Page 2401 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 2401
Chapter 146 Acute Coronary Syndromes 2143
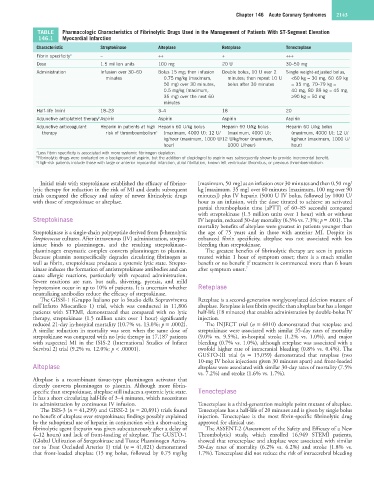
TABLE Pharmacologic Characteristics of Fibrinolytic Drugs Used in the Management of Patients With ST-Segment Elevation
146.1 Myocardial Infarction
Characteristic Streptokinase Alteplase Reteplase Tenecteplase
Fibrin specificity a – ++ + +++
Dose 1.5 million units 100 mg 20 U 30–50 mg
Administration Infusion over 30–60 Bolus 15 mg; then infusion Double bolus, 10 U over 2 Single weight-adjusted bolus,
minutes 0.75 mg/kg (maximum, minutes; then repeat 10 U <60 kg = 30 mg, 60–69 kg
50 mg) over 30 minutes, bolus after 30 minutes = 35 mg, 70–79 kg =
0.5 mg/kg (maximum, 40 mg, 80–89 kg = 45 mg,
35 mg) over the next 60 ≥90 kg = 50 mg
minutes
Half-life (min) 18–23 3–4 18 20
Adjunctive antiplatelet therapy Aspirin Aspirin Aspirin Aspirin
b
Adjunctive anticoagulant Heparin in patients at high Heparin 60 U/kg bolus Heparin 60 U/kg bolus Heparin 60 U/kg bolus
therapy risk of thromboembolism c (maximum, 4000 U); 12 U/ (maximum, 4000 U); (maximum, 4000 U); 12 U/
kg/hour (maximum, 1000 U/12 U/kg/hour (maximum, kg/hour (maximum, 1000 U/
hour) 1000 U/hour) hour)
a Less fibrin specificity is associated with more systemic fibrinogen depletion.
b Fibrinolytic drugs were evaluated on a background of aspirin, but the addition of clopidogrel to aspirin was subsequently shown to provide incremental benefit.
c High-risk patients include those with large or anterior myocardial infarction, atrial fibrillation, known left ventricular thrombus, or previous thromboembolism.
Initial trials with streptokinase established the efficacy of fibrino- [maximum, 50 mg] as an infusion over 30 minutes and then 0.50 mg/
lytic therapy for reduction in the risk of MI and death; subsequent kg [maximum. 35 mg] over 60 minutes [maximum, 100 mg over 90
trials compared the efficacy and safety of newer fibrinolytic drugs minutes]) plus IV heparin (5000 U IV bolus, followed by 1000 U/
with those of streptokinase or alteplase. hour as an infusion, with the dose titrated to achieve an activated
partial thromboplastin time [aPTT] of 60–85 seconds) compared
with streptokinase (1.5 million units over 1 hour) with or without
Streptokinase IV heparin, reduced 30-day mortality (6.3% vs. 7.3%; p = .001). The
mortality benefits of alteplase were greatest in patients younger than
Streptokinase is a single-chain polypeptide derived from β-hemolytic the age of 75 years and in those with anterior MI. Despite its
Streptococcus cultures. After intravenous (IV) administration, strepto- enhanced fibrin specificity, alteplase was not associated with less
kinase binds to plasminogen, and the resulting streptokinase– bleeding than streptokinase.
plasminogen enzymatic complex converts plasminogen to plasmin. The greatest benefits of fibrinolytic therapy are seen in patients
Because plasmin nonspecifically degrades circulating fibrinogen as treated within 1 hour of symptom onset; there is a much smaller
well as fibrin, streptokinase produces a systemic lytic state. Strepto- benefit or no benefit if treatment is commenced more than 6 hours
kinase induces the formation of antistreptokinase antibodies and can after symptom onset. 7
cause allergic reactions, particularly with repeated administration.
Severe reactions are rare, but rash, shivering, pyrexia, and mild
hypotension occur in up to 10% of patients. It is uncertain whether Reteplase
neutralizing antibodies reduce the efficacy of streptokinase.
The GISSI-1 (Gruppo Italiano per lo Studio della Sopravvivenza Reteplase is a second-generation nonglycosylated deletion mutant of
nell’Infarto Miocardico 1) trial, which was conducted in 11,806 alteplase. Reteplase is less fibrin specific than alteplase but has a longer
patients with STEMI, demonstrated that compared with no lytic half-life (18 minutes) that enables administration by double-bolus IV
therapy, streptokinase (1.5 million units over 1 hour) significantly injection.
reduced 21-day in-hospital mortality (10.7% vs. 13.0%; p = .0002). The INJECT trial (n = 6010) demonstrated that reteplase and
A similar reduction in mortality was seen when the same dose of streptokinase were associated with similar 35-day rates of mortality
streptokinase was compared with no lytic therapy in 17,187 patients (9.0% vs. 9.5%), in-hospital stroke (1.2% vs. 1.0%), and major
with suspected MI in the ISIS-2 (International Studies of Infarct bleeding (0.7% vs. 1.0%), although reteplase was associated with a
Survival 2) trial (9.2% vs. 12.0%; p < .00001). twofold higher rate of intracranial bleeding (0.8% vs. 0.4%). The
GUSTO-III trial (n = 15,059) demonstrated that reteplase (two
10-mg IV bolus injections given 30 minutes apart) and front-loaded
Alteplase alteplase were associated with similar 30-day rates of mortality (7.5%
vs. 7.2%) and stroke (1.6% vs. 1.7%).
Alteplase is a recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator that
directly converts plasminogen to plasmin. Although more fibrin-
specific than streptokinase, alteplase still induces a systemic lytic state. Tenecteplase
It has a short circulating half-life of 3–4 minutes, which necessitates
its administration by continuous IV infusion. Tenecteplase is a third-generation multiple point mutant of alteplase.
The ISIS-3 (n = 41,299) and GISSI-2 (n = 20,891) trials found Tenecteplase has a half-life of 20 minutes and is given by single bolus
no benefit of alteplase over streptokinase; findings possibly explained injection. Tenecteplase is the most fibrin-specific fibrinolytic drug
by the suboptimal use of heparin in conjunction with a short-acting approved for clinical use.
fibrinolytic agent (heparin was given subcutaneously after a delay of The ASSENT-2 (Assessment of the Safety and Efficacy of a New
4–12 hours) and lack of front-loading of alteplase. The GUSTO-1 Thrombolytic) study, which enrolled 16,949 STEMI patients,
(Global Utilization of Streptokinase and Tissue Plasminogen Activa- showed that tenecteplase and alteplase were associated with similar
tor to Treat Occluded Arteries 1) trial (n = 41,021) demonstrated 30-day rates of mortality (6.2% vs. 6.2%) and stroke (1.8% vs.
that front-loaded alteplase (15 mg bolus, followed by 0.75 mg/kg 1.7%). Tenecteplase did not reduce the risk of intracerebral bleeding