Page 539 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 539
454 Part V Red Blood Cells
polymerase complexes that catalyze gene transcription. Mutations The α-globin genes (HBA2, HBA1) are duplicated and their
within the promoter can affect the level of gene transcription and the encoded amino acid sequences are identical; therefore, only a single
amount of globin made. Surrounding and within each gene are other α-globin polypeptide results. Minor differences within the second
sequence elements that play important roles in its transcriptional intervening sequence and the 3′ flanking regions of the α-globin gene
regulation (see Fig. 33.6). These clusters, called enhancers and silencers permit identification of transcripts from each gene. The 5′ or α 2-gene
(see Chapter 1), may lie within introns or 5′ and 3′ to the coding is expressed more efficiently than the 3′ or α 1-gene, so abnormalities
sequences; in some instances, they are quite remote from the gene. of this gene are more likely to be clinically apparent. Both clusters
The higher order structure of DNA in chromatin may permit close contain genes that are actively transcribed, as well as pseudogenes
approximation of these remote enhancers to the gene during tran- whose defective structures prohibit expression at any time.
scription. Enhancers play important roles in the tissue-specific regula- The gene 3′ to the α 1-gene is the Θ-gene (HBQ1), a somewhat
tion of globin gene expression. Representative regulatory sequences mysterious element of the α-gene cluster. Although Θ-gene tran-
near the globin genes are shown in Fig. 33.6 (enhancer-like element). scripts are found in fetal tissue and adult erythroid marrow, it is
DNA elements controlling globin genes are described in more detail unclear whether this gene’s translation product is able to participate
later. in the formation of a functional tetramer. The Θ-globin protein has
The α-like and β-like globin genes are ordered in the 5′ to 3′ been found in vivo, but deletion of the Θ-globin gene does not appear
direction in the same sequence expressed during embryonic, fetal, to have any implications for developing fetuses. In vitro, Θ-globin
and adult development (Fig. 33.8). The functional significance of this mRNA is correctly spliced, and Θ-globin cDNA can direct synthesis
arrangement is unclear. However, evidence suggests that the ordering of a translatable mRNA and a Θ-globin protein.
of the ε, γ, δ, and β genes could be an important factor influencing The β-like–globin gene cluster consists of the embryonic ε-gene
the ability of each locus to interact with distant control elements at (HBE), transcribed only during the first 6–11 weeks of life; the
different developmental stages. duplicated γ-globin genes (HBG2, HBG1) that code for the dominant
The α-like and β-like gene clusters probably are the result of an non–α-globin of fetal life; and the δ- (HBD) and β-globin (HBB)
ancient duplication of a primordial globin gene that existed early in genes that code for the Hbs of adults. The coding sequences of the
the history of vertebrates, approximately 500 million years ago. Each two γ-globin genes are identical, except at codon 136, where the 5′
gene cluster probably developed from the duplication of ancestral or Gγ-gene codes for glutamic acid; the 3′ or Aγ-gene encodes an
genes and subsequent divergence through eons of evolution. Within alanine residue. These genes are unequally expressed during fetal
the α-like gene cluster, the ζ-globin gene (HBZ) is expressed only development. A switch in their relative rates of expression leads to a
very early in embryogenesis and participates in the formation of similar disparity between the amounts of Gγ and Aγ chains in adults.
embryonic Hbs. A µ, α-like globin gene (HBM), originally consid- Although the Gγ/Aγ switch is interesting from the standpoint of the
ered a pseudogene (ψα2), codes for a 141 amino acid α-globin–like control of gene expression, it is of little clinical importance. HbF in
chain, is expressed in erythroid cells in a highly regulated fashion; fetuses and adults contains a mixture of Gγ and Aγ chains; the
however, an associated protein has not been found. functional qualities of these Hbs are identical.
The δ- and β-globin genes are probably the result of a duplication
event that occurred more than 40 million years ago. The β-globin
gene has become the predominant gene, coding for most non–α-
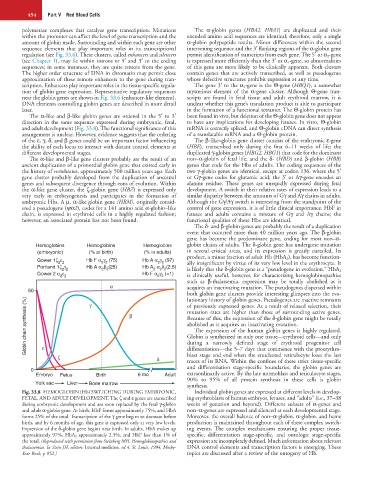
Hemoglobins Hemoglobins Hemoglobins globin chains of adults. The δ-globin gene has undergone mutation
(embryonic) (% at birth) (% in adults) in several critical areas, and its expression is greatly curtailed. Its
Gower 1ζ ε Hb F α γ (75) Hb A α γ (97) product, a minor fraction of adult Hb (HbA 2 ), has become function-
2 2
2 2
ally insignificant by virtue of its very low level in the erythrocyte. It
2 2
Portland 1ζ γ Hb A α β (25) Hb A α δ (2.5)
2 2 2 2 2 2 2 is likely that the δ-globin gene is a “pseudogene in evolution.” HbA 2
Gower 2 α ε Hb F α γ (<1)
2 2 2 2 is clinically useful, however, for characterizing hemoglobinopathies
such as β-thalassemia. expression may be totally abolished as it
α acquires an inactivating mutation. The pseudogenes dispersed within
50
both globin gene clusters provide interesting glimpses into the evo-
lutionary history of globin genes. Pseudogenes are inactive remnants
Globin chain synthesis (%) β mutation rates are higher than those of surrounding active genes.
γ
of previously expressed genes. As a result of relaxed selection, their
Because of this, the expression of the δ-globin gene might be totally
abolished as it acquires an inactivating mutation.
The expression of the human globin genes is highly regulated.
Globin is synthesized in only one tissue—erythroid cells—and only
ε
differentiation—the 5–7 days that commence with the proerythro-
blast stage and end when the enucleated reticulocyte loses the last
ζ δ during a narrowly defined stage of erythroid progenitor cell
traces of its RNA. Within the confines of these strict tissue-specific
0 and differentiation stage-specific boundaries, the globin genes are
Embryo Fetus Birth 6 mo Adult extraordinarily active. By the late normoblast and reticulocyte stages,
90% to 95% of all protein synthesis in these cells is globin
Yolk sac Liver Bone marrow synthesis.
Fig. 33.8 HEMOGLOBIN (Hb) SWITCHING DURING EMBRYONIC, Individual globin genes are expressed at different levels in develop-
FETAL, AND ADULT DEVELOPMENT. The ζ and ε genes are transcribed ing erythroblasts of human embryos, fetuses, and “adults” (i.e., 37–38
during embryonic development and are soon replaced by the fetal γ-globin weeks of gestation and beyond). Different subsets of α-genes and
and adult α-globin gene. At birth, HbF forms approximately 75%, and HbA non–α-genes are expressed and silenced at each developmental stage.
forms 25% of the total. Transcription of the γ gene begins to decrease before Moreover, the overall balance of non–α-globin, α-globin, and heme
birth, and by 6 months of age, this gene is expressed only at very low levels. production is maintained throughout each of these complex switch-
Expression of the δ-globin gene begins near birth. In adults, HbA makes up ing events. The complex mechanisms ensuring the proper tissue-
approximately 97%, HbA 2 approximately 2.5%, and HbF less than 1% of specific, differentiation stage-specific, and ontologic stage-specific
the total. (Reproduced with permission from Steinberg MH: Hemoglobinopathies and expression are incompletely defined. Much information about relevant
thalassemias. In Stein JH, editors: Internal medicine, ed 4, St. Louis, 1994, Mosby- DNA control elements and transcription factors is emerging. These
Year Book, p 852.) topics are discussed after a review of the ontogeny of Hb.