Page 1631 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1631
1452 Part VIII Comprehensive Care of Patients with Hematologic Malignancies
15
a bloodstream infection arising from a different source (e.g., the GI therapy. Vancomycin is administered if staphylococcal disease is
tract). 12 suspected or if the patient is clinically unstable while cultures are
Consensus guidelines on the management of patients with febrile pending. Severely ill patients are often also treated with an aminogly-
13
neutropenia have been published. Empiric antibiotics are recom- coside for the first 48 to 72 hours of illness, although data in support
mended for all febrile patients with neutropenia, but the type of of this approach are lacking.
antibiotics and the site of administration (i.e., hospital vs. outpatient) Therapeutic changes to the antimicrobial regimens are made in
depends on the severity of immunosuppression, expected duration of response to culture results, but the cultures are negative about 50%
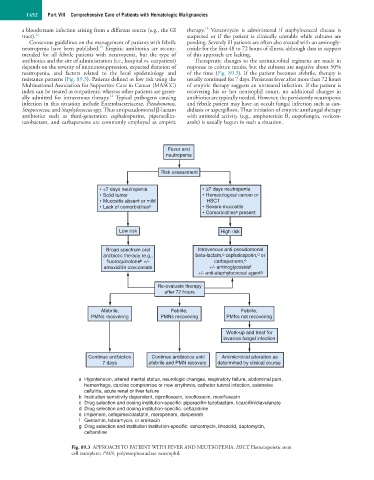
neutropenia, and factors related to the local epidemiology and of the time (Fig. 89.3). If the patient becomes afebrile, therapy is
resistance patterns (Fig. 89.3). Patients defined as low risk using the usually continued for 7 days. Persistent fever after more than 72 hours
Multinational Association for Supportive Care in Cancer (MASCC) of empiric therapy suggests an untreated infection. If the patient is
index can be treated as outpatients, whereas other patients are gener- recovering his or her neutrophil count, no additional changes in
14
ally admitted for intravenous therapy. Typical pathogens causing antibiotics are typically needed. However, the persistently neutropenic
infection in this situation include Enterobacteriaceae, Pseudomonas, and febrile patient may have an occult fungal infection such as can-
Streptococcus, and Staphylococcus spp. Thus antipseudomonal β-lactam didiasis or aspergillosis. Thus initiation of empiric antifungal therapy
antibiotics such as third-generation cephalosporins, piperacillin- with antimold activity (e.g., amphotericin B, caspofungin, voricon-
tazobactam, and carbapenems are commonly employed as empiric azole) is usually begun in such a situation.
Fever and
neutropenia
Risk assessment
• <7 days neutropenia • ≥7 days neutropenia
• Solid tumor • Hematological cancer or
• Mucositis absent or mild HSCT
• Lack of comorbidities a • Severe mucositis
• Comorbidities a present
Low risk High risk
Broad spectrum oral Intravenous anti-pseudomonal
c
d
antibiotic therapy (e.g., beta-lactam, cephalosporin, or
fluoroquinolone +/- carbapenerm, e
b
amoxicillin clavulanate +/- aminoglycoside f
+/- anti-staphylococcal agent g
Re-evaluate therapy
after 72 hours
Afebrile, Febrile, Febrile,
PMNs recovering PMNs recovering PMNs not recovering
Work-up and treat for
invasive fungal infection
Continue antibiotics Continue antibiotics until Antimicrobial alteration as
7 days afebrile and PMN recovery determined by clinical course
a Hypotension, altered mental status, neurologic changes, respiratory failure, abdominal pain,
hemorrhage, cardiac compromise or new arrythmia, catheter tunnel infection, extensive
cellulitis, acute renal or liver failure
b Institution sensitivity dependent, ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin, moxifloxacin
c Drug selection and dosing institution-specific: piperacillin tazobactam, ticarcillin/clavulanate
d Drug selection and dosing institution-specific: ceftazidime
e imipenem, cefepime/cilastatin, meropenem, doripenem
f Gentamin, tobramycin, or amikacin
g Drug selection and institution institution-specific: vancomycin, linezolid, daptomycin,
ceftaroline
Fig. 89.3 APPROACH TO PATIENT WITH FEVER AND NEUTROPENIA. HSCT, Hematopoietic stem
cell transplant; PMN, polymorphonuclear neutrophil.