Page 178 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 178
136 Part II Cellular Basis of Hematology
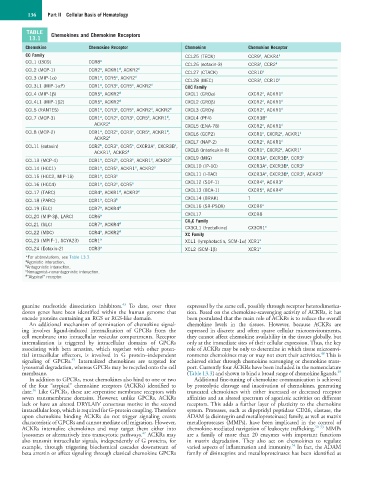
TABLE Chemokines and Chemokine Receptors
13.1
Chemokine Chemokine Receptor Chemokine Chemokine Receptor
CC Family CCL25 (TECK) CCR9 , ACKR4 d
a
CCL1 (I309) CCR8 a CCL26 (eotaxin-3) CCR3 , CCR2 b
a
d
a
CCL2 (MCP-1) CCR2 , ACKR1 , ACKR2 d a
CCL27 (CTACK) CCR10
a
a
CCL3 (MIP-1α) CCR1 , CCR5 , ACKR2 d a a
CCL28 (MEC) CCR3 , CCR10
a
a
a
CCL3L1 (MIP-1αP) CCR1 , CCR3 , CCR5 , ACKR2 d CXC Family
CCL4 (MIP-1β) CCR5 , ACKR2 d CXCL1 (GROα) CXCR2 , ACKR1 d
a
a
CCL4L1 (MIP-1β2) CCR5 , ACKR2 d CXCL2 (GROβ) CXCR2 , ACKR1 d
a
a
d
a
a
a
a
CCL5 (RANTES) CCR1 , CCR3 , CCR5 , ACKR2 , ACKR2 d CXCL3 (GROγ) CXCR2 , ACKR1 d
b
d
a
a
a
CCL7 (MCP-3) CCR1 , CCR2 , CCR3 , CCR5 , ACKR1 , CXCL4 (PF4) CXCR3B a
ACKR2 d CXCL5 (ENA-78) CXCR2 , ACKR1 d
a
CCL8 (MCP-2) CCR1 , CCR2 , CCR3 , CCR5 , ACKR1 , CXCL6 (GCP2) CXCR1 , CXCR2 , ACKR1 d
a
d
a
a
a
a
a
ACKR2 d
CXCL7 (NAP-2) CXCR2 , ACKR1 d
a
b
a
c
c
CCL11 (eotaxin) CCR2 , CCR3 , CCR5 , CXCR3A , CXCR3B , a a d
a
ACKR1 , ACKR2 d CXCL8 (interleukin-8) CXCR1 , CXCR2 , ACKR1
d
a
a
CXCL9 (MIG) CXCR3A , CXCR3B , CCR3 b
a
a
a
d
CCL13 (MCP-4) CCR1 , CCR2 , CCR3 , ACKR1 , ACKR2 d
a
a
a
CCL14 (HCC1) CCR1 , CCR5 , ACKR1 , ACKR2 d CXCL10 (IP-10) CXCR3A , CXCR3B , CCR3 b
d
a
a
b
a
a
CCL15 (HCC2, MIP-1δ) CCR1 , CCR3 a CXCL11 (I-TAC) CXCR3A , CXCR3B , CCR3 , ACKR3 d
a
CCL16 (HCC4) CCR1 , CCR2 , CCR5 a CXCL12 (SDF-1) CXCR4 , ACKR3 d
a
a
a
d
a
CCL17 (TARC) CCR4 , ACKR1 , ACKR2 d CXCL13 (BCA-1) CXCR5 , ACKR4 d
a
CCL18 (PARC) CCR1 , CCR3 b CXCL14 (BRAK) ?
a
CCL19 (ELC) CCR7 , ACKR4 d CXCL16 (SR-PSOX) CXCR6 a
CCL20 (MIP-3β, LARC) CCR6 a CXCL17 CXCR8
CX 3 C Family
CCL21 (SLC) CCR7 , ACKR4 d
a
CX3CL1 (fractalkine) CX3CR1 a
CCL22 (MDC) CCR4 , ACKR2 d XC Family
a
CCL23 (MPIF-1, SCYA23) CCR1 a XCL1 (lymphotactin, SCM-1α) XCR1 a
CCL24 (Eotaxin-2) CCR3 a XCL2 (SCM-1β) XCR1 a
*For abbreviations, see Table 13.3.
a Agonistic interaction.
b Antagonistic interaction.
c Nonagonist–nonantagonistic interaction.
d “Atypical” receptor.
43
guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitors. To date, over three expressed by the same cell, possibly through receptor heterodimeriza-
dozen genes have been identified within the human genome that tion. Based on the chemokine-scavenging activity of ACKRs, it has
encode proteins containing an RGS or RGS-like domain. been postulated that the main role of ACKRs is to reduce the overall
An additional mechanism of termination of chemokine signal- chemokine levels in the tissues. However, because ACKRs are
ing involves ligand-induced internalization of GPCRs from the expressed in discrete and often sparse cellular microenvironments,
cell membrane into intracellular vesicular compartments. Receptor they cannot affect chemokine availability in the tissues globally, but
internalization is triggered by intracellular domains of GPCRs only at the immediate sites of their cellular expression. Thus, the key
associating with beta arrestins, which together with other poten- role of ACKRs may be only to determine in which tissue microenvi-
48
tial intracellular effectors, is involved in G protein–independent ronments chemokines may or may not exert their activities. This is
45
signaling of GPCRs. Internalized chemokines are targeted for achieved either through chemokine scavenging or chemokine trans-
lysosomal degradation, whereas GPCRs may be recycled onto the cell port. Currently four ACKRs have been included in the nomenclature
membrane. (Table 13.3) and shown to bind a broad range of chemokine ligands. 49
In addition to GPCRs, most chemokines also bind to one or two Additional fine-tuning of chemokine communication is achieved
of the four “atypical” chemokine receptors (ACKRs) identified to by proteolytic cleavage and inactivation of chemokines, generating
46
date. Like GPCRs, these are serpentine membrane receptors with truncated chemokines with either increased or decreased receptor
seven transmembrane domains. However, unlike GPCRs, ACKRs affinities and an altered spectrum of agonistic activities on different
lack or have an altered DRYLAIV consensus motive in the second receptors. This adds a further layer of plasticity to the chemokine
intracellular loop, which is required for G-protein coupling. Therefore system. Proteases, such as dipeptidyl peptidase CD26, elastase, the
upon chemokine binding ACKRs do not trigger signaling events ADAM (a disintegrin and metalloproteinase) family, as well as matrix
characteristic of GPCRs and cannot mediate cell migration. However, metalloproteases (MMPs), have been implicated in the control of
ACKRs internalize chemokines and may target them either into chemokine-mediated navigation of leukocyte trafficking. 50–53 MMPs
47
lysosomes or alternatively into transcytotic pathways. ACKRs may are a family of more than 20 enzymes with important functions
also transmit intracellular signals, independently of G proteins, for in matrix degradation. They also act on chemokines to regulate
54
example, through triggering biochemical cascades downstream of varied aspects of inflammation and immunity. In fact, the ADAM
beta arrestin or affect signaling through classical chemokine GPCRs family of disintegrins and metalloproteinases has been identified as