Page 2204 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 2204
Chapter 131 Diseases of Platelet Number 1951
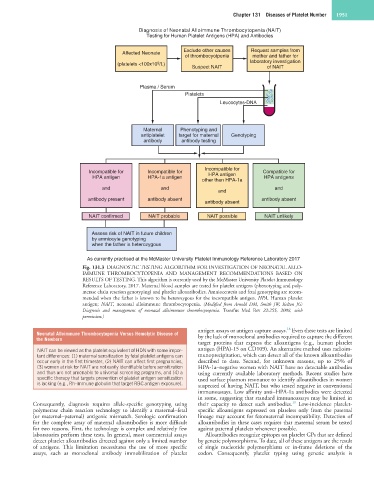
Diagnosis of Neonatal Alloimmune Thrombocytopenia (NAIT)
Testing for Human Platelet Antigens (HPA) and Antibodies
Affected Neonate Exclude other causes Request samples from
of thrombocyotpenia mother and father for
(platelets <100x10 /L) laboratory investigation
9
Suspect NAIT of NAIT
Plasma / Serum
Platelets
Leucocytes-DNA
Maternal Phenotyping and
antiplatelet target for maternal Genotyping
antibody antibody testing
Incompatible for
Incompatible for Incompatible for Compatible for
HPA antigen HPA-1a antigen HPA antigen HPA antigens
other than HPA-1a
and and and
and
antibody present antibody absent antibody absent
antibody absent
NAIT confirmed NAIT probable NAIT possible NAIT unlikely
Assess risk of NAIT in future children
by amniocyte genotyping
when the father is heterozygous
As currently practised at the McMaster University Platelet Immunology Reference Laboratory 2017
Fig. 131.3 DIAGNOSTIC TESTING ALGORITHM FOR INVESTIGATION OF NEONATAL ALLO-
IMMUNE THROMBOCYTOPENIA AND MANAGEMENT RECOMMENDATIONS BASED ON
RESULTS OF TESTING. This algorithm is currently used by the McMaster University Platelet Immunology
Reference Laboratory, 2017. Maternal blood samples are tested for platelet antigens (phenotyping and poly-
merase chain reaction genotyping) and platelet alloantibodies. Amniocentesis and fetal genotyping are recom-
mended when the father is known to be heterozygous for the incompatible antigen. HPA, Human platelet
antigen; NAIT, neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia. (Modified from Arnold DM, Smith JW, Kelton JG:
Diagnosis and management of neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia. Transfus Med Rev 22:255, 2008, with
permission.)
18
antigen assays or antigen capture assays. Even these tests are limited
Neonatal Alloimmune Thrombocytopenia Versus Hemolytic Disease of
the Newborn by the lack of monoclonal antibodies required to capture the different
target proteins that express the alloantigens (e.g., human platelet
NAIT can be viewed as the platelet equivalent of HDN with some impor- antigen (HPA)-15 on CD109). An alternative method uses radioim-
tant differences: (1) maternal sensitization by fetal platelet antigens can munoprecipitation, which can detect all of the known alloantibodies
occur early in the first trimester, (2) NAIT can affect first pregnancies, described to date. Second, for unknown reasons, up to 25% of
(3) women at risk for NAIT are not easily identifiable before sensitization HPA-1a–negative women with NAIT have no detectable antibodies
and thus are not amenable to universal screening programs, and (4) a using currently available laboratory methods. Recent studies have
specific therapy that targets prevention of platelet antigen sensitization used surface plasmon resonance to identify alloantibodies in women
is lacking (e.g., Rh-immune globulin that target RBC antigen exposure). suspected of having NAIT, but who tested negative in conventional
immunoassays. Low affinity anti–HPA-1a antibodies were detected
in some, suggesting that standard immunoassays may be limited in
19
Consequently, diagnosis requires allele-specific genotyping using their capacity to detect such antibodies. Low-incidence platelet-
polymerase chain reaction technology to identify a maternal–fetal specific alloantigens expressed on platelets only from the paternal
(or maternal–paternal) antigenic mismatch. Serologic confirmation lineage may account for fetomaternal incompatibility. Detection of
for the complete array of maternal alloantibodies is more difficult alloantibodies in these cases requires that maternal serum be tested
for two reasons. First, the technology is complex and relatively few against paternal platelets whenever possible.
laboratories perform these tests. In general, most commercial assays Alloantibodies recognize epitopes on platelet GPs that are defined
detect platelet alloantibodies directed against only a limited number by genetic polymorphisms. To date, all of these antigens are the result
of antigens. This limitation necessitates the use of more specific of single nucleotide polymorphisms or in-frame deletions of the
assays, such as monoclonal antibody immobilization of platelet codon. Consequently, platelet typing using genetic analysis is