Page 402 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 402
324 Part IV Disorders of Hematopoietic Cell Development
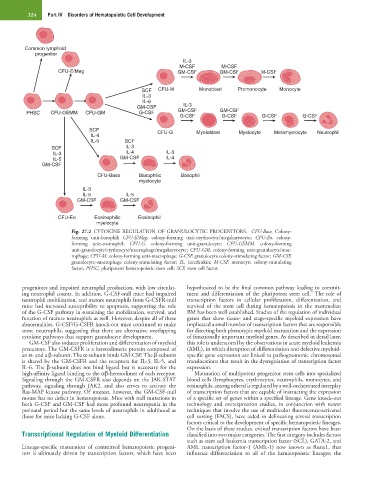
Common lymphoid
progenitor
IL-3
M-CSF M-CSF
CFU-E/Meg GM-CSF GM-CSF M-CSF
SCF CFU-M Monoblast Promonocyte Monocyte
IL-3
IL-6
GM-CSF IL-3
PHSC CFU-GEMM CFU-GM G-CSF GM-CSF GM-CSF
G-CSF G-CSF G-CSF G-CSF
SCF CFU-G Myeloblast Myelocyte Metamyelocyte Neutrophil
IL-4
IL-5 SCF
SCF IL-3
IL-3 IL-4 IL-3
IL-5 GM-CSF IL-4
GM-CSF
CFU-Baso Basophilic Basophil
myelocyte
IL-3
IL-5 IL-5
GM-CSF GM-CSF
CFU-Eo Eosinophilic Eosinophil
myelocyte
Fig. 27.2 CYTOKINE REGULATION OF GRANULOCYTIC PROGENITORS. CFU-Baso, Colony-
forming unit-basophil; CFU-E/Meg, colony-forming unit-erythrocyte/megakaryocyte; CFU-Eo, colony-
forming unit-eosinophil; CFU-G, colony-forming unit-granulocyte; CFU-GEMM, colony-forming
unit-granulocyte/erythrocyte/macrophage/megakaryocyte; CFU-GM, colony-forming unit-granulocyte/mac-
rophage; CFU-M, colony-forming unit-macrophage; G-CSF, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor; GM-CSF,
granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating factor; IL, interleukin; M-CSF, monocyte colony-stimulating
factor; PHSC, pluripotent hematopoietic stem cell; SCF, stem cell factor.
progenitors and impaired neutrophil production, with low circulat- hypothesized to be the final common pathway leading to commit-
9
ing neutrophil counts. In addition, G-CSF-null mice had impaired ment and differentiation of the pluripotent stem cell. The role of
neutrophil mobilization, and mature neutrophils from G-CSFR-null transcription factors in cellular proliferation, differentiation, and
mice had increased susceptibility to apoptosis, supporting the role survival of the stem cell during hematopoiesis in the mammalian
of the G-CSF pathway in sustaining the mobilization, survival, and BM has been well established. Studies of the regulation of individual
function of mature neutrophils as well. However, despite all of these genes that show tissue- and stage-specific myeloid expression have
abnormalities, G-CSF/G-CSFR knock-out mice continued to make implicated a small number of transcription factors that are responsible
some neutrophils, suggesting that there are alternative overlapping for directing both phenotypic myeloid maturation and the expression
cytokine pathways that support granulocyte development. of functionally important myeloid genes. As described in detail later,
GM-CSF also induces proliferation and differentiation of myeloid this role is underscored by the observations in acute myeloid leukemia
precursors. The GM-CSFR is a heterodimeric protein composed of (AML), in which disruption of differentiation and defective myeloid-
an α- and a β-subunit. The α-subunit binds GM-CSF. The β-subunit specific gene expression are linked to pathognomonic chromosomal
is shared by the GM-CSFR and the receptors for IL-3, IL-5, and translocations that result in the dysregulation of transcription factor
IL-6. The β-subunit does not bind ligand but is necessary for the expression.
high-affinity ligand binding to the αβ-heterodimer of each receptor. Maturation of multipotent progenitor stem cells into specialized
Signaling through the GM-CSFR also depends on the JAK-STAT blood cells (lymphocytes, erythrocytes, neutrophils, monocytes, and
pathway, signaling through JAK2, and also serves to activate the eosinophils, among others) is regulated by a well-orchestrated interplay
Ras-MAP kinase pathway. Of interest, however, the GM-CSF-null of transcription factors that are capable of instructing the expression
mouse has no defect in hematopoiesis. Mice with null mutations in of a specific set of genes within a specified lineage. Gene knock-out
both G-CSF and GM-CSF had more profound neutropenia in the technology and overexpression studies, in conjunction with newer
perinatal period but the same levels of neutrophils in adulthood as techniques that involve the use of multicolor fluorescence-activated
those for mice lacking G-CSF alone. cell sorting (FACS), have aided in delineating several transcription
factors critical to the development of specific hematopoietic lineages.
On the basis of these studies, critical transcription factors have been
Transcriptional Regulation of Myeloid Differentiation classified into two major categories. The first category includes factors
such as stem cell leukemia transcription factor (SCL), GATA-2, and
Lineage-specific maturation of committed hematopoietic progeni- AML transcription factor-1 (AML-1) now known as Runx1, that
tors is ultimately driven by transcription factors, which have been influence differentiation to all of the hematopoietic lineages; the