Page 264 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 264
Chapter 20 B-Cell Development 215
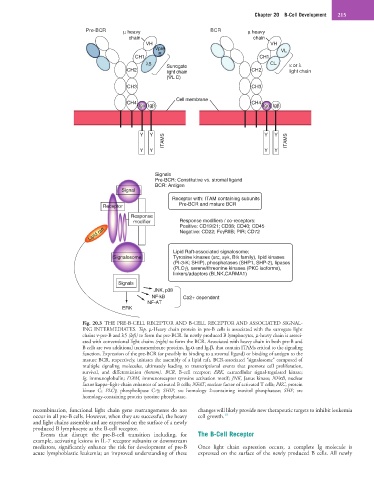
Pre-BCR µ heavy BCR µ heavy
chain chain
VH VH
Vpre VL
B
CH1 CH1
λ5 Surrogate CL κ or λ
CH2 light chain CH2 light chain
(ΨL C)
CH3 CH3
Cell membrane
CH4 CH4
Igα Igβ Igα Igβ
Y Y Y Y
ITAMS ITAMS
Y Y Y Y
Signals
Pre-BCR: Constitutive vs. stromal ligand
BCR: Antigen
Signal
Receptor with: ITAM containing subunits
Pre-BCR and mature BCR
Receptor
Response
modifier Response modifiers / co-receptors:
Positive: CD19/21; CD38; CD40; CD45
Lipid raft Negative: CD22; FcγRIIB; PIR; CD72
Lipid Raft-associated signalosome;
Signalosome Tyrosine kinases (src, syk, Btk family), lipid kinases
(PI-3-K; SHIP), phosphatases (SHP1, SHP-2), lipases
(PLCγ), serene/threonine kinases (PKC isoforms),
linkers/adaptors (BLNK,CARMA1)
Signals
JNK, p38
NF-kB Ca2+ dependent
NF-AT
ERK
Fig. 20.3 THE PRE-B-CELL RECEPTOR AND B-CELL RECEPTOR AND ASSOCIATED SIGNAL-
ING INTERMEDIATES. Top, µ-Heavy chain protein in pre-B cells is associated with the surrogate light
chains v-pre-B and λ5 (left) to form the pre-BCR. In newly produced B lymphocytes, µ-heavy chain is associ-
ated with conventional light chains (right) to form the BCR. Associated with heavy chain in both pre-B and
B cells are two additional transmembrane proteins, Ig-α and Ig-β, that contain ITAMs critical to the signaling
function. Expression of the pre-BCR (or possibly its binding to a stromal ligand) or binding of antigen to the
mature BCR, respectively, initiates the assembly of a lipid raft, BCR-associated “signalosome” composed of
multiple signaling molecules, ultimately leading to transcriptional events that promote cell proliferation,
survival, and differentiation (bottom). BCR, B-cell receptor; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase;
Ig, immunoglobulin; ITAM, immunoreceptor tyrosine activation motif; JNK, Janus kinase; NFκB, nuclear
factor kappa–light-chain enhancer of activated B cells; NFAT, nuclear factor of activated T cells; PKC, protein
kinase C; PLCγ, phospholipase C-γ; SHIP, src homology 2-containing inositol phosphatase; SHP, src
homology-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase.
recombination, functional light chain gene rearrangements do not changes will likely provide new therapeutic targets to inhibit leukemia
occur in all pre-B cells. However, when they are successful, the heavy cell growth. 15
and light chains assemble and are expressed on the surface of a newly
produced B lymphocyte as the B-cell receptor.
Events that disrupt the pre-B-cell transition including, for The B-Cell Receptor
example, activating lesions in IL-7 receptor subunits or downstream
mediators, significantly enhance the risk for development of pre-B Once light chain expression occurs, a complete Ig molecule is
acute lymphoblastic leukemia; an improved understanding of these expressed on the surface of the newly produced B cells. All newly