Page 351 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 351
Chapter 25 Tolerance and Autoimmunity 287
cTEC mTEC/DC
Clonal
deletion
MHC MHC
TCR TCR
Strong
Immature Adequate Positively TCR signal
T cell selected tTreg
TCR signal T cell
No TCR signal
Moderate TCR
Death by
neglect signal
Thymus
Periphery
Anergic
T cell
No
IL-6 costimulation
tTreg
T FH MHC
IL-21, IL-4 TGF-β
CD40L TCR APC TCR Mature T cell
CD40 MHC CD80 CD28
B cell IL-6 pTreg
IFN γ IL-12 IL-4 TGF β
Plasma Th 1 Th 2 Th 17
cell
Autoantibodies Type 1 diabetes Asthma Multiple sclerosis
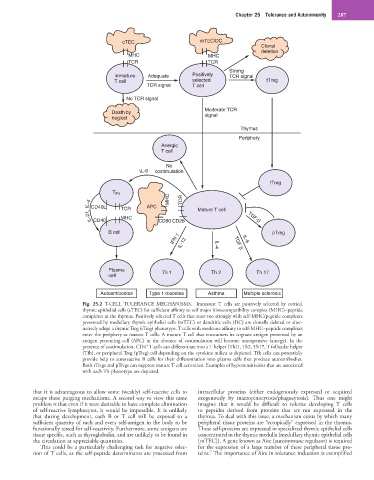
Fig. 25.2 T-CELL TOLERANCE MECHANISMS. Immature T cells are positively selected by cortical
thymic epithelial cells (cTEC) for sufficient affinity to self major histocompatibility complex (MHC)−peptide
complexes in the thymus. Positively selected T cells that react too strongly with self-MHC/peptide complexes
presented by medullary thymic epithelial cells (mTEC) or dendritic cells (DC) are clonally deleted or alter-
natively adopt a thymic Treg (tTreg) phenotype. T cells with moderate affinity to self-MHC−peptide complexes
enter the periphery as mature T cells. A mature T cell that encounters its cognate antigen presented by an
antigen presenting cell (APC) in the absence of costimulation will become unresponsive (anergy). In the
+
presence of costimulation, CD4 T cells can differentiate into a T helper (Th)1, Th2, Th17, T follicular helper
(Tfh), or peripheral Treg (pTreg) cell depending on the cytokine milieu as depicted. Tfh cells can potentially
provide help to autoreactive B cells for their differentiation into plasma cells that produce autoantibodies.
Both tTregs and pTregs can suppress mature T-cell activation. Examples of hypersensitivities that are associated
with each Th phenotype are depicted.
that it is advantageous to allow some (weakly) self-reactive cells to intracellular proteins (either endogenously expressed or acquired
escape these purging mechanisms. A second way to view this same exogenously by macropinocytosis/phagocytosis). Thus one might
problem is that even if it were desirable to have complete elimination imagine that it would be difficult to tolerize developing T cells
of self-reactive lymphocytes, it would be impossible. It is unlikely to peptides derived from proteins that are not expressed in the
that during development, each B or T cell will be exposed to a thymus. To deal with this issue, a mechanism exists by which many
sufficient quantity of each and every self-antigen in the body to be peripheral tissue proteins are “ectopically” expressed in the thymus.
functionally tested for self-reactivity. Furthermore, some antigens are These self-proteins are expressed in specialized thymic epithelial cells
tissue specific, such as thyroglobulin, and are unlikely to be found in concentrated in the thymic medulla (medullary thymic epithelial cells
the circulation at appreciable quantities. [mTEC]). A gene known as Aire (autoimmune regulator) is required
This could be a particularly challenging task for negative selec- for the expression of a large number of these peripheral tissue pro-
7
tion of T cells, as the self-peptide determinants are processed from teins. The importance of Aire in tolerance induction is exemplified