Page 2422 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 2422
2162 Part XII Hemostasis and Thrombosis
Brachial
RIGHT LEFT
114 76
PVR 63 mm Hg 441 cc RIGHT High Thigh PVR 66 mm Hg 591 cc LEFT High Thigh
Gain: .75 mm Hg/20 mm Spd: 25 Amp: 30 Gain: .75 mm Hg/20 mm Spd: 25 Amp: 20
1.15 131 116 1.02
1.14 130 116 1.02
1.08 123 89 0.78
PVR 61 mm Hg 277 cc RIGHT Above Knee PVR 65 mm Hg 404 cc LEFT Above Knee
Gain: .75 mm Hg/20 mm Spd: 25 Amp: 27 RIGHT LEFT Gain: .75 mm Hg/20 mm Spd: 25 Amp: 13
0.90 103 DP 83 0.73
0.89 101 PT 83 0.73
PVR 62 mm Hg 109 cc RIGHT Below Knee PVR 64 mm Hg 159 cc LEFT Below Knee
Gain: .75 mm Hg/20 mm Spd: 25 Amp: 33 ABI: 0.90 ABI: 0.73 Gain: .75 mm Hg/20 mm Spd: 25 Amp: 17
PVR 61 mm Hg 129 cc RIGHT Ankle PVR 44 mm Hg 129 cc LEFT Ankle
Gain: .75 mm Hg/20 mm Spd: 25 Amp: 29 Gain: .75 mm Hg/20 mm Spd: 25 Amp: 07
PVR 63 mm Hg 79 cc RIGHT Metatarsal PVR 57 mm Hg 75 cc LEFT Metatarsal
Gain: .75 mm Hg/20 mm Spd: 25 Amp: 10 Gain: .75 mm Hg/20 mm Spd: 25 Amp: 05
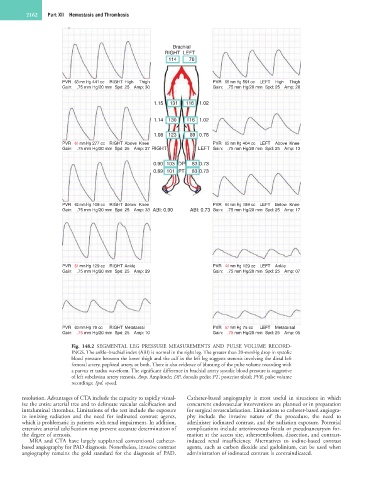
Fig. 148.2 SEGMENTAL LEG PRESSURE MEASUREMENTS AND PULSE VOLUME RECORD-
INGS. The ankle–brachial index (ABI) is normal in the right leg. The greater than 20-mmHg drop in systolic
blood pressure between the lower thigh and the calf in the left leg suggests stenosis involving the distal left
femoral artery, popliteal artery, or both. There is also evidence of blunting of the pulse volume recording with
a parvus et tardus waveform. The significant difference in brachial artery systolic blood pressure is suggestive
of left subclavian artery stenosis. Amp, Amplitude; DP, dorsalis pedis; PT, posterior tibial; PVR, pulse volume
recordings; Spd, speed.
resolution. Advantages of CTA include the capacity to rapidly visual- Catheter-based angiography is most useful in situations in which
ize the entire arterial tree and to delineate vascular calcification and concurrent endovascular interventions are planned or in preparation
intraluminal thrombus. Limitations of the test include the exposure for surgical revascularization. Limitations to catheter-based angiogra-
to ionizing radiation and the need for iodinated contrast agents, phy include the invasive nature of the procedure, the need to
which is problematic in patients with renal impairment. In addition, administer iodinated contrast, and the radiation exposure. Potential
extensive arterial calcification may prevent accurate determination of complications include arteriovenous fistula or pseudoaneurysm for-
the degree of stenosis. mation at the access site, atheroembolism, dissection, and contrast-
MRA and CTA have largely supplanted conventional catheter- induced renal insufficiency. Alternatives to iodine-based contrast
based angiography for PAD diagnosis. Nonetheless, invasive contrast agents, such as carbon dioxide and gadolinium, can be used when
angiography remains the gold standard for the diagnosis of PAD. administration of iodinated contrast is contraindicated.