Page 350 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 350
286 Part III Immunologic Basis of Hematology
Clonal Memory
disability B
T-cell help
T-cell tolerance
Auto-antigen
Memory
Activated B
B
Memory foundation
Pre-B Immature Virgin
B B
slgM− slgM + slgM + Clonal
anergy Activated Plasma
B
Clonal cell
deletion Clonal
expansion
Bone marrow Spleen
Plasma
cell
Secretion
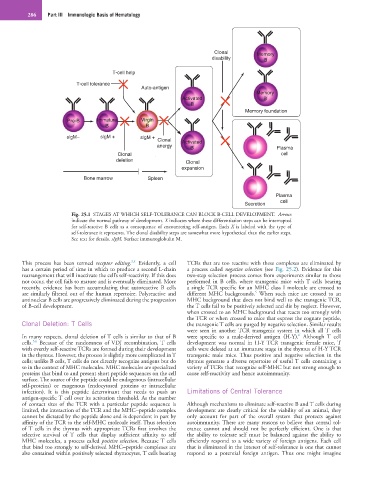
Fig. 25.1 STAGES AT WHICH SELF-TOLERANCE CAN BLOCK B-CELL DEVELOPMENT. Arrows
indicate the normal pathway of development. X indicates where these differentiation steps can be interrupted
for self-reactive B cells as a consequence of encountering self-antigen. Each X is labeled with the type of
self-tolerance it represents. The clonal disability steps are somewhat more hypothetical than the earlier steps.
See text for details. sIgM, Surface immunoglobulin M.
3,4
This process has been termed receptor editing. Evidently, a cell TCRs that are too reactive with these complexes are eliminated by
has a certain period of time in which to produce a second L-chain a process called negative selection (see Fig. 25.2). Evidence for this
rearrangement that will inactivate the cell’s self-reactivity. If this does two-step selection process comes from experiments similar to those
not occur, the cell fails to mature and is eventually eliminated. More performed in B cells, where transgenic mice with T cells bearing
recently, evidence has been accumulating that autoreactive B cells a single TCR specific for an MHC class I molecule are crossed to
5
are similarly filtered out of the human repertoire. Polyreactive and different MHC backgrounds. When such mice are crossed to an
antinuclear B cells are progressively eliminated during the progression MHC background that does not bind well to the transgenic TCR,
of B-cell development. the T cells fail to be positively selected and die by neglect. However,
when crossed to an MHC background that reacts too strongly with
the TCR or when crossed to mice that express the cognate peptide,
Clonal Deletion: T Cells the transgenic T cells are purged by negative selection. Similar results
were seen in another TCR transgenic system in which all T cells
6
In many respects, clonal deletion of T cells is similar to that of B were specific to a male-derived antigen (H-Y). Although T cell
5,6
cells. Because of the randomness of VDJ recombination, T cells development was normal in H-Y TCR transgenic female mice, T
with overtly self-reactive TCRs are formed during their development cells were deleted at an immature stage in the thymus of H-Y TCR
in the thymus. However, the process is slightly more complicated in T transgenic male mice. Thus positive and negative selection in the
cells; unlike B cells, T cells do not directly recognize antigens but do thymus generate a diverse repertoire of useful T cells containing a
so in the context of MHC molecules. MHC molecules are specialized variety of TCRs that recognize self-MHC but not strong enough to
proteins that bind to and present short peptide sequences on the cell cause self-reactivity and hence autoimmunity.
surface. The source of the peptide could be endogenous (intracellular
self-proteins) or exogenous (endocytosed proteins or intracellular
infection). It is this peptide determinant that needs to push an Limitations of Central Tolerance
antigen-specific T cell over its activation threshold. As the number
of contact sites of the TCR with a particular peptide sequence is Although mechanisms to eliminate self-reactive B and T cells during
limited, the interaction of the TCR and the MHC−peptide complex development are clearly critical for the viability of an animal, they
cannot be dictated by the peptide alone and is dependent in part by only account for part of the overall system that protects against
affinity of the TCR to the self-MHC molecule itself. Thus selection autoimmunity. There are many reasons to believe that central tol-
of T cells in the thymus with appropriate TCRs first involves the erance cannot and should not be perfectly efficient. One is that
selective survival of T cells that display sufficient affinity to self the ability to tolerate self must be balanced against the ability to
MHC molecules, a process called positive selection. Because T cells efficiently respond to a wide variety of foreign antigens. Each cell
that bind too strongly to self-derived MHC−peptide complexes are that is eliminated in the interest of self-tolerance is one that cannot
also contained within positively selected thymocytes, T cells bearing respond to a potential foreign antigen. Thus one might imagine