Page 1794 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1794
1598 Part X Transplantation
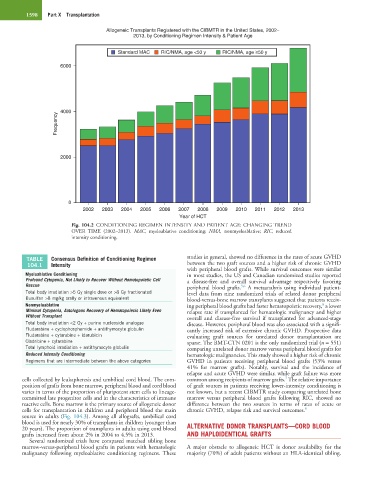
Allogeneic Transplants Registered with the CIBMTR in the United States, 2002−
2013, by Conditioning Regimen Intensity & Patient Age
Standard MAC RIC/NMA, age <50 y RIC/NMA, age ≥50 y
6000
Frequency 4000
2000
0
2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013
Year of HCT
Fig. 104.2 CONDITIONING REGIMEN INTENSITY AND PATIENT AGE: CHANGING TREND
OVER TIME (2002–2013). MAC, myeloablative conditioning; NMA, nonmyeloablative; RIC, reduced
intensity conditioning.
TABLE Consensus Definition of Conditioning Regimen studies in general, showed no difference in the rates of acute GVHD
104.1 Intensity between the two graft sources and a higher risk of chronic GVHD
with peripheral blood grafts. While survival outcomes were similar
Myeloablative Conditioning in most studies, the US and Canadian randomized studies reported
Profound Cytopenia, Not Likely to Recover Without Hematopoietic Cell a disease-free and overall survival advantage respectively favoring
Rescue peripheral blood grafts. A metaanalysis using individual patient-
5,6
Total body irradiation >5 Gy single dose or >8 Gy fractionated level data from nine randomized trials of related donor peripheral
Busulfan >8 mg/kg orally or intravenous equivalent blood-versus-bone marrow transplants suggested that patients receiv-
Nonmyeloablative ing peripheral blood grafts had faster hematopoietic recovery, a lower
6
Minimal Cytopenia, Autologous Recovery of Hematopoiesis Likely Even relapse rate if transplanted for hematologic malignancy and higher
Without Transplant overall and disease-free survival if transplanted for advanced-stage
Total body irradiation <2 Gy + purine nucleoside analogue disease. However, peripheral blood was also associated with a signifi-
Fludarabine + cyclophosphamide + antithymocyte globulin cantly increased risk of extensive chronic GVHD. Prospective data
Fludarabine + cytarabine + idarubicin evaluating graft sources for unrelated donor transplantation are
Cladribine + cytarabine sparse. The BMT-CTN 0201 is the only randomized trial (n = 551)
Total lymphoid irradiation + antithymocyte globulin comparing unrelated donor marrow versus peripheral blood grafts for
Reduced Intensity Conditioning hematologic malignancies. This study showed a higher risk of chronic
Regimens that are intermediate between the above categories GVHD in patients receiving peripheral blood grafts (53% versus
41% for marrow grafts). Notably, survival and the incidence of
relapse and acute GVHD were similar, while graft failure was more
7
cells collected by leukapheresis and umbilical cord blood. The com- common among recipients of marrow grafts. The relative importance
position of grafts from bone marrow, peripheral blood and cord blood of graft sources in patients receiving lower-intensity conditioning is
varies in terms of the proportion of pluripotent stem cells to lineage- not known, but a recent CIBMTR study comparing unrelated bone
committed late progenitor cells and in the characteristics of immune marrow versus peripheral blood grafts following RIC, showed no
reactive cells. Bone marrow is the primary source of allogeneic donor difference between the two sources in terms of rates of acute or
cells for transplantation in children and peripheral blood the main chronic GVHD, relapse risk and survival outcomes. 8
source in adults (Fig. 104.3). Among all allografts, umbilical cord
blood is used for nearly 30% of transplants in children (younger than
20 years). The proportion of transplants in adults using cord blood ALTERNATIVE DONOR TRANSPLANTS—CORD BLOOD
grafts increased from about 2% in 2004 to 4.5% in 2013. AND HAPLOIDENTICAL GRAFTS
Several randomized trials have compared matched sibling bone
marrow-versus-peripheral blood grafts in patients with hematologic A major obstacle to allogeneic HCT is donor availability for the
malignancy following myeloablative conditioning regimens. These majority (70%) of adult patients without an HLA-identical sibling.