Page 487 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 487
408 Part IV Disorders of Hematopoietic Cell Development
A B C
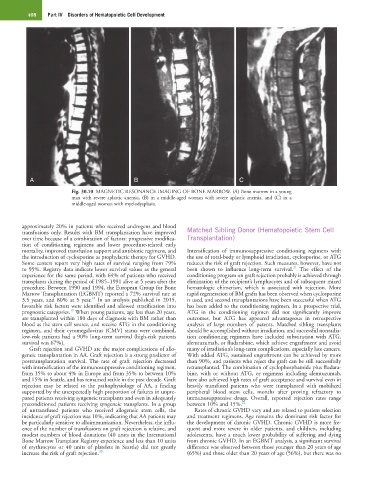
Fig. 30.10 MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING OF BONE MARROW. (A) Bone marrow in a young
man with severe aplastic anemia, (B) in a middle-aged woman with severe aplastic anemia, and (C) in a
middle-aged woman with myelodysplasia.
approximately 20% in patients who received androgens and blood
transfusions only. Results with BM transplantation have improved Matched Sibling Donor (Hematopoietic Stem Cell
over time because of a combination of factors: progressive modifica- Transplantation)
tion of conditioning regimens and lower procedure-related early
mortality, improved transfusion support and antibiotic regimens, and Intensification of immunosuppressive conditioning regimens with
the introduction of cyclosporine as prophylactic therapy for GVHD. the use of total-body or lymphoid irradiation, cyclosporine, or ATG
Some centers report very high rates of survival ranging from 79% reduces the risk of graft rejection. Such measures, however, have not
21
to 95%. Registry data indicate lower survival values as the general been shown to influence long-term survival. The effect of the
experience for the same period, with 64% of patients who received conditioning program on graft rejection probably is achieved through
transplants during the period of 1985–1991 alive at 5 years after the elimination of the recipient’s lymphocytes and of subsequent mixed
procedure. Between 1990 and 1994, the European Group for Bone hematologic chimerism, which is associated with rejection. More
Marrow Transplantation (EGBMT) reported a 72% survival rate at rapid regeneration of BM grafts has been observed when cyclosporine
18
3.5 years, and 80% at 5 year. In an analysis published in 2015, is used, and second transplantations have been successful when ATG
favorable risk factors were identified and allowed stratification into has been added to the conditioning regimen. In a prospective trial,
19
prognostic categories. When young patients, age less than 20 years, ATG in the conditioning regimen did not significantly improve
are transplanted within 180 days of diagnosis with BM rather than outcomes, but ATG has appeared advantageous in retrospective
blood as the stem cell source, and receive ATG in the conditioning analysis of large numbers of patents. Matched sibling transplants
regimen, and their cytomegalovirus (CMV) status were combined, should be accomplished without irradiation, and successful nonradia-
low-risk patients had a 90% long-term survival (high-risk patients tion conditioning regimens have included substitution with ATG,
survival was 67%). alemtuzumab, or fludarabine, which achieve engraftment and avoid
Graft rejection and GVHD are the major complications of allo- many of irradiation’s long-term complications, especially late cancers.
geneic transplantation in AA. Graft rejection is a strong predictor of With added ATG, sustained engraftment can be achieved by more
posttransplantation survival. The rate of graft rejection decreased than 90%, and patients who reject the graft can be still successfully
with intensification of the immunosuppressive conditioning regimen, retransplanted. The combination of cyclophosphamide plus fludara-
from 15% to about 4% in Europe and from 35% to between 10% bine, with or without ATG, or regimens including alemtuzumab,
and 15% in Seattle, and has remained stable in the past decade. Graft have also achieved high rates of graft acceptance and survival even in
rejection may be related to the pathophysiology of AA, a finding heavily transfused patients who were transplanted with mobilized
supported by the unexpectedly high proportion of failures in unpre- peripheral blood stem cells, months after proving refractory to
pared patients receiving syngeneic transplants and even in adequately immunosuppressive drugs. Overall, reported rejection rates range
preconditioned patients receiving syngeneic transplants. In a group between 10% and 15%. 22
of untransfused patients who received allogeneic stem cells, the Rates of chronic GVHD vary and are related to patient selection
incidence of graft rejection was 10%, indicating that AA patients may and treatment regimens. Age remains the dominant risk factor for
be particularly sensitive to alloimmunization. Nevertheless, the influ- the development of chronic GVHD. Chronic GVHD is more fre-
ence of the number of transfusions on graft rejection is relative, and quent and more severe in older patients, and children, including
modest numbers of blood donations (40 units in the International adolescents, have a much lower probability of suffering and dying
Bone Marrow Transplant Registry experience and less than 10 units from chronic GVHD. In an EGBMT analysis, a significant survival
of erythrocytes or 40 units of platelets in Seattle) did not greatly difference was observed between those younger than 20 years of age
increase the risk of graft rejection. 20 (65%) and those older than 20 years of age (56%), but there was no