Page 1772 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1772
1576 Part IX Cell-Based Therapies
NK DC
HIV
CD4
NK L ymph nodes
CMV NK AML
NK Lung
Bone marrow
Epithelial
ILC
HCV
NK Liver
Donor
Recipient
NK
NK Endometrium CD34
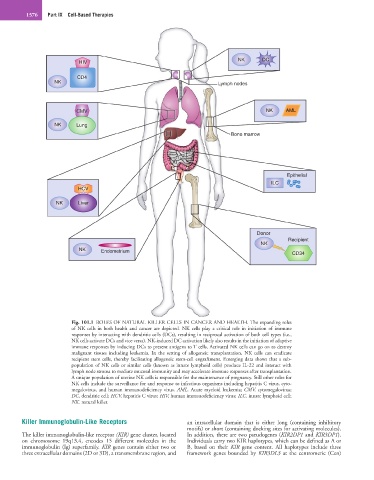
Fig. 101.1 ROLES OF NATURAL KILLER CELLS IN CANCER AND HEALTH. The expanding roles
of NK cells in both health and cancer are depicted. NK cells play a critical role in initiation of immune
responses by interacting with dendritic cells (DCs), resulting in reciprocal activation of both cell types (i.e.,
NK cells activate DCs and vice versa). NK-induced DC activation likely also results in the initiation of adaptive
immune responses by inducing DCs to present antigens to T cells. Activated NK cells can go on to destroy
malignant tissues including leukemia. In the setting of allogeneic transplantation, NK cells can eradicate
recipient stem cells, thereby facilitating allogeneic stem-cell engraftment. Emerging data shows that a sub-
population of NK cells or similar cells (known as innate lymphoid cells) produce IL-22 and interact with
lymph node stroma to mediate mucosal immunity and may accelerate immune responses after transplantation.
A unique population of uterine NK cells is responsible for the maintenance of pregnancy. Still other roles for
NK cells include the surveillance for and response to infectious organisms including hepatitis C virus, cyto-
megalovirus, and human immunodeficiency virus. AML, Acute myeloid leukemia; CMV, cytomegalovirus;
DC, dendritic cell; HCV, hepatitis C virus; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; ILC, innate lymphoid cell;
NK, natural killer.
Killer Immunoglobulin-Like Receptors an intracellular domain that is either long (containing inhibitory
motifs) or short (containing docking sites for activating molecules).
The killer immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) gene cluster, located In addition, there are two pseudogenes (KIR2DP1 and KIR3DP1).
on chromosome 19q13.4, encodes 15 different molecules in the Individuals carry two KIR haplotypes, which can be defined as A or
immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily. KIR genes contain either two or B, based on their KIR gene content. All haplotypes include three
three extracellular domains (2D or 3D), a transmembrane region, and framework genes bounded by KIR3DL3 at the centromeric (Cen)