Page 1799 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1799
Chapter 104 Indications and Outcomes of Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation for Hematologic Malignancies in Adults 1603
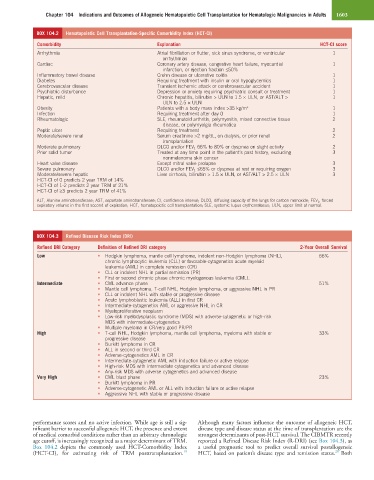
BOX 104.2 Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation-Specific Comorbidity Index (HCT-CI)
Comorbidity Explanation HCT-CI score
Arrhythmia Atrial fibrillation or flutter, sick sinus syndrome, or ventricular 1
arrhythmias
Cardiac Coronary artery disease, congestive heart failure, myocardial 1
infarction, or ejection fraction ≤50%
Inflammatory bowel disease Crohn disease or ulcerative colitis 1
Diabetes Requiring treatment with insulin or oral hypoglycemics 1
Cerebrovascular disease Transient ischemic attack or cerebrovascular accident 1
Psychiatric disturbance Depression or anxiety requiring psychiatric consult or treatment 1
Hepatic, mild Chronic hepatitis, bilirubin > ULN to 1.5 × ULN, or AST/ALT > 1
ULN to 2.5 × ULN
Obesity Patients with a body mass index >35 kg/m + 1
Infection Requiring treatment after day 0 1
Rheumatologic SLE, rheumatoid arthritis, polymyositis, mixed connective tissue 2
disease, or polymyalgia rheumatica
Peptic ulcer Requiring treatment 2
Moderate/severe renal Serum creatinine >2 mg/dL, on dialysis, or prior renal 2
transplantation
Moderate pulmonary DLCO and/or FEV 1 66% to 80% or dyspnea on slight activity 2
Prior solid tumor Treated at any time point in the patient’s past history, excluding 3
nonmelanoma skin cancer
Heart valve disease Except mitral valve prolapse 3
Severe pulmonary DLCO and/or FEV 1 ≤65% or dyspnea at rest or requiring oxygen 3
Moderate/severe hepatic Liver cirrhosis, bilirubin > 1.5 × ULN, or AST/ALT > 2.5 × ULN 3
HCT-CI of 0 predicts 2 year TRM of 14%
HCT-CI of 1-2 predicts 2 year TRM of 21%
HCT-CI of ≥3 predicts 2 year TRM of 41%
ALT, Alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; CI, confidence interval; DLCO, diffusing capacity of the lungs for carbon monoxide; FEV 1, forced
expiratory volume in the first second of expiration; HCT, hematopoietic cell transplantation; SLE, systemic lupus erythematosus; ULN, upper limit of normal.
BOX 104.3 Refined Disease Risk Index (DRI)
Refined DRI Category Definition of Refined DRI category 2-Year Overall Survival
Low • Hodgkin lymphoma, mantle cell lymphoma, indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), 66%
chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or favorable-cytogenetics acute myeloid
leukemia (AML) in complete remission (CR)
• CLL or indolent NHL in partial remission (PR)
• First or second chronic phase chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML).
Intermediate • CML advance phase 51%
• Mantle cell lymphoma, T-cell NHL, Hodgkin lymphoma, or aggressive NHL in PR
• CLL or indolent NHL with stable or progressive disease
• Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) in first CR
• Intermediate-cytogenetics AML or aggressive NHL in CR
• Myeloproliferative neoplasm
• Low-risk myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) with adverse-cytogenetic or high-risk
MDS with intermediate-cytogenetics
• Multiple myeloma in CR/very good PR/PR
High • T-cell NHL, Hodgkin lymphoma, mantle cell lymphoma, myeloma with stable or 33%
progressive disease
• Burkitt lymphoma in CR
• ALL in second or third CR
• Adverse-cytogenetics AML in CR
• Intermediate-cytogenetic AML with induction failure or active relapse
• High-risk MDS with intermediate cytogenetics and advanced disease
• Any-risk MDS with adverse cytogenetics and advanced disease
Very High • CML blast phase 23%
• Burkitt lymphoma in PR
• Adverse-cytogenetic AML or ALL with induction failure or active relapse
• Aggressive NHL with stable or progressive disease
performance scores and no active infection. While age is still a sig- Although many factors influence the outcome of allogeneic HCT,
nificant barrier to successful allogeneic HCT, the presence and extent disease type and disease status at the time of transplantation are the
of medical comorbid conditions rather than an arbitrary chronologic strongest determinants of post-HCT survival. The CIBMTR recently
age cutoff, is increasingly recognized as a major determinant of TRM. reported a Refined Disease Risk Index (R-DRI) (see Box 104.3), as
Box 104.2 depicts the commonly used HCT-Comorbidity Index a useful prognostic tool to predict overall survival postallogeneic
19
20
(HCT-CI), for estimating risk of TRM posttransplantation. HCT, based on patient’s disease type and remission status. Both