Page 98 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 98
Chapter 7 Signaling Transduction and Metabolomics 69
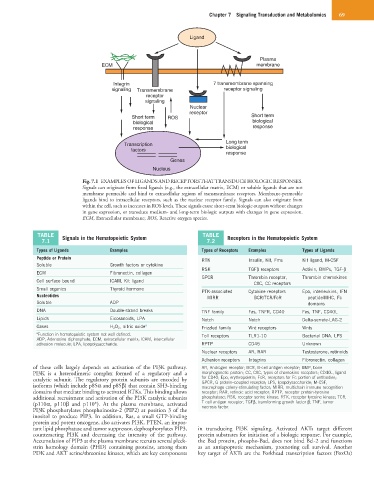
Ligand
Plasma
ECM membrane
Integrin 7 transmembrane spanning
signaling Transmembrane receptor signaling
receptor
signaling
Nuclear
receptor
Short term ROS Short term
biological biological
response response
Long term
Transcription
factors biological
response
Genes
Nucleus
Fig. 7.1 EXAMPLES OF LIGANDS AND RECEPTORS THAT TRANSDUCE BIOLOGIC RESPONSES.
Signals can originate from fixed ligands (e.g., the extracellular matrix, ECM) or soluble ligands that are not
membrane permeable and bind to extracellular regions of transmembrane receptors. Membrane-permeable
ligands bind to intracellular receptors, such as the nuclear receptor family. Signals can also originate from
within the cell, such as increases in ROS levels. These signals cause short-term biologic outputs without changes
in gene expression, or transduce medium- and long-term biologic outputs with changes in gene expression.
ECM, Extracellular membrane; ROS, Reactive oxygen species.
TABLE Signals in the Hematopoietic System TABLE Receptors in the Hematopoietic System
7.1 7.2
Types of Ligands Examples Types of Receptors Examples Types of Ligands
Peptide or Protein RTK Insulin, Kit, Fms Kit ligand, M-CSF
Soluble Growth factors or cytokine
RSK TGFβ receptors Activin, BMPs, TGF-β
ECM Fibronectin, collagen
GPCR Thrombin receptor, Thrombin chemokines
Cell surface bound ICAM, Kit ligand
CXC, CC receptors
Small organics Thyroid hormone PTK-associated Cytokine receptors Epo, interleukins, IFN
Nucleotides MIRR BCR/TCR/FcR peptide/MHC, Fc
Soluble ADP domains
DNA Double-strand breaks TNF family Fas, TNFR, CD40 Fas, TNF, CD40L
Lipids Eicosanoids, LPA Notch Notch Delta-serrate-LAG-2
Gases H 2 O 2 , nitric oxide a Frizzled family Wnt receptors Wnts
a Function in hematopoietic system not well defined. Toll receptors TLR1-10 Bacterial DNA, LPS
ADP, Adenosine diphosphate; ECM, extracellular matrix; ICAM, intercellular
adhesion molecule; LPA, lipopolysaccharide. RPTP CD45 Unknown
Nuclear receptors AR, RAR Testosterone, retinoids
Adhesion receptors Integrins Fibronectin, collagen
of these cells largely depends on activation of the PI3K pathway. AR, Androgen receptor; BCR, B-cell antigen receptor; BMP, bone
PI3K is a heterodimeric complex formed of a regulatory and a morphogenetic protein; CC, CXC, types of chemokine receptors; CD40L, ligand
catalytic subunit. The regulatory protein subunits are encoded by for CD40; Epo, erythropoietin; FcR, receptors for Fc portion of antibodies;
GPCR, G protein–coupled receptor; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; M-CSF,
isoforms (which include p85α and p85β) that contain SH3-binding macrophage colony-stimulating factor; MIRR, multichain immune recognition
domains that mediate binding to activated RTKs. This binding allows receptor; RAR, retinoic acid receptor; RPTP, receptor protein-tyrosine
additional recruitment and activation of the PI3K catalytic subunits phosphatase; RSK, receptor serine kinase; RTK, receptor tyrosine kinase; TCR,
(p110α, p110β and p110*). At the plasma membrane, activated T-cell antigen receptor; TGFβ, transforming growth factor β; TNF, tumor
necrosis factor.
PI3K phosphorylates phosphoinosite-2 (PIP2) at position 3 of the
inositol to produce PIP3. In addition, Ras, a small GTP-binding
protein and potent oncogene, also activates PI3K. PTEN, an impor-
tant lipid phosphatase and tumor suppressor, dephosphorylates PIP3, in transducing PI3K signaling. Activated AKTs target different
counteracting PI3K and decreasing the intensity of the pathway. protein substrates for initiation of a biologic response. For example,
Accumulation of PIP3 at the plasma membrane recruits several pleck- the Bad protein, phospho-Bad, does not bind Bcl-2 and functions
strin homology domain (PHD) containing proteins, among them as an antiapoptotic mechanism, promoting cell survival. Another
PDK and AKT serine/threonine kinases, which are key components key target of AKTs are the Forkhead transcription factors (FoxOs)