Page 403 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 403
Chapter 27 Granulocytopoiesis and Monocytopoiesis 325
Erythrocyte
GATA-1
HSC Megakaryocyte
TAL-1
Rbtn-2
Mast cell
GATA-2 Neutrophil
PU.1 C/EBPα,ε
Ikaros
PU.1, C/EBPβ
E2A, Pax5 Monocyte
C/EBPα,β,ε
Eosinophil
T B
Lymphocytes
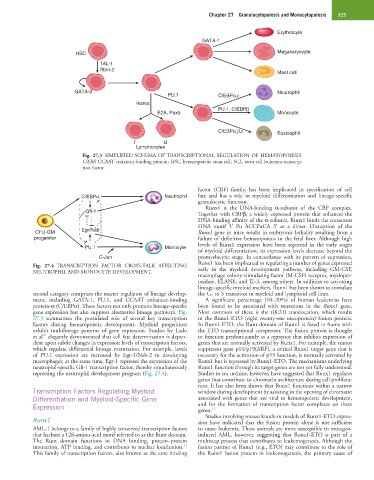
Fig. 27.3 SIMPLIFIED SCHEMA OF TRANSCRIPTIONAL REGULATION OF HEMATOPOIESIS.
C/EBP, CCAAT enhancer-binding protein; HSC, hematopoietic stem cell; SCL, stem cell leukemia transcrip-
tion factor.
factor (CBF) family, has been implicated in specification of cell
C/EBPα Neutrophil fate and has a role in myeloid differentiation and lineage-specific
granulocytic function.
Runx1 is the DNA-binding α-subunit of the CBF complex.
Gfi-1
Together with CBFβ, a widely expressed protein that enhances the
DNA-binding affinity of the α-subunit, Runx1 binds the consensus
DNA motif 5′ Pu ACCPuCA 3′ as a dimer. Disruption of the
Egr/Nab
CFU-GM Runx1 gene in mice results in embryonic lethality resulting from a
progenitor failure of definitive hematopoiesis in the fetal liver. Although high
PU.1 Monocyte levels of Runx1 expression have been reported in the early stages
of myeloid differentiation, its expression levels decrease beyond the
C-Jun promyelocytic stage. In concordance with its pattern of expression,
Runx1 has been implicated in regulating a number of genes expressed
Fig. 27.4 TRANSCRIPTION FACTOR CROSS-TALK AFFECTING early in the myeloid development pathway, including GM-CSF,
NEUTROPHIL AND MONOCYTE DEVELOPMENT.
macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF) receptor, myeloper-
oxidase, ELANE, and IL-3, among others. In addition to activating
lineage-specific myeloid markers, Runx1 has been shown to stimulate
second category comprises the master regulators of lineage develop- the G 1 to S transition in myeloid and lymphoid cell lines.
ment, including GATA-1, PU.1, and CCAAT enhancer-binding A significant percentage (10–20%) of human leukemias have
protein-α (C/EBPα). These factors not only promote lineage-specific been found to be associated with mutations in the Runx1 gene.
gene expression but also suppress alternative lineage pathways. Fig. Most common of these is the t(8;21) translocation, which results
27.3 summarizes the postulated role of several key transcription in the Runx1-ETO (eight twenty-one oncoprotein) fusion protein.
factors during hematopoietic development. Myeloid progenitors In Runx1-ETO, the Runt domain of Runx1 is fused in frame with
exhibit multilineage patterns of gene expression. Studies by Laslo the ETO transcriptional corepressor. The fusion protein is thought
10
et al elegantly demonstrated that cell fate determination is depen- to function predominantly as a repressor that inhibits expression of
dent upon subtle changes in expression levels of transcription factors, genes that are normally activated by Runx1. For example, the tumor
which regulate differential lineage maturation. For example, levels suppressor gene p14/p19(ARF), a critical Runx1 target gene that is
of PU.1 expression are increased by Egr-1/Nab-2 in developing necessary for the activation of p53 function, is normally activated by
macrophages; at the same time, Egr-1 represses the expression of the Runx1 but is repressed by Runx1-ETO. The mechanisms underlying
neutrophil-specific Gfi-1 transcription factor, thereby simultaneously Runx1 function through its target genes are not yet fully understood.
repressing the neutrophil development program (Fig. 27.4). Studies in sea urchins, however, have suggested that Runx1 regulates
genes that contribute to chromatin architecture during cell prolifera-
tion. It has also been shown that Runx1 functions within a narrow
Transcription Factors Regulating Myeloid window during development by assisting in the opening of chromatin
Differentiation and Myeloid-Specific Gene associated with genes that are vital to hematopoietic development,
Expression and for the formation of transcription factor complexes on these
12
genes.
Studies involving mouse knock-in models of Runx1-ETO expres-
Runx1 sion have indicated that the fusion protein alone is not sufficient
AML-1 belongs to a family of highly conserved transcription factors to cause leukemia. These animals are more susceptible to mutagen-
that harbors a 128-amino-acid motif referred to as the Runt domain. induced AML, however, suggesting that Runx1-ETO is part of a
The Runt domain functions in DNA binding, protein–protein multistep process that contributes to leukemogenesis. Although the
11
interaction, ATP binding, and contributes to nuclear localization. fusion partner of Runx1 (e.g., ETO) may contribute to the role of
This family of transcription factors, also known as the core binding the Runx1 fusion protein in leukemogenesis, the primary cause of