Page 1023 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1023
998 Part VII: Neutrophils, Eosinophils, Basophils, and Mast Cells Chapter 65: Neutropenia and Neutrophilia 999
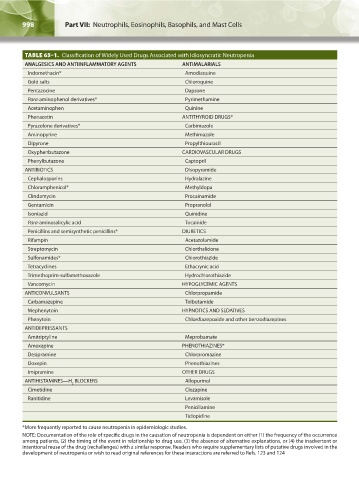
TABLE 65–1. Classification of Widely Used Drugs Associated with Idiosyncratic Neutropenia
ANALGESICS AND ANTIINFLAMMATORY AGENTS ANTIMALARIALS
Indomethacin* Amodiaquine
Gold salts Chloroquine
Pentazocine Dapsone
Para-aminophenol derivatives* Pyrimethamine
Acetaminophen Quinine
Phenacetin ANTITHYROID DRUGS*
Pyrazolone derivatives* Carbimazole
Aminopyrine Methimazole
Dipyrone Propylthiouracil
Oxyphenbutazone CARDIOVASCULAR DRUGS
Phenylbutazone Captopril
ANTIBIOTICS Disopyramide
Cephalosporins Hydralazine
Chloramphenicol* Methyldopa
Clindamycin Procainamide
Gentamicin Propranolol
Isoniazid Quinidine
Para-aminosalicylic acid Tocainide
Penicillins and semisynthetic penicillins* DIURETICS
Rifampin Acetazolamide
Streptomycin Chlorthalidone
Sulfonamides* Chlorothiazide
Tetracyclines Ethacrynic acid
Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole Hydrochlorothiazide
Vancomycin HYPOGLYCEMIC AGENTS
ANTICONVULSANTS Chlorpropamide
Carbamazepine Tolbutamide
Mephenytoin HYPNOTICS AND SEDATIVES
Phenytoin Chlordiazepoxide and other benzodiazepines
ANTIDEPRESSANTS
Amitriptyline Meprobamate
Amoxapine PHENOTHIAZINES*
Desipramine Chlorpromazine
Doxepin Phenothiazines
Imipramine OTHER DRUGS
ANTIHISTAMINES—H BLOCKERS Allopurinol
2
Cimetidine Clozapine
Ranitidine Levamisole
Penicillamine
Ticlopidine
*More frequently reported to cause neutropenia in epidemiologic studies.
NOTE: Documentation of the role of specific drugs in the causation of neutropenia is dependent on either (1) the frequency of the occurrence
among patients, (2) the timing of the event in relationship to drug use, (3) the absence of alternative explanations, or (4) the inadvertent or
intentional reuse of the drug (rechallenges) with a similar response. Readers who require supplementary lists of putative drugs involved in the
development of neutropenia or wish to read original references for these interactions are referred to Refs. 123 and 124
Kaushansky_chapter 65_p0991-1004.indd 998 9/17/15 6:44 PM