Page 1044 - Williams Hematology ( PDFDrive )
P. 1044
1018 Part VII: Neutrophils, Eosinophils, Basophils, and Mast Cells Chapter 66: Disorders of Neutrophil Function 1019
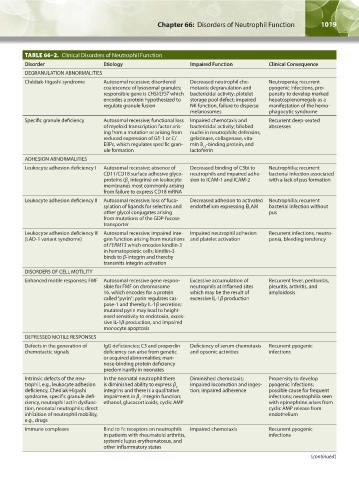
TABLE 66–2. Clinical Disorders of Neutrophil Function
Disorder Etiology Impaired Function Clinical Consequence
DEGRANULATION ABNORMALITIES
Chédiak-Higashi syndrome Autosomal recessive; disordered Decreased neutrophil che- Neutropenia; recurrent
coalescence of lysosomal granules; motaxis; degranulation and pyogenic infections, pro-
responsible gene is CHSI/LYST which bactericidal activity; platelet pensity to develop marked
encodes a protein hypothesized to storage pool defect; impaired hepatosplenomegaly as a
regulate granule fusion NK function, failure to disperse manifestation of the hemo-
melanosomes phagocytic syndrome
Specific granule deficiency Autosomal recessive; functional loss Impaired chemotaxis and Recurrent deep-seated
of myeloid transcription factor aris- bactericidal activity; bilobed abscesses
ing from a mutation or arising from nuclei in neutrophils; defensins,
reduced expression of Gfi-1 or C/ gelatinase, collagenase, vita-
EBPε, which regulates specific gran- min B -binding protein, and
12
ule formation lactoferrin
ADHESION ABNORMALITIES
Leukocyte adhesion deficiency I Autosomal recessive; absence of Decreased binding of C3bi to Neutrophilia; recurrent
CD11/CD18 surface adhesive glyco- neutrophils and impaired adhe- bacterial infection associated
proteins (β integrins) on leukocyte sion to ICAM-1 and ICAM-2 with a lack of pus formation
2
membranes most commonly arising
from failure to express CD18 mRNA
Leukocyte adhesion deficiency II Autosomal recessive; loss of fuco- Decreased adhesion to activated Neutrophilia; recurrent
sylation of ligands for selectins and endothelium expressing ELAM bacterial infection without
other glycol conjugates arising pus
from mutations of the GDP-fucose
transporter
Leukocyte adhesion deficiency III Autosomal recessive; impaired inte- Impaired neutrophil adhesion Recurrent infections, neutro-
(LAD-1 variant syndrome) grin function arising from mutations and platelet activation penia, bleeding tendency
of FERMT3 which encodes kindlin-3
in hematopoietic cells; kindlin-3
binds to β-integrin and thereby
transmits integrin activation
DISORDERS OF CELL MOTILITY
Enhanced motile responses; FMF Autosomal recessive gene respon- Excessive accumulation of Recurrent fever, peritonitis,
sible for FMF on chromosome neutrophils at inflamed sites pleuritis, arthritis, and
16, which encodes for a protein which may be the result of amyloidosis
called “pyrin”; pyrin regulates cas- excessive IL-1β production
pase-1 and thereby IL-1β secretion;
mutated pyrin may lead to height-
ened sensitivity to endotoxin, exces-
sive IL-1β production, and impaired
monocyte apoptosis
DEPRESSED MOTILE RESPONSES
Defects in the generation of IgG deficiencies; C3 and properdin Deficiency of serum chemotaxis Recurrent pyogenic
chemotactic signals deficiency can arise from genetic and opsonic activities infections
or acquired abnormalities; man-
nose-binding protein deficiency
predominantly in neonates
Intrinsic defects of the neu- In the neonatal neutrophil there Diminished chemotaxis; Propensity to develop
trophil, e.g., leukocyte adhesion is diminished ability to express β impaired locomotion and inges- pyogenic infections;
2
deficiency, Chédiak-Higashi integrins and there is a qualitative tion; impaired adherence possible cause for frequent
syndrome, specific granule defi- impairment in β -integrin function; infections; neutrophilia seen
2
ciency, neutrophil actin dysfunc- ethanol, glucocorticoids, cyclic AMP with epinephrine arises from
tion, neonatal neutrophils; direct cyclic AMP release from
inhibition of neutrophil mobility, endothelium
e.g., drugs
Immune complexes Bind to Fc receptors on neutrophils Impaired chemotaxis Recurrent pyogenic
in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, infections
systemic lupus erythematosus, and
other inflammatory states
(continued )
Kaushansky_chapter 66_p1005-1042.indd 1019 9/21/15 10:48 AM