Page 1776 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1776
1580 Part IX Cell-Based Therapies
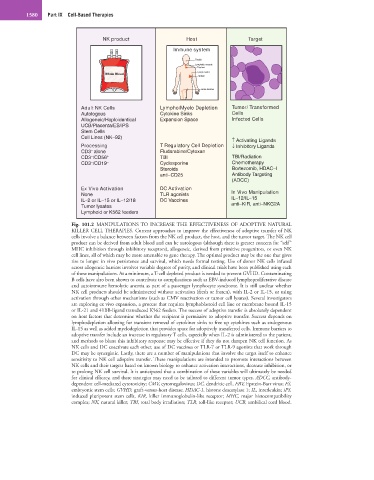
NK product Host Target
Immune system
Tonsils
Lymphatic vessels
Thymus
Lymph nodes
Spleen
Bone marrow
Adult NK Cells Lympho/Myelo Depletion Tumor/ Transformed
Autologous Cytokine Sinks Cells
Allogeneic/Haploidentical Expansion Space Infected Cells
UCB/Placenta/ES/iPS
Stem Cells
Cell Lines (NK−92) ↑ Activating Ligands
Processing T Regulatory Cell Depletion ↓ Inhibitory Ligands
−
CD3 alone Fludarabine/Cytoxan
−
CD3 /CD56 + TBI TBI/Radiation
−
CD3 /CD19 − Cyclosporine Chemotherapy
Steroids Bortezomib, HDAC−I
anti−CD25 Antibody Targeting
(ADCC)
Ex Vivo Activation DC Activation
None TLR agonists In Vivo Manipulation
IL−2 or IL−15 or IL−12/18 DC Vaccines IL−12/IL−15
Tumor lysates anti−KIR, anti−NKG2A
Lymphoid or K562 feeders
Fig. 101.2 MANIPULATIONS TO INCREASE THE EFFECTIVENESS OF ADOPTIVE NATURAL
KILLER CELL THERAPIES. Current approaches to improve the effectiveness of adoptive transfer of NK
cells involve a balance between factors from the NK cell product, the host, and the tumor target. The NK cell
product can be derived from adult blood and can be autologous (although there is greater concern for “self”
MHC inhibition through inhibitory receptors), allogeneic, derived from primitive progenitors, or even NK
cell lines, all of which may be more amenable to gene therapy. The optimal product may be the one that gives
rise to longer in vivo persistence and survival, which needs formal testing. Use of donor NK cells infused
across allogeneic barriers involves variable degrees of purity, and clinical trials have been published using each
of these manipulations. At a minimum, a T-cell depleted product is needed to prevent GVHD. Contaminating
B cells have also been shown to contribute to complications such as EBV-induced lymphoproliferative disease
and autoimmune hemolytic anemia as part of a passenger lymphocyte syndrome. It is still unclear whether
NK cell products should be administered without activation (fresh or frozen), with IL-2 or IL-15, or using
activation through other mechanisms (such as CMV reactivation or tumor cell lysates). Several investigators
are exploring ex vivo expansion, a process that requires lymphoblastoid cell line or membrane bound IL-15
or IL-21 and 41BB-ligand transduced K562 feeders. The success of adoptive transfer is absolutely dependent
on host factors that determine whether the recipient is permissive to adoptive transfer. Success depends on
lymphodepletion allowing for transient removal of cytokines sinks to free up cytokines such as endogenous
IL-15 as well as added myelodepletion that provides space for adoptively transferred cells. Immune barriers to
adoptive transfer include an increase in regulatory T cells, especially when IL-2 is administered to the patient,
and methods to blunt this inhibitory response may be effective if they do not dampen NK cell function. As
NK cells and DC coactivate each other, use of DC vaccines or TLR-7 or TLR-9 agonists that work through
DC may be synergistic. Lastly, there are a number of manipulations that involve the target itself to enhance
sensitivity to NK cell adoptive transfer. These manipulations are intended to promote interactions between
NK cells and their targets based on known biology to enhance activation interactions, decrease inhibition, or
to prolong NK cell survival. It is anticipated that a combination of these variables will ultimately be needed
for clinical efficacy, and these strategies may need to be tailored to different tumor types. ADCC, antibody-
dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity; CMV, cytomegalovirus; DC, dendritic cell, EBV, Epstein-Barr virus; ES,
embryonic stem cells; GVHD, graft-versus-host disease; HDAC-1, histone deacetylase 1; IL, interleukin; iPS,
induced pluripotent stem cells, KIR, killer immunoglobulin-like receptor; MHC, major histocompatibility
complex; NK, natural killer; TBI, total body irradiation; TLR, toll-like receptor; UCB, umbilical cord blood.