Page 352 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 352
288 Part III Immunologic Basis of Hematology
Heterozygous for Tg+ Heterozygous for B cells generally remained quiescent in a normal animal, suggesting
autoAg expression that B cells that are not usually regulated by self-tolerance (perhaps
because they recognize the self-antigen only weakly) may be the
T G A g precursors of pathogenic autoantibodies in disease.
Peripheral Control of Self-Reactive Lymphocytes:
Preventing Activation
TG+Ag Autoantigen The recognition that potentially self-reactive lymphocytes exist in
TG and Ag present the peripheral lymphoid repertoire of normal individuals, despite
central tolerance, raises the question of why they do not usually
T G TG only Autoantigen cause disease. One reason is the second layer of immune tolerance
that prevents activation of self-reactive lymphocytes that exist in the
absent
periphery. This layer consists of several facets, which are described in
the following sections.
A g
Ag only
Absence of Self-Antigen
Neither The simplest explanation for why a self-specific lymphocyte is not
spontaneously activated in the peripheral lymphoid compartment is
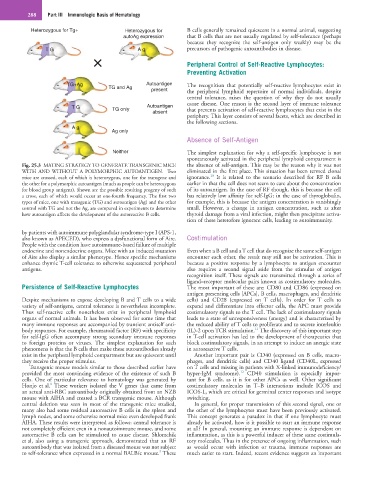
Fig. 25.3 MATING STRATEGY TO GENERATE TRANSGENIC MICE the absence of self-antigen. This may be the reason why it was not
WITH AND WITHOUT A POLYMORPHIC AUTOANTIGEN. Two eliminated in the first place. This situation has been termed clonal
10
mice are crossed, each of which is heterozygous, one for the transgene and ignorance. It is related to the scenario described for RF B cells
the other for a polymorphic autoantigen (much as people can be heterozygous earlier in that the cell does not seem to care about the concentration
for blood group antigens). Shown are the possible resulting progeny of such of its autoantigen. In the case of RF though, this is because the cell
a cross, each of which would occur at one-fourth frequency. The first two has relatively low affinity for self-IgG; in the case of thyroglobulin,
types of mice, one with transgenic (TG) and autoantigen (Ag) and the other for example, this is because the antigen concentration is vanishingly
control with TG and not the Ag, are compared in experiments to determine small. However, a change in antigen concentration, such as after
how autoantigen affects the development of the autoreactive B cells. thyroid damage from a viral infection, might then precipitate activa-
tion of these heretofore ignorant cells, leading to autoimmunity.
by patients with autoimmune polyglandular syndrome-type I (APS-1,
also known as APECED), who express a dysfunctional form of Aire. Costimulation
People with the condition have autoimmune-based failure of multiple
endocrine and nonendocrine organs. Mice with an induced mutation Even when a B cell and a T cell that do recognize the same self-antigen
of Aire also display a similar phenotype. Hence specific mechanisms encounter each other, the result may still not be activation. This is
enhance thymic T-cell tolerance to otherwise sequestered peripheral because a positive response by a lymphocyte to antigen encounter
antigens. also requires a second signal aside from the stimulus of antigen
recognition itself. These signals are transmitted through a series of
ligand–receptor molecular pairs known as costimulatory molecules.
Persistence of Self-Reactive Lymphocytes The most important of these are: CD80 and CD86 (expressed on
antigen presenting cells [APCs], B cells, macrophages, and dendritic
Despite mechanisms to expose developing B and T cells to a wide cells) and CD28 (expressed on T cells). In order for T cells to
variety of self-antigens, central tolerance is nevertheless incomplete. expand and differentiate into effector cells, the APC must provide
Thus self-reactive cells nonetheless exist in peripheral lymphoid costimulatory signals to the T cell. The lack of costimulatory signals
organs of normal animals. It has been observed for some time that leads to a state of unresponsiveness (anergy) and is characterized by
many immune responses are accompanied by transient antiself anti- the reduced ability of T cells to proliferate and to secrete interleukin
11
body responses. For example, rheumatoid factor (RF) with specificity (IL)-2 upon TCR stimulation. The discovery of this important step
for self-IgG often accompany strong secondary immune responses in T-cell activation has led to the development of therapeutics that
to foreign proteins or viruses. The simplest explanation for such block costimulatory signals, in an attempt to induce an anergic state
phenomena is that the B cells that make these autoantibodies already in autoreactive T cells.
exist in the peripheral lymphoid compartment but are quiescent until Another important pair is CD40 (expressed on B cells, macro-
they receive the proper stimulus. phages, and dendritic cells) and CD40 ligand (CD40L, expressed
Transgenic mouse models similar to those described earlier have on T cells and missing in patients with X-linked immunodeficiency/
12
provided the most convincing evidence of the existence of such B hyper-IgM syndrome). CD40 stimulation is especially impor-
cells. One of particular relevance to hematology was generated by tant for B cells, as it is for other APCs as well. Other significant
8
Honjo et al. These workers isolated the V genes that came from costimulatory molecules in T–B interactions include ICOS and
an actual anti-RBC autoantibody originally obtained from an NZB ICOS-L, which are critical for germinal center responses and isotype
mouse with AIHA and created a BCR transgenic mouse. Although switching.
central deletion was seen in most of the transgenic mice studied, In general, for proper transmission of this second signal, one or
many also had some residual autoreactive B cells in the spleen and the other of the lymphocytes must have been previously activated.
lymph nodes, and some otherwise normal mice even developed frank This concept generates a paradox in that if one lymphocyte must
AIHA. These results were interpreted as follows: central tolerance is already be activated, how is it possible to start an immune response
not completely efficient even in a nonautoimmune mouse, and some at all? In general, mounting an immune response is dependent on
autoreactive B cells can be stimulated to cause disease. Shlomchik inflammation, as this is a powerful inducer of these same costimula-
et al, also using a transgenic approach, demonstrated that an RF tory molecules. Thus in the presence of ongoing inflammation, such
autoantibody that was isolated from a diseased mouse was not subject as would occur with infection or trauma, immune responses are
9
to self-tolerance when expressed in a normal BALB/c mouse. These much easier to start. Indeed, recent evidence suggests an important