Page 154 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 154
112 Part II Cellular Basis of Hematology
A BCR-ABL B C D TET2
AML1-ETO DNMT3A
JAK2V617F ASXL1
IDH1/2
HSC LSC Preleukemic
(CD34+ CD38−) LSC population stem cells
#1 FLT3
PML-RARA N/KRAS
Progenitors
(CD34+ CD38+) LSC LSC
population
#2
Mature Acute
blood promyelocytic Frank Frank
cells leukemia leukemia leukemia
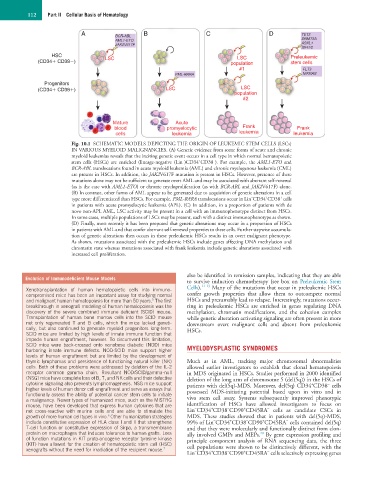
Fig. 10.1 SCHEMATIC MODELS DEPICTING THE ORIGIN OF LEUKEMIC STEM CELLS (LSCs)
IN VARIOUS MYELOID MALIGNANCIES. (A) Genetic evidence from some forms of acute and chronic
myeloid leukemias reveals that the inciting genetic event occurs in a cell type in which normal hematopoietic
+
−
−
stem cells (HSCs) are enriched (lineage-negative (Lin )CD34 CD38 ). For example, the AML1-ETO and
BCR-ABL translocations found in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML)
are present in HSCs. In addition, the JAK2V617F mutation is present in HSCs. However, presence of these
mutations alone may not be sufficient to generate overt AML and may be associated with aberrant self-renewal
(as is the case with AML1-ETO) or chronic myeloproliferation (as with BCR-ABL and JAK2V617F) alone.
(B) In contrast, other forms of AML appear to be generated due to acquisition of genetic alterations in a cell
+
−
+
type more differentiated than HSCs. For example, PML-RARA translocations occur in Lin CD34 CD38 cells
in patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL). (C) In addition, in a proportion of patients with de
novo non-APL AML, LSC activity may be present in a cell with an immunophenotype distinct from HSCs.
In some cases, multiple populations of LSCs may be present, each with a distinct immunophenotype as shown.
(D) Finally, most recently it has been proposed that genetic alterations may occur in a proportion of HSCs
in patients with AML and that confer aberrant self-renewal properties to these cells. Further stepwise accumula-
tion of genetic alterations then occurs in these preleukemic HSCs results in an overt malignant phenotype.
As shown, mutations associated with the preleukemic HSCs include genes affecting DNA methylation and
chromatin state whereas mutations associated with frank leukemia include genetic alterations associated with
increased cell proliferation.
also be identified in remission samples, indicating that they are able
Evolution of Immunodeficient Mouse Models
to survive induction chemotherapy (see box on Preleukemic Stem
Xenotransplantation of human hematopoietic cells into immuno- Cells). 11–13 Many of the mutations that occur in preleukemic HSCs
compromised mice has been an important assay for studying normal confer growth properties that allow them to outcompete normal
5
and malignant human hematopoiesis for more than 50 years. The first HSCs and presumably lead to relapse. Interestingly, mutations occur-
breakthrough in xenograft modeling of human hematopoiesis was the ring in preleukemic HSCs are enriched in genes regulating DNA
discovery of the severe combined immune deficient (SCID) mouse. methylation, chromatin modifications, and the cohesion complex
Transplantation of human bone marrow cells into the SCID mouse while genetic alteration activating signaling are often present in more
not only regenerated T and B cells, which the mice lacked geneti- downstream overt malignant cells and absent from preleukemic
cally, but also continued to generate myeloid progenitors long-term. HSCs.
SCID mice are limited by high levels of innate immune function that
impede human engraftment, however. To circumvent this limitation,
SCID mice were back-crossed onto nonobese diabetic (NOD) mice
harboring innate immune defects. NOD-SCID mice support higher MYELODYSPLASTIC SYNDROMES
levels of human engraftment but are limited by the development of
thymic lymphomas and persistence of functioning natural killer (NK) Much as in AML, tracking major chromosomal abnormalities
cells. Both of these problems were addressed by deletion of the IL-2 allowed earlier investigators to establish that clonal hematopoiesis
receptor common gamma chain. Resultant NOD/SCID/gamma-null in MDS originated in HSCs. Studies performed in 2000 identified
(NSG) mice have complete loss of B, T, and NK cells and their defective deletion of the long arm of chromosome 5 (del(5q)) in the HSCs of
cytokine signaling also prevents lymphomagenesis. NSG mice support patients with del(5q)-MDS. Moreover, del(5q) CD34 CD38 cells
−
+
higher levels of human donor cell engraftment and serve as assays that possessed MDS-initiating potential based upon in vitro and in
functionally assess the ability of potential cancer stem cells to initiate
a malignancy. Newer types of humanized mice, such as the MISTRG vivo stem cell assay. Systems subsequently improved phenotypic
mouse, have been developed that express human cytokines that are identification of HSCs have allowed investigators to focus on
−
−
+
−
+
not cross-reactive with murine cells and are able to stimulate the Lin CD34 CD38 CD90 CD45RA cells as candidate CSCs in
6
growth of more human cell types in vivo. Other humanization strategies MDS. These studies showed that in patients with del(5q)-MDS,
−
+
−
+
−
include constitutive expression of HLA class I and II that strengthens 99% of Lin CD34 CD38 CD90 CD45RA cells contained del(5q)
T-cell function or constitutive expression of Sirpa, a transmembrane and that they were molecularly and functionally distinct from clon-
protein on macrophages that induces tolerance to human grafts. Loss ally involved GMPs and MEPs. By gene expression profiling and
20
of function mutations in KIT proto-oncogene receptor tyrosine kinase principle component analysis of RNA sequencing data, the three
(KIT) have allowed for the creation of hematopoietic stem cell (HSC) cell populations were shown to be distinctively different, with the
xenografts without the need for irradiation of the recipient mouse. 7 − + − + −
Lin CD34 CD38 CD90 CD45RA cells selectively expressing genes