EPX) cells) Oncostatin-M (OSM) Fibrosis, angiogenesis, paracrine mobilization
Major basic protein-1 Cytotoxic effects (parasites, microbes, tissue of eosinophils via upregulated SDF-1
(MBP-1) cells) production in fibroblasts
Lipid Membrane-Derived Substances
Major basic protein-2 Cytotoxic effects (parasites, microbes, tissue
(MBP-2) cells) PAF Bronchoconstriction, edema formation
Eosinophil cationic Cytotoxic effects, mucus secretion, fibrosis TXB2 Platelet aggregation
protein (ECP) LTC4 Mucus secretion
Eosinophil-derived Cytotoxic effects (antiviral, RNase activity) 15-HETE Diverse effects on blood and tissue cells
neurotoxin (EDN) PGE1 and PGE2 Diverse effects on platelets, endothelial cells,
Chemokines fibroblasts and other tissue cells
Interleukin-8 (IL-8) Leukocyte recruitment and activation Antifibrinolytic Mediators
MIP-1-alpha (CCL3) Leukocyte recruitment and activation PAI-2 Antifibrinolytic and prothrombotic
RANTES (CCL5) Leukocyte recruitment and activation Extracellular DNA traps Fibrin deposition, antibacterial effect
Eotaxin (CCL11) Further eosinophil recruitment
CCL, chemokine (C-C motif) ligand; GM-CSF, granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor; LTC4, leukotriene C4; MIP-1-alpha, macrophage inflammatory
protein-1-alpha; PAF, platelet-activating factor; PAI-2, plasminogen activator inhibitor-2; RANTES, regulated on activation, normal T-cell expressed and secreted;
TGF, transforming growth factor; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; TXB2, thromboxane B2.
TABLE Conditions Associated With Eosinophilia
71.2
Reactive Conditions Endocrinologic Conditions
Helminth infections (filariasis, toxocariasis, schistosomiasis, trichinosis, Addison disease
onchocerciasis, fascioliasis, strongyloidiasis, ascariasis, hookworm, Neoplastic Conditions Involving the Hematopoietic System
echinococcus/hydatid disease) Myeloid neoplasms
Fungal infections (aspergillosis, coccidioidomycosis, cryptococcosis) Mast cell neoplasms
Scabies and other infestations Lymphoid neoplasms
Bacterial infections (convalescent phase of pneumococcal pneumonia, Paraneoplastic Conditions
chlamydial pneumonia, scarlet fever, other bacterial infections)
Viral infections (HIV infection, chronic active hepatitis) Solid tumors/malignancy
Lymphoproliferative neoplasms (B- or T-cell lymphoma, Hodgkin disease)
Allergic reactions (asthma, rhinitis, bronchitis, urticaria, Langerhans cell histiocytosis
Atopic diseases (atopic asthma, atopic dermatitis)
Drug reactions (allergic, toxic) Idiopathic Forms a
Administration of IL-2, IL-3, or GM-CSF Idiopathic eosinophilia
Autoimmune diseases/connective tissue diseases/vasculitis (Sjögren HE of uncertain (undetermined) significance (HE US )
syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, lupus erythematodes, hypersensitivity Idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome (HES I )
vasculitis, bullous pemphigoid, others) Hereditary HE of unknown etiology
Acute and chronic graft-versus-host disease
Angioblastic lymphoid hyperplasia (Kimura disease)
Lymphocytic/lymphoid variant HES (HES L )
a Idiopathic mild eosinophilia (500–1500 eosinophils/µL blood = less than HE) of unknown etiology.
HE, Hypereosinophilia; HES, hypereosinophilic syndrome; HES I , idiopathic HES; HES L, lymphoid variant HES; HE US, hypereosinophilia of undetermined (unknown) clinical
significance; GM-CSF, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; IL-2, interleukin-2; IL-3, interleukin-3.