Page 158 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 158
116 Part II Cellular Basis of Hematology
A
Splenic marginal FL,
zone lymphoma Marginal GCB-type
zone DLBCL
Naive B Mantle Centrocyte Memory B cell
cell zone GC B
cell
CLL,IGHV
mutated
CLL,IGHV MCL
unmutated Pre-plasmablast Plasmablast Plasma cell
Centroblast
ABC-type
DLBCL
B
Long-term hematopoietic
Long-term hematopoietic
stem cells stem cells
Self renewal
Self renewal
Intermediate
Intermediate progenitor
progenitor cells
cells
Self renewal
Precursor B cell
Precursor
B cell
Self Mature B cell
renewal malignancy
Mature B cell
malignancy
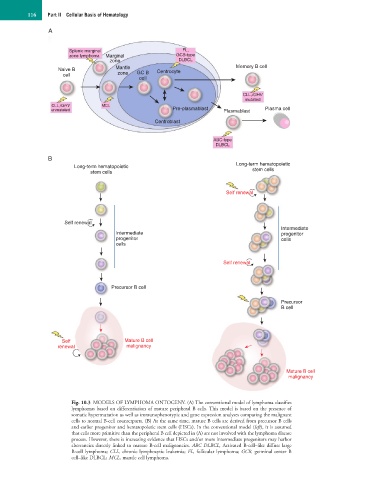
Fig. 10.3 MODELS OF LYMPHOMA ONTOGENY. (A) The conventional model of lymphoma classifies
lymphomas based on differentiation of mature peripheral B cells. This model is based on the presence of
somatic hypermutation as well as immunophenotypic and gene expression analyses comparing the malignant
cells to normal B-cell counterparts. (B) At the same time, mature B cells are derived from precursor B cells
and earlier progenitor and hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs). In the conventional model (left), it is assumed
that cells more primitive than the peripheral B cell depicted in (A) are not involved with the lymphoma disease
process. However, there is increasing evidence that HSCs and/or more intermediate progenitors may harbor
aberrancies directly linked to mature B-cell malignancies. ABC DLBCL, Activated B-cell–like diffuse large
B-cell lymphoma; CLL, chronic lymphocytic leukemia; FL, follicular lymphoma; GCB, germinal center B
cell–like DLBCL; MCL, mantle cell lymphoma.