Page 730 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 730
Chapter 44 Red Blood Cell Enzymopathies 617
Glutathione production
GSH GSSG
Glucose
ATD Hexokinase NADP NADPH
NADP
NADPH
ADP
6PG
Glucose 6-P 6PG
Glucose Glucose and phosphate dehydrogenase
Glucose and phosphate dehydrogenase
Glycolysis phosphoisomerase
Pentose shunt
Fructose 6-P Pentose shunt
ATD
Phosphofructokinase
ADP
Fructose 1, 6-biP
Aldolase
Glyceraldehyde 3-P DHAP
Triosephosphate
NAD
isomerase
NADH
Glyceraldehyde phosphate
dehydrogenase
1, 3-BPG Rapoport-
Rapoport-
Synthase
Synthase
BPG
ATD Phosphoglycerate BPG Luebering 2.3-BPG
Luebering
2.3-BPG
mutase
Phosphatase
ADP kinase mutase Phosphatase
Shunt
3-P-Glycerate Shunt
Phosphoglyceromutase
2-P-Glycerate
Enolase
Phosphoenolpyruvate
ADH Pyruvate
ATD Kinase
NADH Lactate
dehydrogenase
NAD
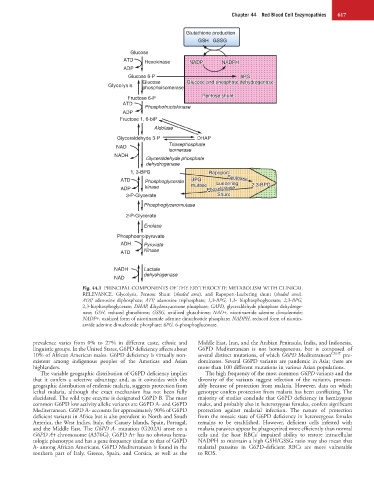
Fig. 44.1 PRINCIPAL COMPONENTS OF THE ERYTHROCYTE METABOLISM WITH CLINICAL
RELEVANCE. Glycolysis, Pentose Shunt (shaded area), and Rapoport-Luebering shunt (shaded area).
ADP, adenosine diphosphate; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; 1,3-BPG, 1,3- bisphosphoglycerate; 2,3-BPG,
2,3-bisphosphoglycerate; DHAP, dihydroxyacetone phosphate; GAPD, glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydroge-
nase; GSH, reduced glutathione; GSSG, oxidized glutathione; NAD+, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide;
NADP+, oxidized form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; NADPH, reduced form of nicotin-
amide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; 6PG, 6-phosphogluconate.
prevalence varies from 0% to 27% in different caste, ethnic and Middle East, Iran, and the Arabian Peninsula, India, and Indonesia.
linguistic groups. In the United States, G6PD deficiency affects about G6PD Mediterranean is not homogeneous, but is composed of
10% of African American males. G6PD deficiency is virtually non- several distinct mutations, of which G6PD Mediterranean C563T pre-
existent among indigenous peoples of the Americas and Asian dominates. Several G6PD variants are pandemic in Asia; there are
highlanders. more than 100 different mutations in various Asian populations.
The variable geographic distribution of G6PD deficiency implies The high frequency of the most common G6PD variants and the
that it confers a selective advantage and, as it coincides with the diversity of the variants suggest selection of the variants, presum-
geographic distribution of endemic malaria, suggests protection from ably because of protection from malaria. However, data on which
lethal malaria, although the exact mechanism has not been fully genotype confers protection from malaria has been conflicting. The
elucidated. The wild type enzyme is designated G6PD B. The most majority of studies conclude that G6PD deficiency in hemizygous
common G6PD low activity allelic variants are G6PD A- and G6PD males, and probably also in heterozygous females, confers significant
Mediterranean. G6PD A- accounts for approximately 90% of G6PD protection against malarial infection. The nature of protection
deficient variants in Africa but is also prevalent in North and South from the mosaic state of G6PD deficiency in heterozygous females
America, the West Indies, Italy, the Canary Islands, Spain, Portugal, remains to be established. However, deficient cells infested with
and the Middle East. The G6PD A- mutation (G202A) arose on a malaria parasites appear be phagocytized more efficiently than normal
G6PD A+ chromosome (A376G). G6PD A+ has no obvious hema- cells and the host RBCs’ impaired ability to restore intracellular
tologic phenotype and has a gene frequency similar to that of G6PD NADPH to maintain a high GSH/GSSG ratio may also mean that
A- among African Americans. G6PD Mediterranean is found in the malarial parasites in G6PD-deficient RBCs are more vulnerable
southern part of Italy, Greece, Spain, and Corsica, as well as the to ROS.