Page 1806 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1806
1610 Part X Transplantation
are found in association with each other at an observed frequency histocompatibility workshops (Table 105.4). The advent of poly-
that exceeds their expected frequency. The probability of identifying merase chain reaction (PCR) in the 1980s revolutionized donor
a matched donor for a given patient is higher when the patient and typing and matching and has greatly accelerated understanding of
donor share a similar ethnic background. Linked HLA genes are the HLA barrier in transplantation. Guidelines for typing volunteer
inherited from each parent as a haplotype in classic Mendelian donors using DNA-based methods are available. To transition from
fashion (see Assessment of Human Leukocyte Antigen Haplotypes
later). HLA gene and haplotype frequencies provide important data
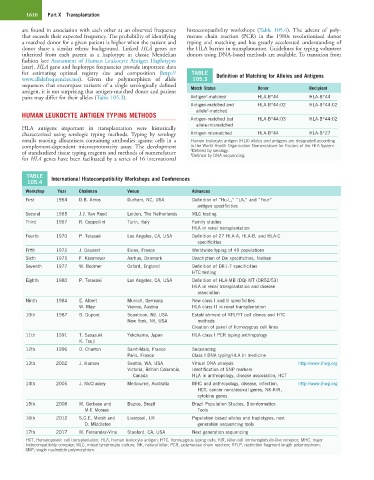
for estimating optimal registry size and composition (http:// TABLE Definition of Matching for Alleles and Antigens
www.allelefrequencies.net). Given the polymorphism of allele 105.3
sequences that encompass variants of a single serologically defined Match Status Donor Recipient
antigen, it is not surprising that antigen-matched donor and patient
a
pairs may differ for their alleles (Table 105.3). Antigen -matched HLA-B*44 HLA-B*44
Antigen-matched and HLA-B*44:02 HLA-B*44:02
b
allele -matched
HUMAN LEUKOCYTE ANTIGEN TYPING METHODS
Antigen-matched but HLA-B*44:03 HLA-B*44:02
allele-mismatched
HLA antigens important in transplantation were historically
characterized using serologic typing methods. Typing by serology Antigen-mismatched HLA-B*44 HLA-B*27
entails reacting alloantisera containing antibodies against cells in a Human leukocyte antigen (HLA) alleles and antigens are designated according
complement-dependent microcytotoxicity assay. The development to the World Health Organization Nomenclature for Factors of the HLA System.
a
of standardized tissue typing reagents and methods of nomenclature b Defined by serology.
Defined by DNA sequencing.
for HLA genes have been facilitated by a series of 16 international
TABLE International Histocompatibility Workshops and Conferences
105.4
Workshop Year Chairman Venue Advances
First 1964 D.B. Amos Durham, NC, USA Definition of “Hu-L,” “LA,” and “Four”
antigen specificities
Second 1965 J.J. Van Rood Leiden, The Netherlands MLC testing
Third 1967 R. Ceppellini Turin, Italy Family studies
HLA in renal transplantation
Fourth 1970 P. Terasaki Los Angeles, CA, USA Definition of 27 HLA-A, HLA-B, and HLA-C
specificities
Fifth 1972 J. Dausset Evian, France Worldwide typing of 49 populations
Sixth 1975 F. Kissmeyer Aarhus, Denmark Description of Dw specificities, Nielsen
Seventh 1977 W. Bodmer Oxford, England Definition of DR1-7 specificities
HTC testing
Eighth 1980 P. Terasaki Los Angeles, CA, USA Definition of HLA-MB (DQ) MT (DR52/53)
HLA in renal transplantation and disease
association
Ninth 1984 E. Albert Munich, Germany New class I and II specificities
W. Mayr Vienna, Austria HLA class II in renal transplantation
10th 1987 B. Dupont Scanticon, NJ, USA Establishment of RFLP/T cell clones and HTC
New York, NY, USA methods
Creation of panel of homozygous cell lines
11th 1991 T. Sasazuki Yokohama, Japan HLA class I PCR typing anthropology
K. Tsuji
12th 1996 D. Charron Saint-Malo, France Sequencing
Paris, France Class I DNA typing/HLA in medicine
13th 2002 J. Hansen Seattle, WA, USA Virtual DNA analysis http://www.ihwg.org
Victoria, British Columbia, Identification of SNP markers
Canada HLA in anthropology, disease association, HCT
14th 2005 J. McCluskey Melbourne, Australia MHC and anthropology, disease, infection, http://www.ihwg.org
HCT, cancer nonclassical genes, NK-KIR,
cytokine genes
15th 2008 M. Gerbase and Buzios, Brazil Brazil Population Studies, Bioinformatics
M-E Moraes Tools
16th 2012 S.G.E. Marsh and Liverpool, UK Population-based alleles and haplotypes; next
D. Middleton generation sequencing tools
17th 2017 M. Fernandez-Vina Stanford, CA, USA Next generation sequencing
HCT, Hematopoietic cell transplantation; HLA, human leukocyte antigen; HTC, homozygous typing cells; KIR, killer-cell immunoglobulin-like receptor; MHC, major
histocompatibility complex; MLC, mixed lymphocyte culture; NK, natural killer; PCR, polymerase chain reaction; RFLP, restriction fragment length polymorphism;
SNP, single nucleotide polymorphism.