Page 538 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 538
Chapter 33 Pathobiology of the Human Erythrocyte and Its Hemoglobins 453
A
B
enhancer-like
element
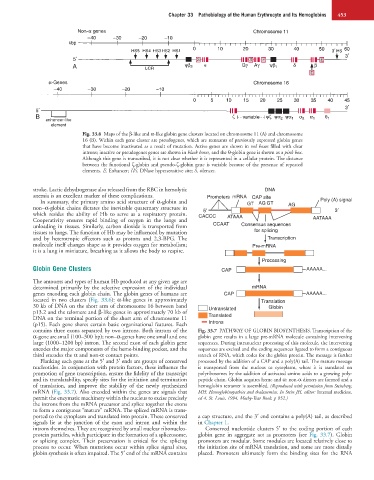
Fig. 33.6 Maps of the β-like and α-like globin gene clusters located on chromosome 11 (A) and chromosome
16 (B). Within each gene cluster are pseudogenes, which are remnants of previously expressed globin genes
that have become inactivated as a result of mutation. Active genes are shown in red boxes filled with clear
introns; inactive or pseudogenes genes are shown in black boxes, and the θ-globin gene is shown as a pink box.
Although this gene is transcribed, it is not clear whether it is represented in a cellular protein. The distance
between the functional ζ-globin and pseudo-ζ-globin gene is variable because of the presence of repeated
elements. E, Enhancer; HS, DNase hypersensitive site; S, silencer.
stroke. Lactic dehydrogenase also released from the RBC in hemolytic DNA
anemia is an excellent marker of these complications. Promoters mRNA CAP site
In summary, the primary amino acid structure of α-globin and GT AG GT Poly (A) signal
non–α-globin chains dictates the inevitable quaternary structure in 5′ AG 3′
which resides the ability of Hb to serve as a respiratory protein. CACCC ATAAA
Cooperativity ensures rapid binding of oxygen in the lungs and AATAAA
unloading in tissues. Similarly, carbon dioxide is transported from CCAAT Consensus sequences
tissues to lungs. The function of Hb may be influenced by mutation for splicing
and by heterotropic effectors such as protons and 2,3-BPG. The Transcription
molecule itself changes shape as it provides oxygen for metabolism; Pre-mRNA
it is a lung in miniature, breathing as it allows the body to respire.
Processing
Globin Gene Clusters CAP AAAAA...
The amounts and types of human Hb produced at any given age are
determined primarily by the selective expression of the individual mRNA
genes encoding each globin chain. The globin genes of humans are CAP AAAAA...
located in two clusters (Fig. 33.6): α-like genes in approximately Translation
30 kb of DNA on the short arm of chromosome 16 between band Untranslated Globin
p13.2 and the telomere and β-like genes in approximately 70 kb of
DNA on the terminal portion of the short arm of chromosome 11 Translated
(p15). Each gene shares certain basic organizational features. Each Introns
contains three exons separated by two introns. Both introns of the Fig. 33.7 PATHWAY OF GLOBIN BIOSYNTHESIS. Transcription of the
α-gene are small (100–300 bp); non–α-genes have one small and one globin gene results in a large pre-mRNA molecule containing intervening
large (1000–1200 bp) intron. The second exon of each globin gene sequences. During intranuclear processing of this molecule, the intervening
encodes the major components of the heme-binding pocket, and the sequences are excised and the coding sequences ligated to form a contiguous
third encodes the α and non-α contact points. stretch of RNA, which codes for the globin protein. The message is further
Flanking each gene at the 5′ and 3′ ends are groups of conserved processed by the addition of a CAP and a poly(A) tail. The mature message
nucleotides. In conjunction with protein factors, these influence the is transported from the nucleus to cytoplasm, where it is translated on
promotion of gene transcription, ensure the fidelity of the transcript polyribosomes by the addition of activated amino acids to a growing poly-
and its translatability, specify sites for the initiation and termination peptide chain. Globin acquires heme and α: non-α dimers are formed and a
of translation, and improve the stability of the newly synthesized hemoglobin tetramer is assembled. (Reproduced with permission from Steinberg,
mRNA (Fig. 33.7). Also encoded within the genes are signals that MH: Hemoglobinopathies and thalassemias. In Stein JH, editor: Internal medicine,
permit the enzymatic machinery within the nucleus to excise precisely ed 4, St. Louis, 1994, Mosby-Year Book, p 852.)
the introns from the mRNA precursor and splice together the exons
to form a contiguous “mature” mRNA. The spliced mRNA is trans-
ported to the cytoplasm and translated into protein. These conserved a cap structure, and the 3′ end contains a poly(A) tail, as described
signals lie at the junction of the exon and intron and within the in Chapter 1.
introns themselves. They are recognized by small nuclear ribonucleo- Conserved nucleotide clusters 5′ to the coding portion of each
protein particles, which participate in the formation of a spliceosome, globin gene in aggregate act as promoters (see Fig. 33.7). Globin
or splicing complex. Their preservation is critical for the splicing promoters are modular. Some modules are located relatively close to
process to occur. When mutations occur within splice signal sites, the initiation site of mRNA translation, and some are more distally
globin synthesis is often impaired. The 5′ end of the mRNA contains placed. Promoters ultimately form the binding sites for the RNA