Page 1954 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 1954
1734 Part XI Transfusion Medicine
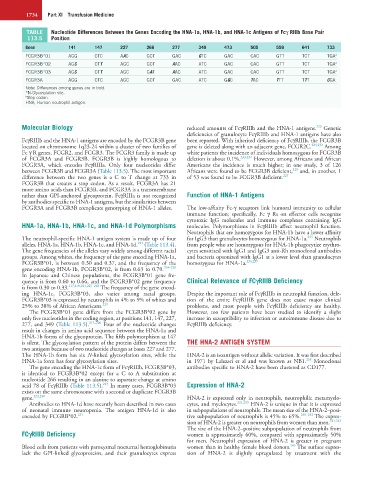
TABLE Nucleotide Differences Between the Genes Encoding the HNA-1a, HNA-1b, and HNA-1c Antigens of Fcγ RIIIb Base Pair
113.5 Position
Gene 141 147 227 266 277 349 473 505 559 641 733
FCGR3B*01 AGG CTC AAC GCT GAC GTC GAC CAC GTT TCT TGA a
FCGR3B*02 AGC CTT AGC GCT AAC ATC GAC CAC GTT TCT TGA a
FCGR3B*03 AGC CTT AGC GAT AAC ATC GAC CAC GTT TCT TGA a
FCGR3A AGG CTC AGC GCT GAC ATC GGC TAC TTT TTT CGA
Note: Differences among genes are in bold.
*N-Glycosylation site.
a Stop codon.
HNA, Human neutrophil antigen.
Molecular Biology reduced amounts of FcγRIIIb and the HNA-1 antigens. Genetic
220
deficiencies of granulocyte FcγRIIIb and HNA-1 antigens have also
FcγRIIIb and the HNA-1 antigens are encoded by the FCGR3B gene been reported. With inherited deficiency of FcγRIIIb, the FCGR3B
located on chromosome 1q23-24 within a cluster of two families of gene is deleted along with an adjacent gene, FCGR2C. 224,232 Among
Fc γ R genes, FCGR2, and FCGR3. The FCGR3 family is made up white patients the incidence of individuals homozygous for FCGR3B
of FCGR3A and FCGR3B. FCGR3B is highly homologous to deletion is about 0.1%. 233,234 However, among Africans and African
FCGR3A, which encodes FcγRIIIa. Only four nucleotides differ Americans the incidence is much higher; in one study, 3 of 126
229
between FCGR3B and FCGR3A (Table 113.5). The most important Africans were found to be FCGR3B deficient, and, in another, 1
difference between the two genes is a C to T change at 733 in of 53 was found to be FCGR3B deficient. 227
FCGR3B that creates a stop codon. As a result, FCGR3A has 21
more amino acids than FCGR3B, and FCGR3A is a transmembrane
rather than GPI-anchored glycoprotein. FcγRIIIa is not recognized Function of HNA-1 Antigens
by antibodies specific to HNA-1 antigens, but the similarities between
FCGR3A and FCGR3B complicate genotyping of HNA-1 alleles. The low-affinity Fc-γ receptors link humoral immunity to cellular
immune function; specifically, Fc γ Rs on effector cells recognize
cytotoxic IgG molecules and immune complexes containing IgG
HNA-1a, HNA-1b, HNA-1c, and HNA-1d Polymorphisms molecules. Polymorphisms in FcγRIIIb affect neutrophil function.
Neutrophils that are homozygous for HNA-1b have a lower affinity
235
The neutrophil-specific HNA-1 antigen system is made up of four for IgG3 than granulocytes homozygous for HNA-1a. Neutrophils
223
alleles, HNA-1a, HNA-1b, HNA-1c, and HNA-1d. (Table 113.4). from people who are homozygous for HNA-1b phagocytize erythro-
The gene frequencies of the alleles vary widely among different racial cytes sensitized with IgG1 and IgG3 anti-Rh monoclonal antibodies
groups. Among whites, the frequency of the gene encoding HNA-1a, and bacteria opsonized with IgG1 at a lower level than granulocytes
FCGR3B*01, is between 0.30 and 0.37, and the frequency of the homozygous for HNA-1a. 236,237
gene encoding HNA-1b, FCGR3B*02, is from 0.63 to 0.70. 224–228
In Japanese and Chinese populations, the FCGR3B*01 gene fre-
quency is from 0.60 to 0.66, and the FCGR3B*02 gene frequency Clinical Relevance of FCγRIIIB Deficiency
is from 0.30 to 0.33. 217,218,221,225–228 The frequency of the gene encod-
ing HNA-1c, FCGR3B*03, also varies among racial groups. Despite the important role of FcγRIIIb in neutrophil function, dele-
FCGR3B*03 is expressed by neutrophils in 4% to 5% of whites and tion of the entire FcγRIIIB gene does not cause major clinical
25% to 38% of African Americans. 229 problems, and most people with FcγRIIIb deficiency are healthy.
The FCGR3B*01 gene differs from the FCGR3B*02 gene by However, too few patients have been studied to identify a slight
only five nucleotides in the coding region, at positions 141, 147, 227, increase in susceptibility to infection or autoimmune disease due to
277, and 349 (Table 113.5). 217–220 Four of the nucleotide changes FcγRIIIb deficiency.
result in changes in amino acid sequence between the HNA-1a and
HNA-1b forms of the glycoprotein. The fifth polymorphism at 147
is silent. The glycosylation pattern of the protein differs between the THE HNA-2 ANTIGEN SYSTEM
two antigens because of two nucleotide changes at bases 227 and 277.
The HNA-1b form has six N-linked glycosylation sites, while the HNA-2 is an isoantigen without allelic variation. It was first described
238
HNA-1a form has four glycosylation sites. in 1971 by Lalezari et al and was known as NB1. Monoclonal
The gene encoding the HNA-1c form of FcγRIIIb, FCGR3B*03, antibodies specific to HNA-2 have been clustered as CD177.
is identical to FCGR3B*02 except for a C to A substitution at
nucleotide 266 resulting in an alanine to aspartate change at amino
223
acid 78 of FcγRIIIb (Table 113.5). In many cases, FCGR3B*03 Expression of HNA-2
exists on the same chromosome with a second or duplicate FCGR3B
gene. 223,230 HNA-2 is expressed only in neutrophils, neutrophilic metamyelo-
Antibodies to HNA-1d have recently been described in two cases cytes, and myelocytes. 221,239 HNA-2 is unique in that it is expressed
of neonatal immune neutropenia. The antigen HNA-1d is also in subpopulations of neutrophils. The mean size of the HNA-2–posi-
encoded by FCGRB*02. 231 tive subpopulation of neutrophils is 45% to 65%. 240–242 The expres-
sion of HNA-2 is greater on neutrophils from women than men. 241,243
The size of the HNA-2–positive subpopulation of neutrophils from
FCγRIIIB Deficiency women is approximately 60%, compared with approximately 50%
for men. Neutrophil expression of HNA-2 is greater in pregnant
243
Blood cells from patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria women than in healthy female blood donors. The surface expres-
lack the GPI-linked glycoproteins, and their granulocytes express sion of HNA-2 is slightly upregulated by treatment with the