Page 1420 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1420
1266 Part VII Hematologic Malignancies
Germinal
center
Naive B cells reaction
Somatic
hypermutation
FDC
Memory B
Helper cell
T cells
Plasma cell
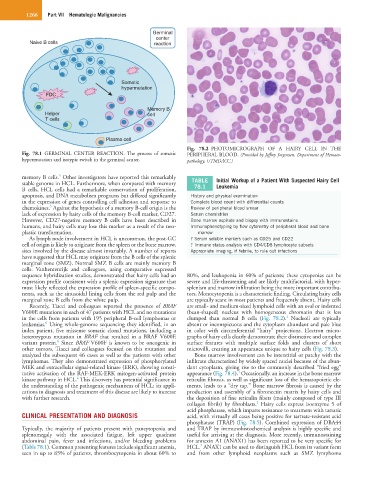
Fig. 78.2 PHOTOMICROGRAPH OF A HAIRY CELL IN THE
Fig. 78.1 GERMINAL CENTER REACTION. The process of somatic PERIPHERAL BLOOD. (Provided by Jeffrey Jorgensen, Department of Hemato-
hypermutation and isotypic switch in the germinal center. pathology, UTMDACC.)
5
memory B cells. Other investigators have reported this remarkably TABLE Initial Workup of a Patient With Suspected Hairy Cell
stable genome in HCL. Furthermore, when compared with memory 78.1 Leukemia
B cells, HCL cells had a remarkable conservation of proliferation,
apoptosis, and DNA metabolism programs but differed significantly History and physical examination
in the expression of genes controlling cell adhesion and response to Complete blood count with differential counts
5
chemokines. Against the hypothesis of a memory B-cell origin is the Review of peripheral blood smear
lack of expression by hairy cells of the memory B-cell marker, CD27. Serum chemistries
However, CD27-negative memory B cells have been described in Bone marrow aspirate and biopsy with immunostains
humans, and hairy cells may lose this marker as a result of the neo- Immunophenotyping by flow cytometry of peripheral blood and bone
plastic transformation. marrow
As lymph node involvement in HCL is uncommon, the post-GC ? Serum soluble markers such as CD25 and CD22
cell of origin is likely to originate from the spleen or the bone marrow, ? Immune status analysis with CD4/CD8 lymphocyte subsets
sites involved by the disease almost invariably. A number of reports Appropriate imaging, if febrile, to rule out infections
have suggested that HCL may originate from the B cells of the splenic
marginal zone (SMZ). Normal SMZ B cells are mainly memory B
cells. Vanhentenrijk and colleagues, using comparative expressed
sequence hybridization studies, demonstrated that hairy cells had an 80%, and leukopenia in 60% of patients; these cytopenias can be
expression profile consistent with a splenic expression signature that severe and life-threatening and are likely multifactorial, with hyper-
most likely reflected the expression profile of spleen-specific compo- splenism and marrow infiltration being the more important contribu-
nents, such as the sinusoidal lining cells from the red pulp and the tors. Monocytopenia is a characteristic finding. Circulating hairy cells
marginal zone B cells from the white pulp. are typically scant in most patients and frequently absent. Hairy cells
Recently, Tiacci and colleagues reported the presence of BRAF are small- and medium-sized lymphoid cells with an oval or indented
V600E mutations in each of 47 patients with HCL and no mutations (bean-shaped) nucleus with homogeneous chromatin that is less
1
in the cells from patients with 195 peripheral B-cell lymphomas or clumped than normal B cells (Fig. 78.2). Nucleoli are typically
6
leukemias. Using whole-genome sequencing they identified, in an absent or inconspicuous and the cytoplasm abundant and pale blue
index patient, five missense somatic clonal mutations, including a in color with circumferential “hairy” projections. Electron micro-
heterozygous mutation in BRAF that resulted in a BRAF V600E graphs of hairy cells clearly demonstrate their distinctive and complex
6
variant protein. Since BRAF V600F is known to be oncogenic in surface features with multiple surface folds and clusters of short
other tumors, Tiacci and colleagues focused on this mutation and microvilli, creating an appearance unique to hairy cells (Fig. 78.3).
analyzed the subsequent 46 cases as well as the patients with other Bone marrow involvement can be interstitial or patchy with the
lymphomas. They also demonstrated expression of phosphorylated infiltrate characterized by widely spaced nuclei because of the abun-
MEK and extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK), showing consti- dant cytoplasm, giving rise to the commonly described “fried egg”
1
tutive activation of the RAF-MEK-ERK mitogen-activated protein appearance (Fig. 78.4). Occasionally, an increase in the bone marrow
6
kinase pathway in HCL. This discovery has potential significance in reticulin fibrosis, as well as significant loss of the hematopoietic ele-
the understanding of the pathogenic mechanisms of HCL; its appli- ments, leads to a “dry tap.” Bone marrow fibrosis is caused by the
cations in diagnosis and treatment of this disease are likely to increase production and assembly of a fibronectin matrix by hairy cells and
with further research. the deposition of fine reticulin fibers (mainly composed of type III
2
collagen fibrils) by fibroblasts. Hairy cells express isoenzyme 5 of
acid phosphatase, which imparts resistance to treatment with tartaric
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND DIAGNOSIS acid, with virtually all cases being positive for tartrate-resistant acid
phosphatase (TRAP) (Fig. 78.5). Combined expression of DBA44
Typically, the majority of patients present with pancytopenia and and TRAP by immunohistochemical analysis is highly specific and
splenomegaly with the associated fatigue, left upper quadrant useful for arriving at the diagnosis. More recently, immunostaining
abdominal pain, fever and infections, and/or bleeding problems for annexin A1 (ANAX1) has been reported to be very specific for
7
(Table 78.1). Common presenting features include significant anemia, HCL. ANAX1 can be used to distinguish HCL from its variant form
seen in up to 85% of patients, thrombocytopenia in about 60% to and from other lymphoid neoplasms such as SMZ lymphoma