Page 461 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 461
382 Part IV Disorders of Hematopoietic Cell Development
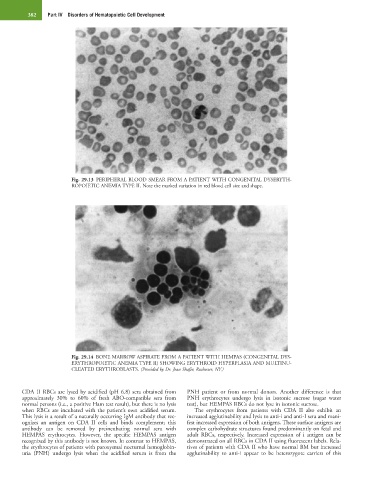
Fig. 29.13 PERIPHERAL BLOOD SMEAR FROM A PATIENT WITH CONGENITAL DYSERYTH-
ROPOIETIC ANEMIA TYPE II. Note the marked variation in red blood cell size and shape.
Fig. 29.14 BONE MARROW ASPIRATE FROM A PATIENT WITH HEMPAS (CONGENITAL DYS-
ERYTHROPOIETIC ANEMIA TYPE II) SHOWING ERYTHROID HYPERPLASIA AND MULTINU-
CLEATED ERYTHROBLASTS. (Provided by Dr. Jean Shafer, Rochester, NY.)
CDA II RBCs are lysed by acidified (pH 6.8) sera obtained from PNH patient or from normal donors. Another difference is that
approximately 30% to 60% of fresh ABO-compatible sera from PNH erythrocytes undergo lysis in isotonic sucrose (sugar water
normal persons (i.e., a positive Ham test result), but there is no lysis test), but HEMPAS RBCs do not lyse in isotonic sucrose.
when RBCs are incubated with the patient’s own acidified serum. The erythrocytes from patients with CDA II also exhibit an
This lysis is a result of a naturally occurring IgM antibody that rec- increased agglutinability and lysis to anti-i and anti-I sera and mani-
ognizes an antigen on CDA II cells and binds complement; this fest increased expression of both antigens. These surface antigens are
antibody can be removed by preincubating normal sera with complex carbohydrate structures found predominantly on fetal and
HEMPAS erythrocytes. However, the specific HEMPAS antigen adult RBCs, respectively. Increased expression of i antigen can be
recognized by this antibody is not known. In contrast to HEMPAS, demonstrated on all RBCs in CDA II using fluorescent labels. Rela-
the erythrocytes of patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobin- tives of patients with CDA II who have normal BM but increased
uria (PNH) undergo lysis when the acidified serum is from the agglutinability to anti-i appear to be heterozygote carriers of this