Page 265 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 265
216 Part III Immunologic Basis of Hematology
Periosteal
arteriole
and vein
Periosteal
capillaries
Sinus
Radial
artery
Emissary
vein
Nutrient Intersinusoidal
artery Medullary Central space
artery sinus
B lineage receptor CXCR4
IL-7R
Plasma Pre-
cell proB ProB PreB B
CXCL12 rich IL-7 rich IL-7 deficient Exit BM
environment environment environment
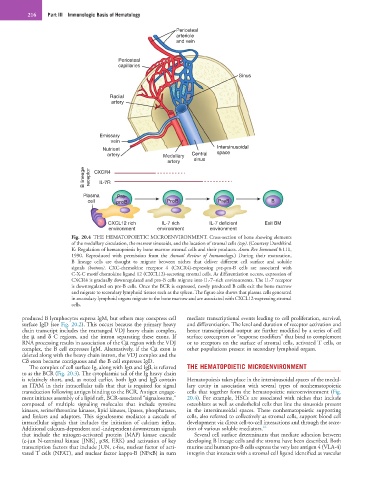
Fig. 20.4 THE HEMATOPOIETIC MICROENVIRONMENT. Cross-section of bone showing elements
of the medullary circulation, the marrow sinusoids, and the location of stromal cells (top). (Courtesy Dorshkind
K: Regulation of hematopoiesis by bone marrow stromal cells and their products. Annu Rev Immunol 8:111,
1990. Reproduced with permission from the Annual Review of Immunology.) During their maturation,
B lineage cells are thought to migrate between niches that deliver different cell surface and soluble
signals (bottom). CXC-chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4)-expressing pre-pro-B cells are associated with
C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 12 (CXCL12)-secreting stromal cells. As differentiation occurs, expression of
CXCR4 is gradually downregulated and pro-B cells migrate into IL-7–rich environments. The IL-7 receptor
is downregulated on pre-B cells. Once the BCR is expressed, newly produced B cells exit the bone marrow
and migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues such as the spleen. The figure also shows that plasma cells generated
in secondary lymphoid organs migrate to the bone marrow and are associated with CXCL12-expressing stromal
cells.
produced B lymphocytes express IgM, but others may coexpress cell mediate transcriptional events leading to cell proliferation, survival,
surface IgD (see Fig. 20.2). This occurs because the primary heavy and differentiation. The level and duration of receptor activation and
chain transcript includes the rearranged VDJ heavy chain complex, hence transcriptional output are further modified by a series of cell
the µ and δ C regions, and the intron separating these exons. If surface coreceptors or “response modifiers” that bind to complement
RNA processing results in association of the Cµ region with the VDJ or to receptors on the surface of stromal cells, activated T cells, or
complex, the B cell expresses IgM. Alternatively, if the Cµ exon is other populations present in secondary lymphoid organs.
deleted along with the heavy chain intron, the VDJ complex and the
Cδ exon become contiguous and the B cell expresses IgD.
The complex of cell surface Ig, along with Igα and Igβ, is referred THE HEMATOPOIETIC MICROENVIRONMENT
to as the BCR (Fig. 20.3). The cytoplasmic tail of the Ig heavy chain
is relatively short, and, as noted earlier, both Igα and Igβ contain Hematopoiesis takes place in the intersinusoidal spaces of the medul-
an ITAM in their intracellular tails that that is required for signal lary cavity in association with several types of nonhematopoietic
transduction following antigen binding to the BCR. Antigen engage- cells that together form the hematopoietic microenvironment (Fig.
ment initiates assembly of a lipid raft, BCR-associated “signalosome,” 20.4). For example, HSCs are associated with niches that include
composed of multiple signaling molecules that include tyrosine osteoblasts as well as endothelial cells that line the sinusoids present
kinases, serine/threonine kinases, lipid kinases, lipases, phosphatases, in the intersinusoidal spaces. These nonhematopoietic supporting
and linkers and adaptors. This signalosome mediates a cascade of cells, also referred to collectively as stromal cells, support blood cell
intracellular signals that includes the initiation of calcium influx. development via direct cell-to-cell interactions and through the secre-
Additional calcium-dependent and -independent downstream signals tion of various soluble mediators. 16
that include the mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase cascade Several cell surface determinants that mediate adhesion between
(c-jun N-terminal kinase [JNK], p38, ERK) and activation of key developing B lineage cells and the stroma have been described. Both
transcription factors that include JUN, c-fos, nuclear factor of acti- murine and human pre-B cells express the very late antigen 4 (VLA-4)
vated T cells (NFAT), and nuclear factor kappa-B (NFκB) in turn integrin that interacts with a stromal cell ligand identified as vascular