Page 400 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 400
322 Part IV Disorders of Hematopoietic Cell Development
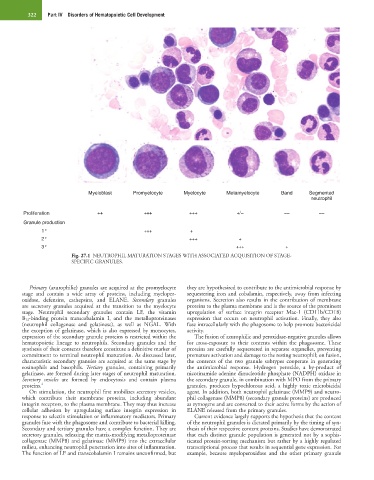
Myeloblast Promyelocyte Myelocyte Metamyelocyte Band Segmented
neutrophil
Proliferation ++ +++ +++ +/− −− −−
Granule production
1° +++ +
2° +++ +
3° +++ +
Fig. 27.1 NEUTROPHIL MATURATION STAGES WITH ASSOCIATED ACQUISITION OF STAGE-
SPECIFIC GRANULES.
Primary (azurophilic) granules are acquired at the promyelocyte they are hypothesized to contribute to the antimicrobial response by
stage and contain a wide array of proteins, including myeloper- sequestering iron and cobalamin, respectively, away from infecting
oxidase, defensins, cathepsins, and ELANE. Secondary granules organisms. Secretion also results in the contribution of membrane
are secretory granules acquired at the transition to the myelocyte proteins to the plasma membrane and is the source of the prominent
stage. Neutrophil secondary granules contain LF, the vitamin upregulation of surface integrin receptor Mac-1 (CD11b/CD18)
B 12 -binding protein transcobalamin I, and the metalloproteinases expression that occurs on neutrophil activation. Finally, they also
(neutrophil collagenase and gelatinase), as well as NGAL. With fuse intracellularly with the phagosome to help promote bactericidal
the exception of gelatinase, which is also expressed by monocytes, activity.
expression of the secondary granule proteins is restricted within the The fusion of azurophilic and peroxidase-negative granules allows
hematopoietic lineage to neutrophils. Secondary granules and the for cross-exposure to their contents within the phagosome. These
synthesis of their contents therefore constitute a definitive marker of proteins are carefully sequestered in separate organelles, preventing
commitment to terminal neutrophil maturation. As discussed later, premature activation and damage to the resting neutrophil; on fusion,
characteristic secondary granules are acquired at the same stage by the contents of the two granule subtypes cooperate in generating
eosinophils and basophils. Tertiary granules, containing primarily the antimicrobial response. Hydrogen peroxide, a by-product of
gelatinase, are formed during later stages of neutrophil maturation. nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase in
Secretory vesicles are formed by endocytosis and contain plasma the secondary granule, in combination with MPO from the primary
proteins. 4 granules, produces hypochlorous acid, a highly toxic microbicidal
On stimulation, the neutrophil first mobilizes secretory vesicles, agent. In addition, both neutrophil gelatinase (MMP9) and neutro-
which contribute their membrane proteins, including abundant phil collagenase (MMP8) (secondary granule proteins) are produced
integrin receptors, to the plasma membrane. They may thus increase as zymogens and are converted to their active forms by the action of
cellular adhesion by upregulating surface integrin expression in ELANE released from the primary granules.
response to selectin stimulation or inflammatory mediators. Primary Current evidence largely supports the hypothesis that the content
granules fuse with the phagosome and contribute to bacterial killing. of the neutrophil granules is dictated primarily by the timing of syn-
Secondary and tertiary granules have a complex function. They are thesis of their respective content proteins. Studies have demonstrated
secretory granules, releasing the matrix-modifying metalloproteinase that each distinct granule population is generated not by a sophis-
collagenase (MMP8) and gelatinase (MMP9) into the extracellular ticated protein-sorting mechanism but rather by a highly regulated
milieu, enhancing neutrophil penetration into sites of inflammation. transcriptional process that results in sequential gene expression. For
The function of LF and transcobalamin I remains unconfirmed, but example, because myeloperoxidase and the other primary granule