Page 1627 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1627
1448 Part VIII Comprehensive Care of Patients with Hematologic Malignancies
Integuement Phagocytes
Mucosal barrier injury Monocytopenia
Indwelling catheters
Radiation
Neutropenia
Surgery
Antibiotics
Humoral immunity Immunoglobin- deficiency Splenectomy Breaks in skin (Anti-T-cell abs) immunity
Cell-mediated
Lymphopenia
Corticosteroids
HLA type PRRs Mutations in microbial Fungal ? Bacterial ? Retrovirus Herpes virus
Genetic pathogens Immunomodulatory
Uremia Iron overload
Nutrition status
Ketoacidosis specific risks
Hyperglycemia Patient, age
Metabolic Transplantation Malignancy status Chemotherapy intensity
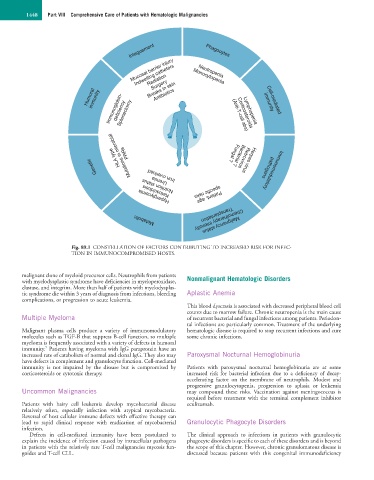
Fig. 89.1 CONSTELLATION OF FACTORS CONTRIBUTING TO INCREASED RISK FOR INFEC-
TION IN IMMUNOCOMPROMISED HOSTS.
malignant clone of myeloid precursor cells. Neutrophils from patients Nonmalignant Hematologic Disorders
with myelodysplastic syndrome have deficiencies in myeloperoxidase,
elastase, and integrins. More than half of patients with myelodysplas-
tic syndrome die within 3 years of diagnosis from infections, bleeding Aplastic Anemia
complications, or progression to acute leukemia.
This blood dyscrasia is associated with decreased peripheral blood cell
counts due to marrow failure. Chronic neutropenia is the main cause
Multiple Myeloma of recurrent bacterial and fungal infections among patients. Periodon-
tal infections are particularly common. Treatment of the underlying
Malignant plasma cells produce a variety of immunomodulatory hematologic disease is required to stop recurrent infections and cure
molecules such as TGF-B that suppress B-cell function, so multiple some chronic infections.
myeloma is frequently associated with a variety of defects in humoral
5
immunity. Patients having myeloma with IgG paraprotein have an
increased rate of catabolism of normal and clonal IgG. They also may Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria
have defects in complement and granulocyte function. Cell-mediated
immunity is not impaired by the disease but is compromised by Patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria are at some
corticosteroids or cytotoxic therapy. increased risk for bacterial infection due to a deficiency of decay-
accelerating factor on the membrane of neutrophils. Modest and
progressive granulocytopenia, progression to aplasia or leukemia
Uncommon Malignancies may compound these risks. Vaccination against meningococcus is
required before treatment with the terminal complement inhibitor
Patients with hairy cell leukemia develop mycobacterial disease eculizumab.
relatively often, especially infection with atypical mycobacteria.
Reversal of host cellular immune defects with effective therapy can
lead to rapid clinical response with eradication of mycobacterial Granulocytic Phagocyte Disorders
infection.
Defects in cell-mediated immunity have been postulated to The clinical approach to infections in patients with granulocytic
explain the incidence of infection caused by intracellular pathogens phagocyte disorders is specific to each of these disorders and is beyond
in patients with the relatively rare T-cell malignancies mycosis fun- the scope of this chapter. However, chronic granulomatous disease is
goides and T-cell CLL. discussed because patients with this congenital immunodeficiency