Page 993 - Hematology_ Basic Principles and Practice ( PDFDrive )
P. 993
876 Part VII Hematologic Malignancies
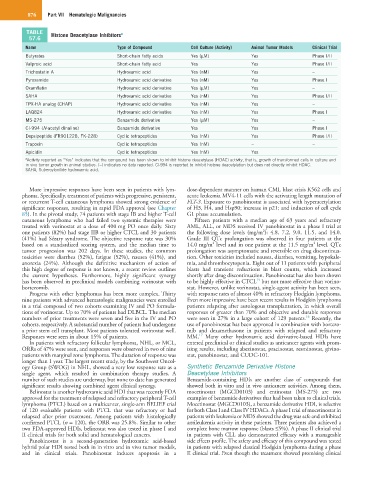
TABLE Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors a
57.6
Name Type of Compound Cell Culture (Activity) Animal Tumor Models Clinical Trial
Butyrates Short-chain fatty acids Yes (µM) Yes Phase I/II
Valproic acid Short-chain fatty acid Yes Yes Phase I/II
Trichostatin A Hydroxamic acid Yes (nM) Yes –
Pyroxamide Hydroxamic acid derivative Yes (nM) Yes Phase I
Oxamflatin Hydroxamic acid derivative Yes (µM) Yes –
SAHA Hydroxamic acid derivative Yes (nM) Yes Phase I/II
TPX-HA analog (CHAP) Hydroxamic acid derivative Yes (nM) Yes –
LAQ824 Hydroxamic acid derivative Yes (nM) Yes Phase I
MS-275 Benzamide derivative Yes (µM) Yes –
CI-994 (N-acetyl dinaline) Benzamide derivative Yes Yes Phase I
Depsipeptide (FR901228, FK-228) Cyclic tetrapeptides Yes (nM) Yes Phase I/II
Trapoxin Cyclic tetrapeptides Yes (nM) – –
Apicidin Cyclic tetrapeptides Yes (nM) Yes –
a Activity reported as “Yes” indicates that the compound has been shown to inhibit histone deacetylase (HDAC) activity, that is, growth of transformed cells in culture and
in vivo tumor growth in animal studies. (–) indicates no data reported. CI-994 is reported to inhibit histone deacetylation but does not directly inhibit HDAC.
SAHA, Suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid.
More impressive responses have been seen in patients with lym- dose-dependent manner on human CML blast crisis K562 cells and
phoma. Specifically, treatment of patients with progressive, persistent, acute leukemia MV4-11 cells with the activating length mutation of
or recurrent T-cell cutaneous lymphoma showed strong evidence of FLT-3. Exposure to panobinostat is associated with hyperacetylation
significant responses, resulting in rapid FDA approval (see Chapter of H3, H4, and Hsp90; increase in p21; and induction of cell cycle
85). In the pivotal study, 74 patients with stage IB and higher T-cell G1 phase accumulation.
cutaneous lymphoma who had failed two systemic therapies were Fifteen patients with a median age of 63 years and refractory
treated with vorinostat at a dose of 400 mg PO once daily. Sixty AML, ALL, or MDS received IV panobinostat in a phase I trial at
2
one patients (82%) had stage IIB or higher CTCL and 30 patients the following dose levels (mg/m ): 4.8, 7.2, 9.0, 11.5, and 14.0.
(41%) had Sézary syndrome. The objective response rate was 30% Grade III QTc prolongation was observed in four patients at the
2
2
based on a standardized scoring system, and the median time to 14.0 mg/m level and in one patient at the 11.5 mg/m level. QTc
tumor progression was 202 days. In these studies, the common prolongation was asymptomatic and reversible on drug discontinua-
toxicities were diarrhea (52%), fatigue (52%), nausea (41%), and tion. Other toxicities included nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, hypokale-
anorexia (24%). Although the definitive mechanism of action of mia, and thrombocytopenia. Eight out of 11 patients with peripheral
this high degree of response is not known, a recent review outlines blasts had transient reductions in blast counts, which increased
the current hypotheses. Furthermore, highly significant synergy shortly after drug discontinuation. Panobinostat has also been shown
15
has been observed in preclinical models combining vorinostat with to be highly effective in CTCL but not more effective than vorino-
bortezomib. stat. However, unlike vorinostat, single-agent activity has been seen,
Progress with other lymphomas has been more complex. Thirty with response rates of almost 40% in refractory Hodgkin lymphoma.
nine patients with advanced hematologic malignancies were enrolled Even more impressive have been recent results in Hodgkin lymphoma
in a trial composed of two cohorts examining IV and PO formula- patients relapsing after autologous transplantation, in which overall
tions of vorinostat. Up to 70% of patients had DLBCL. The median responses of greater than 70% and objective and durable responses
16
numbers of prior treatments were seven and five in the IV and PO were seen in 27% in a large cohort of 129 patents. Recently, the
cohorts, respectively. A substantial number of patients had undergone use of panobinostat has been approved in combination with bortezo-
a prior stem cell transplant. Most patients tolerated vorinostat well. mib and dexamethasone in patients with relapsed and refractory
17
Responses were seen in about 15% of patients. MM. Many other hydroxamic acid derivative-based HDIs have
In patients with refractory follicular lymphoma, NHL, or MCL, entered preclinical or clinical studies as anticancer agents with prom-
ORRs of 47% were seen, and responses were observed in two of nine ising results, including abexinostat, pracinostat, resminostat, givino-
patients with marginal zone lymphoma. The duration of response was stat, panobinostat, and CUDC-101.
longer than 1 year. The largest recent study, by the Southwest Oncol-
ogy Group (SWOG) in NHL, showed a very low response rate as a Synthetic Benzamide Derivative Histone
single agent, which resulted in combination therapy studies. A Deacetylase Inhibitors
number of such studies are underway, but none to date has generated Benzamide-containing HDIs are another class of compounds that
significant results showing combined agent clinical synergy. showed both in vitro and in vivo anticancer activities. Among them,
Belinostat is another hydroxamic acid HDI that was recently FDA mocetinostat (MGCD0103) and entinostat (MS-275) are two
approved for the treatment of relapsed and refractory peripheral T-cell examples of benzamide derivatives that had been taken to clinical trials.
lymphoma (PTCL) based on a multicenter, single-arm BELIEF trial Mocetinostat (MGCD0103), a benzamide derivative HDI, is selective
of 120 evaluable patients with PTCL that was refractory or had for both Class I and Class IV HDACs. A phase I trial of mocetinostat in
relapsed after prior treatment. Among patients with histologically patients with leukemia or MDS showed the drug was safe and exhibited
confirmed PTCL (n = 120), the ORR was 25.8%. Similar to other antileukemia activity in these patients. Three patients also achieved a
two FDA-approved HDIs, belinostat was also tested in phase I and complete bone marrow response (blasts ≤5%). A phase II clinical trial
II clinical trials for both solid and hematological cancers. in patients with CLL also demonstrated efficacy with a manageable
Panobinostat is a second-generation hydroxamic acid-based side effects profile. The safety and efficacy of this compound was tested
hybrid polar HDI tested both in in vitro and in vivo tumor models, in patients with relapsed classical Hodgkin lymphoma during a phase
and in clinical trials. Panobinostat induces apoptosis in a II clinical trial. Even though the treatment showed promising clinical