Page 260 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 260
Chapter 20 B-Cell Development 211
Myeloid and
Erythroid
Bone Marrow
CMP
Lin CD34 Lin CD34 CD43 CD19
CD45RA CD38 CD10 CD19 CD10 IL-7R
CD10 CD62L IL-7R CD79a
LMPP/ Pre-
HSC MPP ELP CLP proB ProB
Lin Sca-1 Lin Sca-1 lo Lin CD43 Lin CD43
CD117 high CD117 lo CD45R CD19 CD45R CD19 Human
Flt3 CD127 CD127 CD24 CD127
Mouse
CD45R CD19
c CD43 Pre- PreB CD34 CD19
Marginal zone BCR CD10 pre-BCR
B cells
Notch2
Notch2
MZ CD45R CD19 CD10
T2 CD19 IgM
T1 BCR B BCR
BAFF
BAFF Transitional
Transitional
B cells
B cells
FO
Follicular B
Follicular B
cells
cells
Spleen
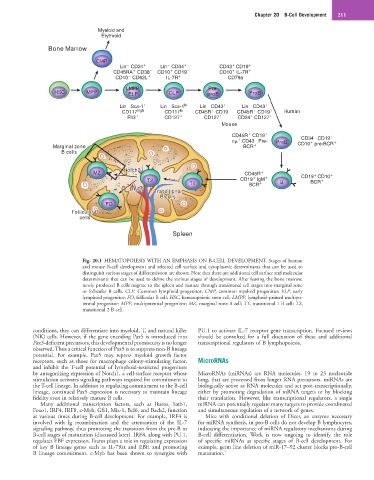
Fig. 20.1 HEMATOPOIESIS WITH AN EMPHASIS ON B-CELL DEVELOPMENT. Stages of human
and mouse B-cell development and selected cell surface and cytoplasmic determinants that can be used to
distinguish various stages of differentiation are shown. Note that there are additional cell surface and molecular
determinants that can be used to define the various stages of development. After leaving the bone marrow,
newly produced B cells migrate to the spleen and mature through transitional cell stages into marginal zone
or follicular B cells. CLP, Common lymphoid progenitor; CMP, common myeloid progenitor; ELP, early
lymphoid progenitor; FO, follicular B cell; HSC, hematopoietic stem cell; LMPP, lymphoid-primed multipo-
tential progenitor; MPP, multipotential progenitor; MZ, marginal zone B cell; T1, transitional 1 B cell; T2,
transitional 2 B cell.
conditions, they can differentiate into myeloid, T, and natural killer PU.1 to activate IL-7 receptor gene transcription. Focused reviews
(NK) cells. However, if the gene encoding Pax5 is introduced into should be consulted for a full discussion of these and additional
Pax5-deficient precursors, this developmental promiscuity is no longer transcriptional regulators of B lymphopoiesis.
observed. Thus a critical function of Pax5 is to suppress non-B lineage
potential. For example, Pax5 may repress myeloid growth factor
receptors, such as those for macrophage colony-stimulating factor, MicroRNAs
and inhibit the T-cell potential of lymphoid-restricted progenitors
by antagonizing expression of Notch1, a cell-surface receptor whose MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are RNA molecules, 19 to 23 nucleotide
stimulation activates signaling pathways required for commitment to long, that are processed from longer RNA precursors. miRNAs are
the T-cell lineage. In addition to regulating commitment to the B-cell biologically active as RNA molecules and act post-transcriptionally,
lineage, continued Pax5 expression is necessary to maintain lineage either by promoting degradation of mRNA targets or by blocking
fidelity even in relatively mature B cells. their translation. However, like transcriptional regulators, a single
Many additional transcription factors, such as Ikaros, Satb1, miRNA can potentially regulate many targets to provide coordinated
Foxo1, IRF4, IRF8, c-Myb, Gfi1, Miz-1, Bcl6, and Bach2, function and simultaneous regulation of a network of genes.
at various times during B-cell development. For example, IRF4 is Mice with conditional deletion of Dicer, an enzyme necessary
involved with Ig recombination and the attenuation of the IL-7 for miRNA synthesis, in pro-B cells do not develop B lymphocytes,
signaling pathway, thus promoting the transition from the pre-B to indicating the importance of miRNA regulatory mechanisms during
B-cell stages of maturation (discussed later). IRF8, along with PU.1, B-cell differentiation. Work is now ongoing to identify the role
regulates EBF expression. Ikaros plays a role in regulating expression of specific miRNAs at specific stages of B-cell development. For
of key B lineage genes such as IL-7Rα and EBF, and promoting example, germ line deletion of miR-17–92 cluster blocks pro-B-cell
B lineage commitment. c-Myb has been shown to synergize with maturation. 7