Page 49 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 49
Chapter 2 Epigenetics and Epigenomics 21
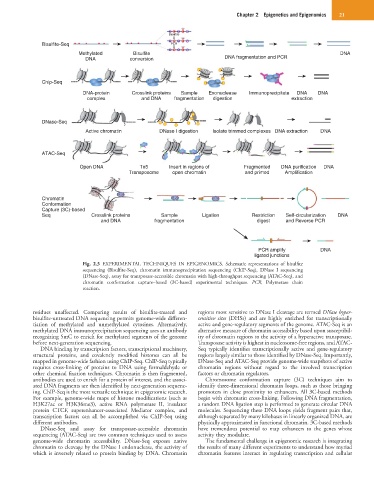
Bisulfite
Bisulfite-Seq PCR
Methylated Bisulfite DNA
DNA conversion DNA fragmentation and PCR
Chlp-Seq
DNA-protein Crosslink proteins Sample Exonuclease Immunoprecipitate DNA DNA
complex and DNA fragmentation digestion extraction
DNase-Seq
Active chromatin DNase I digestion Isolate trimmed complexes DNA extraction DNA
ATAC-Seq
Open DNA Tn5 Insert in regions of Fragmented DNA purification DNA
Transposome open chromatin and primed Amplification
Chromatin
Conformation
Capture (3C)-based
Seq Crosslink proteins Sample Ligation Restriction Self-circularization DNA
and DNA fragmentation digest and Reverse PCR
PCR amplify DNA
ligated junctions
Fig. 2.3 EXPERIMENTAL TECHNIQUES IN EPIGENOMICS. Schematic representations of bisulfite
sequencing (Bisulfite-Seq), chromatin immunoprecipitation sequencing (ChIP-Seq), DNase I sequencing
(DNase-Seq), assay for transposase-accessible chromatin with high-throughput sequencing (ATAC-Seq), and
chromatin conformation capture–based (3C-based) experimental techniques. PCR, Polymerase chain
reaction.
residues unaffected. Comparing results of bisulfite-treated and regions most sensitive to DNase I cleavage are termed DNase hyper-
bisulfite-untreated DNA sequencing permits genome-wide differen- sensitive sites (DHSs) and are highly enriched for transcriptionally
tiation of methylated and unmethylated cytosines. Alternatively, active and gene-regulatory segments of the genome. ATAC-Seq is an
methylated DNA immunoprecipitation sequencing uses an antibody alternative measure of chromatin accessibility based upon susceptibil-
recognizing 5mC to enrich for methylated segments of the genome ity of chromatin regions to the activity of a hyperactive transposase.
before next-generation sequencing. Transposase activity is highest in nucleosome-free regions, and ATAC-
DNA binding by transcription factors, transcriptional machinery, Seq typically identifies transcriptionally active and gene-regulatory
structural proteins, and covalently modified histones can all be regions largely similar to those identified by DNase-Seq. Importantly,
mapped in genome-wide fashion using ChIP-Seq. ChIP-Seq typically DNase-Seq and ATAC-Seq provide genome-wide snapshots of active
requires cross-linking of proteins to DNA using formaldehyde or chromatin regions without regard to the involved transcription
other chemical fixation techniques. Chromatin is then fragmented, factors or chromatin regulators.
antibodies are used to enrich for a protein of interest, and the associ- Chromosome conformation capture (3C) techniques aim to
ated DNA fragments are then identified by next-generation sequenc- identify three-dimensional chromatin loops, such as those bringing
ing. ChIP-Seq is the most versatile technique in epigenomic research. promoters in close proximity to enhancers. All 3C-based methods
For example, genome-wide maps of histone modifications (such as begin with chromatin cross-linking. Following DNA fragmentation,
H3K27ac or H3K36me3), active RNA polymerase II, insulator a random DNA ligation step is performed to generate circular DNA
protein CTCF, superenhancer-associated Mediator complex, and molecules. Sequencing these DNA loops yields fragment pairs that,
transcription factors can all be accomplished via ChIP-Seq using although separated by many kilobases in linearly organized DNA, are
different antibodies. physically approximated in functional chromatin. 3C-based methods
DNase-Seq and assay for transposase-accessible chromatin have tremendous potential to map enhancers to the genes whose
sequencing (ATAC-Seq) are two common techniques used to assess activity they modulate.
genome-wide chromatin accessibility. DNase-Seq exposes native The fundamental challenge in epigenomic research is integrating
chromatin to cleavage by the DNase I endonuclease, the activity of the results of many different experiments to understand how myriad
which is inversely related to protein binding by DNA. Chromatin chromatin features interact in regulating transcription and cellular