Page 501 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 501
Chapter 31 Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria 421
to immunosuppressive therapy. The response rate in this group is Alternate
more than 50%. In fact, finding a minor population of PNH-like Lectin pathway Classical pathway pathway
cells in severe aplastic anemia may predict for response to immuno-
suppressive therapy. The impaired hematopoiesis that occurs in MBL, MASP, C1q, C1r, C1s C3
hypoplastic PNH may respond to antithymocyte globulin and/or C4 + C2 C4 + C2 factor B + D
cyclosporine, but the PNH clone is usually not eradicated. Expansion
of the PNH clone ultimately leading to classical PNH may occur
several months to years after treatment with immunosuppression; C3 convertases
thus patients should be monitored for signs and symptoms of PNH. C4b2a, C3bBb
Immunosuppressive therapy does not benefit patients with classical
PNH. C3b
Management of Anemia C5 convertases
C4b2a3b, C3bBb3b
The cause of anemia in PNH is often multifactorial. In patients with
hypoplastic PNH, bone marrow failure is the major etiologic factor C5a
for anemia. Patients with hypoplastic PNH may respond to immu- C5
nosuppressive therapy. However, in patients with cellular bone
marrow, elevated reticulocyte counts, and a high LDH (classical C6, C7, C8, C9
PNH), intravascular hemolysis is the major mechanism of anemia.
Terminal complement inhibition is highly effective for decreasing C5b Eculizumab
intravascular hemolysis. Iron deficiency caused by intravascular
hemolysis can also contribute to the anemia of PNH; thus, in patients Membrane attack
with absent iron stores, iron replacement therapy is indicated. Folic complex (MAC)
acid supplementation is also recommended in PNH because of the
high red cell turnover. Erythropoietin is rarely beneficial in PNH.
Often red cell transfusions are required to treat severe anemia. PNH Fig. 31.4 OVERVIEW OF THE COMPLEMENT CASCADE. Classic,
patients should receive group-specific blood and blood products. alternative, and lectin pathways converge at the point of C3 activation. The
Washing the red cells with saline, once advocated to minimize lytic pathway is initiated with the formation of C5 convertase and leads to
hemolysis after transfusion in PNH, is unnecessary. the assembly of the C5, C6, C7, C8, (n) C9 MAC. Eculizumab is a mono-
clonal antibody that binds to C5, thereby preventing the formation of C5a
and C5b. C5b is the initiating component of the MAC. FITC, Fluorescein
Eculizumab isothiocyanate; MASP, mannan-binding lectin associated service protease;
MBL, mannose binding lectin.
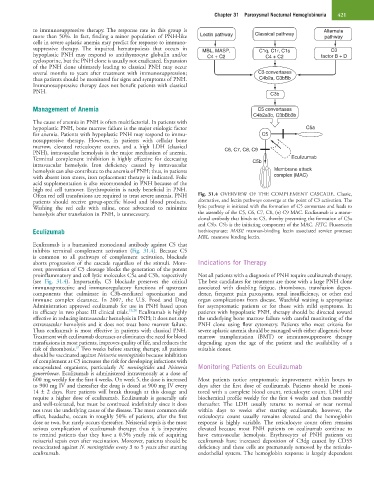
Eculizumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody against C5 that
inhibits terminal complement activation (Fig. 31.4). Because C5
is common to all pathways of complement activation, blockade
aborts progression of the cascade regardless of the stimuli. More- Indications for Therapy
over, prevention of C5 cleavage blocks the generation of the potent
proinflammatory and cell lytic molecules C5a and C5b, respectively Not all patients with a diagnosis of PNH require eculizumab therapy.
(see Fig. 31.4). Importantly, C5 blockade preserves the critical The best candidates for treatment are those with a large PNH clone
immunoprotective and immunoregulatory functions of upstream associated with disabling fatigue, thromboses, transfusion depen-
components that culminate in C3b-mediated opsonization and dence, frequent pain paroxysms, renal insufficiency, or other end
immune complex clearance. In 2007, the U.S. Food and Drug organ complications from disease. Watchful waiting is appropriate
Administration approved eculizumab for use in PNH based upon for asymptomatic patients or for those with mild symptoms. In
its efficacy in two phase III clinical trials. 19,20 Eculizumab is highly patients with hypoplastic PNH, therapy should be directed toward
effective in reducing intravascular hemolysis in PNH; it does not stop the underlying bone marrow failure with careful monitoring of the
extravascular hemolysis and it does not treat bone marrow failure. PNH clone using flow cytometry. Patients who meet criteria for
Thus eculizumab is most effective in patients with classical PNH. severe aplastic anemia should be managed with either allogeneic bone
Treatment with eculizumab decreases or eliminates the need for blood marrow transplantation (BMT) or immunosuppressive therapy
transfusions in most patients, improves quality of life, and reduces the depending upon the age of the patient and the availability of a
21
risk of thrombosis. Two weeks before starting therapy, all patients suitable donor.
should be vaccinated against Neisseria meningitides because inhibition
of complement at C5 increases the risk for developing infections with
encapsulated organisms, particularly N. meningitides and Neisseria Monitoring Patients on Eculizumab
gonorrhoeae. Eculizumab is administered intravenously at a dose of
600 mg weekly for the first 4 weeks. On week 5, the dose is increased Most patients notice symptomatic improvement within hours to
to 900 mg IV and thereafter the drug is dosed at 900 mg IV every days after the first dose of eculizumab. Patients should be moni-
14 ± 2 days. Rare patients will break through at this dosage and tored with a complete blood count, reticulocyte count, LDH and
require a higher dose of eculizumab. Eculizumab is generally safe biochemical profile weekly for the first 4 weeks and then monthly
and well-tolerated, but must be continued indefinitely since it does thereafter. The LDH usually returns to normal or near normal
not treat the underlying cause of the disease. The most common side within days to weeks after starting eculizumab; however, the
effect, headache, occurs in roughly 50% of patients, after the first reticulocyte count usually remains elevated and the hemoglobin
dose or two, but rarely occurs thereafter. Neisserial sepsis is the most response is highly variable. The reticulocyte count often remains
serious complication of eculizumab therapy; thus it is imperative elevated because most PNH patients on eculizumab continue to
to remind patients that they have a 0.5% yearly risk of acquiring have extravascular hemolysis. Erythrocytes of PNH patients on
neisserial sepsis even after vaccination. Moreover, patients should be eculizumab have increased deposition of C3dg caused by CD55
revaccinated against N. meningitides every 3 to 5 years after starting deficiency and these cells are prematurely removed by the reticulo-
eculizumab. endothelial system. The hemoglobin response is largely dependent